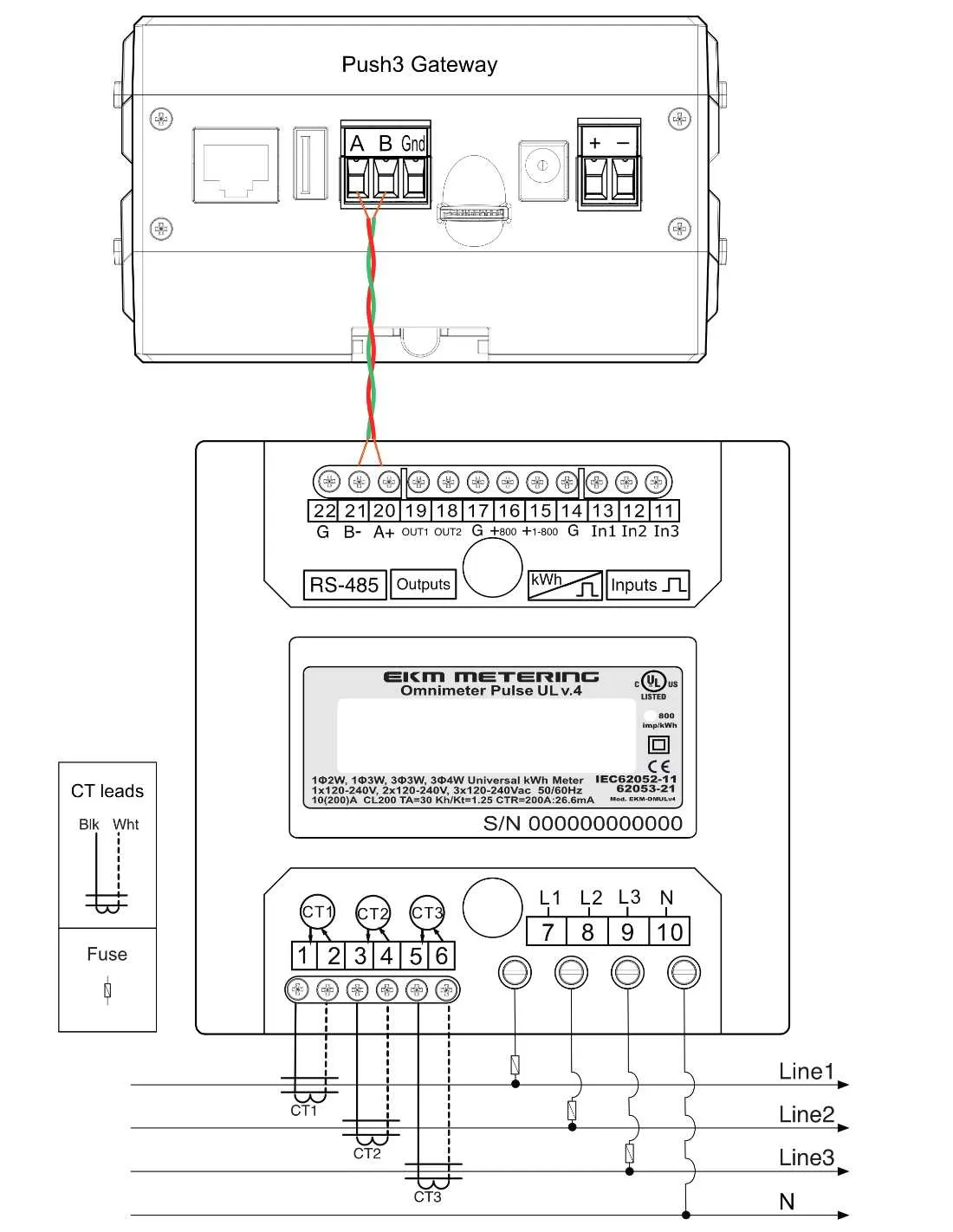
To ensure proper functionality and safety in residential electrical systems, it’s crucial to understand the correct setup for circuits operating at 240 units. Properly connecting the components can help prevent common issues such as overloads, short circuits, or improper power distribution.
Ensure a balanced load distribution across both conductors, which will provide even power flow and minimize potential damage to the system. Avoid overloading any part of the circuit to reduce the risk of overheating or system failures. Proper grounding is essential, so make sure that all safety protocols are followed, especially when dealing with high-load configurations.
