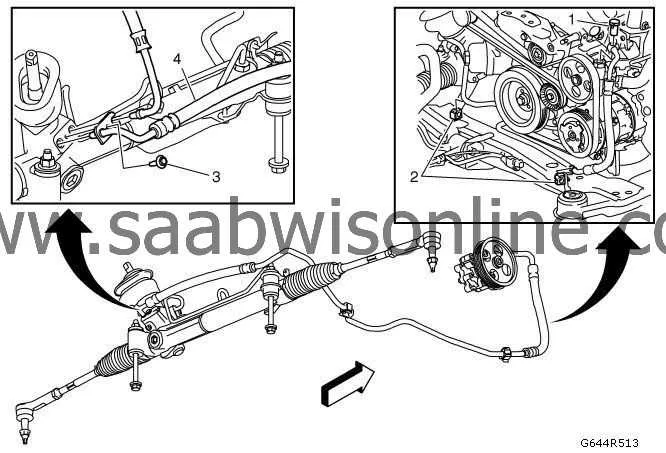
To ensure optimal performance and avoid common issues with vehicle fluid systems, it’s essential to understand the precise flow of hydraulic fluid throughout the vehicle’s components. This schematic will help identify the various connections and paths, ensuring no leaks or blockages hinder your system’s functionality. By following the correct setup, you can maintain the efficiency and safety of the entire mechanism.
Identify Key Connections: First, recognize the main hoses, pumps, and valves that make up the hydraulic system. These elements work in tandem to facilitate smooth control and direction. Ensuring that each part is correctly linked and free from obstructions will prevent strain on the system and reduce the risk of malfunctions.
Maintenance Tip: Always check for wear and tear on flexible hoses, as they are prone to degradation over time. Regular inspection and timely replacement are critical for maintaining pressure levels and overall system health. Don’t overlook the importance of fluid levels; keeping the fluid at an optimal level ensures the longevity of the entire setup.
Hydraulic Fluid System Schematic
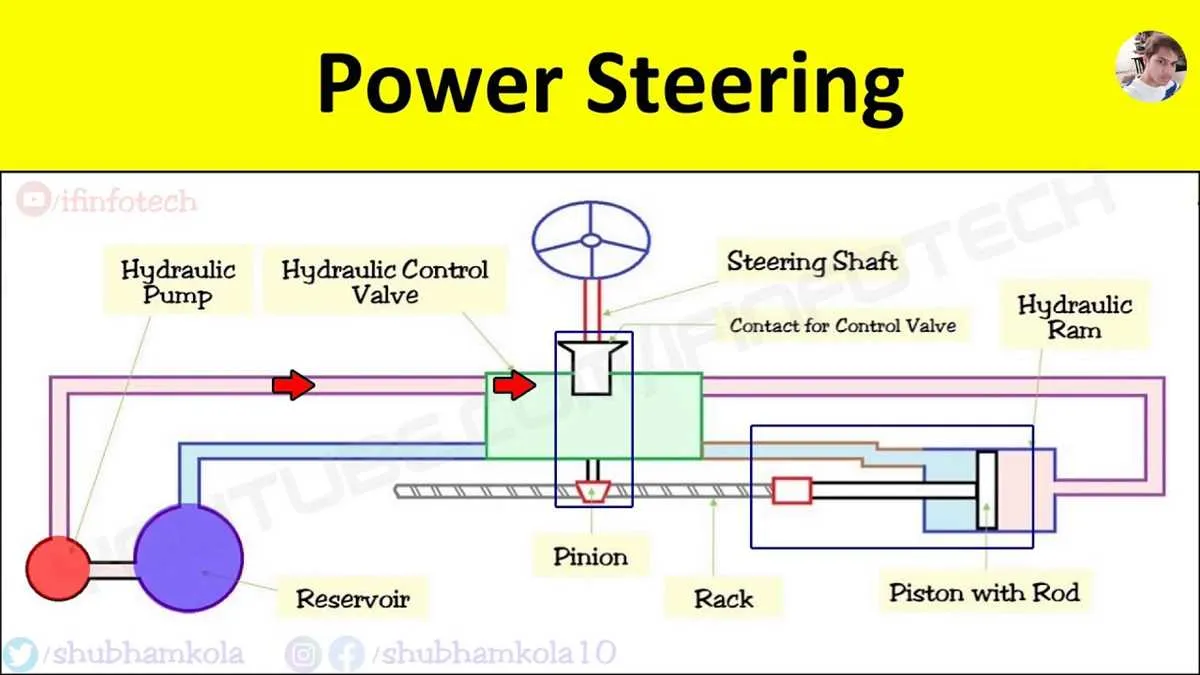
Ensure that the fluid circulation pipes are securely connected to prevent leaks. Check that each hose follows the correct routing from the reservoir to the assistance mechanism. Misrouted or improperly connected hoses can cause pressure loss, leading to inefficient operation.
The high-pressure tube should be connected to the pump output and directed towards the actuator. Make sure the rubber seals around the connections are intact to avoid fluid leakage, which could damage surrounding components or decrease efficiency.