When connecting to an existing service panel, verify that the breaker and the conductor sizes match the system’s requirements. For installations requiring two-phase power delivery, be sure to utilize an appropriate breaker rated for your total system capacity. Always follow local electrical codes to guarantee both performance and safety standards are met.
Connecting 240V AC System Correctly
When installing or modifying an electrical system using 240V AC, follow these guidelines to ensure proper setup and safety.
- Ensure the breaker panel is rated for 240V systems.
- Verify that the neutral line is correctly grounded at the panel to avoid electrical hazards.
- Use wire gauges that meet or exceed the system’s amperage rating, typically 10 AWG or thicker for high-load circuits.
- For outlets, make sure they are compatible with 240V circuits, especially for equipment requiring higher power.
- Employ a double-pole breaker to separate the hot lines, ensuring both are safely connected to the panel.
Pay attention to each leg of the power supply, keeping both hot conductors balanced to prevent power imbalance and potential overloads. Proper grounding throughout the setup is critical for safe operation, particularly in systems with high power demands.
- Each hot line should be connected to opposite sides of the breaker to achieve 240V potential between them.
- Do not exceed the recommended ampacity for conductors; always check local codes and manufacturer guidelines.
- Test the system with a multimeter to verify that each component is functioning correctly before connecting any equipment.
By following these specific steps, you can ensure a reliable and safe power distribution setup for your high-voltage system.
Understanding the Basics of 208V Wiring
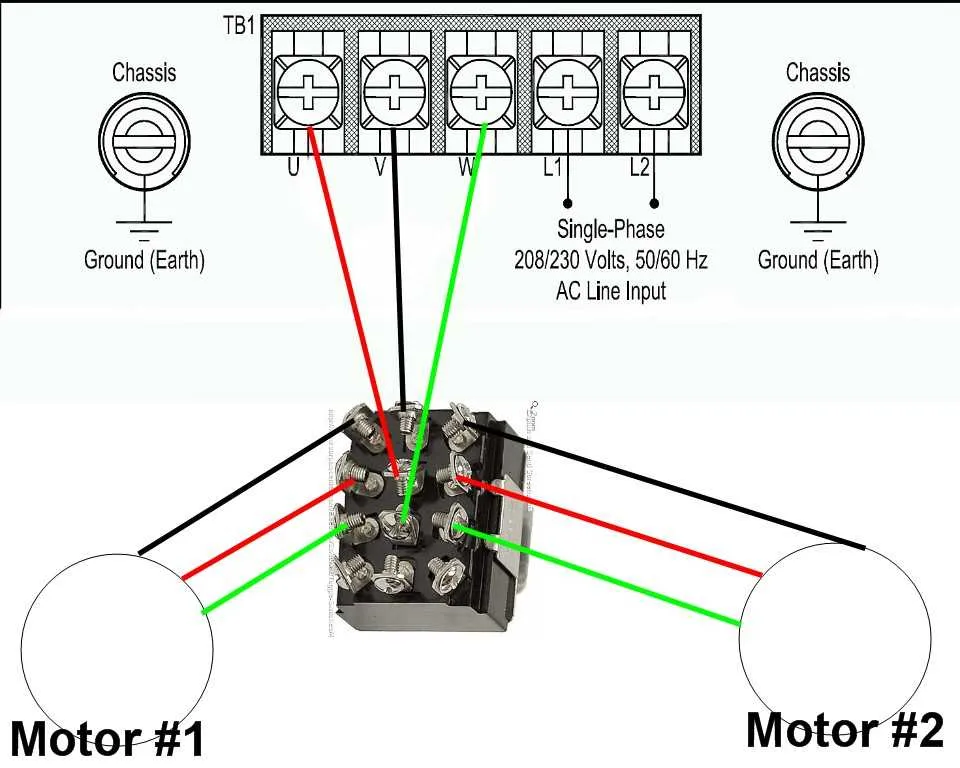
Ensure proper grounding to prevent potential hazards. Use a three-wire configuration to facilitate effective current flow and minimize voltage imbalance. Ensure that the neutral conductor is sized appropriately and securely connected at both the power source and the load end.