Inspect the return line that carries fluid back from the actuator to the reservoir. Any blockage in this section can create an increase in pressure, leading to potential failures. Ensure that no kinks or sharp bends exist in the tubing to guarantee free flow.
Maintain the system by regularly checking for corrosion or wear on the pipes. Corroded or cracked tubes should be replaced immediately to prevent system failure. Also, monitor the condition of the fittings, as they can loosen over time, compromising system integrity.
Understanding the Components of the Hydraulic Control System
To ensure smooth handling and responsiveness of your vehicle, focus on maintaining the key components that assist in effortless directional control. The pump is essential for generating the fluid pressure required to assist the driver. Regular checks of the fluid level and condition will prevent malfunction.
Another crucial element is the valve assembly, which regulates fluid flow to adjust the force needed for turning. If this part becomes blocked or damaged, steering effort increases dramatically. Routine inspections are advised to detect any buildup or wear.
Moreover, the actuator mechanism, often integrated with the column, works in conjunction with the pump and valve. Over time, seals within this component can degrade, causing leakage or pressure loss. Replacing these seals promptly ensures optimal system function.
Lastly, the fluid reservoir should be cleaned and inspected regularly for contamination. Using the wrong type of fluid can lead to system failure, so always refer to manufacturer guidelines when topping off or replacing it.
Identifying Common Issues with Hydraulic Fluid Hoses
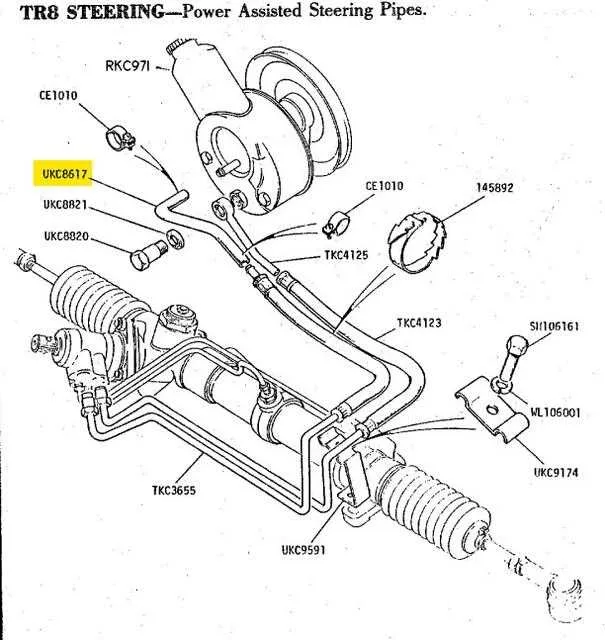
Check for any visible leaks in the hoses, especially around connection points. Leaks often occur due to cracked or worn-out seals. If the fluid level drops rapidly, inspect these areas first. A quick visual check can prevent further damage.
Examine the hoses for signs of abrasion or chafing. Hoses that come into frequent contact with other engine components may wear down and lose their integrity. This can result in fluid loss or a reduction in system performance.
Corrosion is another common issue. Hoses exposed to moisture and chemicals may develop rust or other forms of deterioration, especially at connection points. This can lead to the failure of the hose, causing fluid leaks and inadequate system operation.
If there’s difficulty turning or unusual noise, inspect the fluid hoses for blockages. These can occur due to contaminants or debris, disrupting fluid flow. Cleaning or replacing blocked hoses can restore optimal function.
Connection tightness should also be checked. Loose or improperly secured fittings can cause the hose to become detached under pressure, resulting in fluid leakage. Tighten any connections and ensure the fittings are in good condition to prevent such failures.
Step-by-Step Guide to Inspecting Hydraulic Hoses and Connections
Begin by ensuring the vehicle is off, the engine cool, and the area around the hoses is clean to prevent dirt from contaminating the system.
- Locate the Fluid Reservoir: Identify the container that holds the fluid. Check its level before starting your inspection.
- Inspect for Leaks: Carefully examine each hose and fitting for visible fluid leaks. Look for dampness, wet spots, or dried fluid residue, which may indicate a problem.
- Check Hose Condition: Examine the rubber hoses for cracks, bulges, or abrasions. Pay attention to the areas near the connections and bends where wear is most common.
- Inspect Clamps and Fittings: Ensure all hose clamps are tight and secure. Loose clamps can cause fluid to escape. Check the connections for any signs of corrosion or wear.
- Test Pressure: If applicable, check the system’s pressure using a pressure gauge. Low pressure can point to issues with the hoses or fittings.
- Look for Deterioration: Over time, hoses can deteriorate due to heat, age, or exposure to chemicals. Inspect the hoses for any signs of wear like soft spots or hardening.
- Check for Vibration or Noise: When the engine is running, observe if there’s unusual vibration or noise around the hoses, which could indicate an internal blockage or damaged hose.
If any issues are found during the inspection, replace the affected hoses or tighten connections as necessary. Regular checks can help avoid unexpected failures during operation.