For optimal performance, balance the loads evenly between the two conductors. This reduces the risk of overloading one line and ensures that both conductors carry equal currents. Always verify with a multimeter to check for discrepancies in amperage.
Confirm the correct breaker size according to the total expected load. An undersized breaker will not trip during an overload, while an oversized breaker might fail to protect the circuit. Typically, a double-pole breaker is used to manage the voltage properly.
Common Applications of 208 Volt Systems
These power configurations are frequently utilized in commercial and industrial settings where moderate power requirements are essential. Equipment such as HVAC systems, large motors, and industrial machinery often operate efficiently with this type of supply. It’s ideal for running 3-phase motors, especially in settings where heavy-duty operations take place, like manufacturing plants or large-scale food processing units.
In retail environments, this setup supports refrigeration units, commercial ovens, and air conditioning systems, providing the necessary power for optimal performance. Furthermore, some lighting setups, particularly in larger buildings, also rely on this configuration to balance power demands without overloading the system.
Electricians prefer these systems for providing reliable power to machinery and devices that need a continuous and stable energy flow, especially in businesses that run 24/7. Additionally, these supplies are often used to connect equipment that requires a slightly higher current than typical household sources, ensuring operational efficiency and durability.
Step-by-Step Wiring Process for 208V Circuits
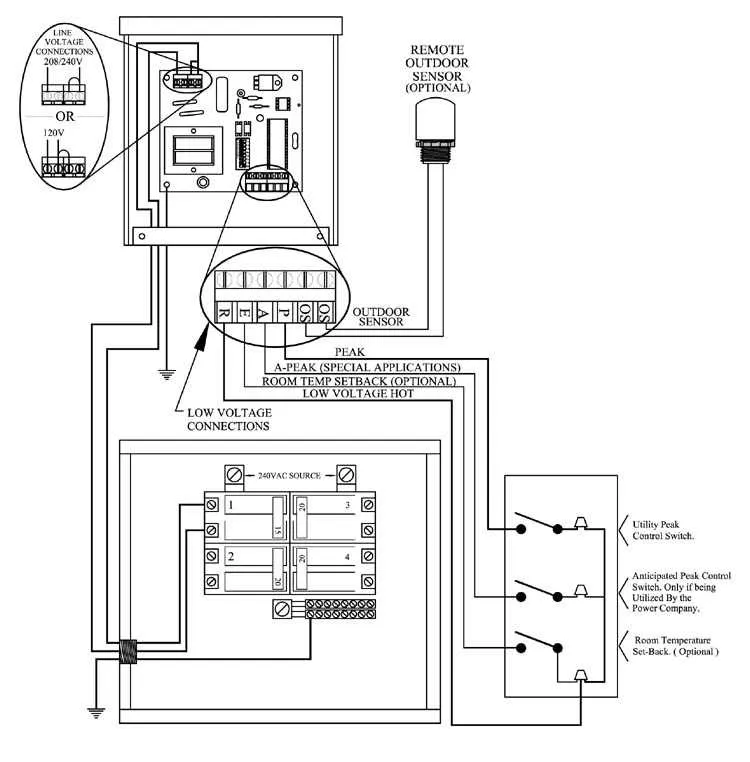
Start by ensuring the power supply is switched off to avoid electrical hazards. Locate the breaker panel and disconnect the relevant circuit by flipping the breaker to the off position. Verify with a multimeter to ensure there is no live current in the lines.
Next, prepare the necessary materials: use 12 AWG copper or aluminum conductor for the installation, ensuring that each wire is appropriately rated for the intended load. Use insulated connectors to prevent accidental short circuits.
Connect the live wires to the terminal blocks in the panel, ensuring the neutral wire is correctly attached to the neutral bus bar. For grounding, attach the ground wire securely to the ground bus bar to maintain safety standards. All connections should be firm to prevent any potential arcing.
Route the conductors carefully, ensuring that no wires are pinched or exposed to potential damage. Fix the cables with the appropriate clamps along their path, ensuring the wire does not sag or make contact with heat sources.
Once the connections are made, double-check that all wires are properly seated and there is no visible damage to the insulation. Tighten the terminal screws without over-tightening, as this can cause wire damage or stress the connections.
Restore power at the panel, turning the breaker back on, and use a voltage tester to confirm correct power delivery across the connected points. If everything is in order, proceed to test the load to verify proper operation of the connected equipment.