
To ensure a smooth and safe setup of your unit, always start by verifying the placement of the unit according to the manufacturer’s specifications. This includes considering the proper distance from walls, clearance for air intake and venting, and ensuring that it is level on the floor to prevent potential issues during operation.
Connect all input and output lines correctly. The cold intake pipe should connect to the designated entry point, while the hot water pipe should lead to the outlet. Pay attention to the direction of water flow marked on the unit to avoid reversing the connections.
Install a reliable venting system according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Make sure the exhaust pipe is correctly installed, leading to the outdoors, and that there are no obstructions in the exhaust route. Regular checks and maintenance of the venting system are crucial for ensuring proper airflow and preventing dangerous buildup of gases.
Finally, check the power supply and safety mechanisms. Ensure the electrical connections are securely fitted and properly grounded to prevent electrical hazards. Set the temperature controls and test the unit thoroughly before regular use. Always follow local regulations for safe and effective operation of your device.
Installation Steps for Your Appliance
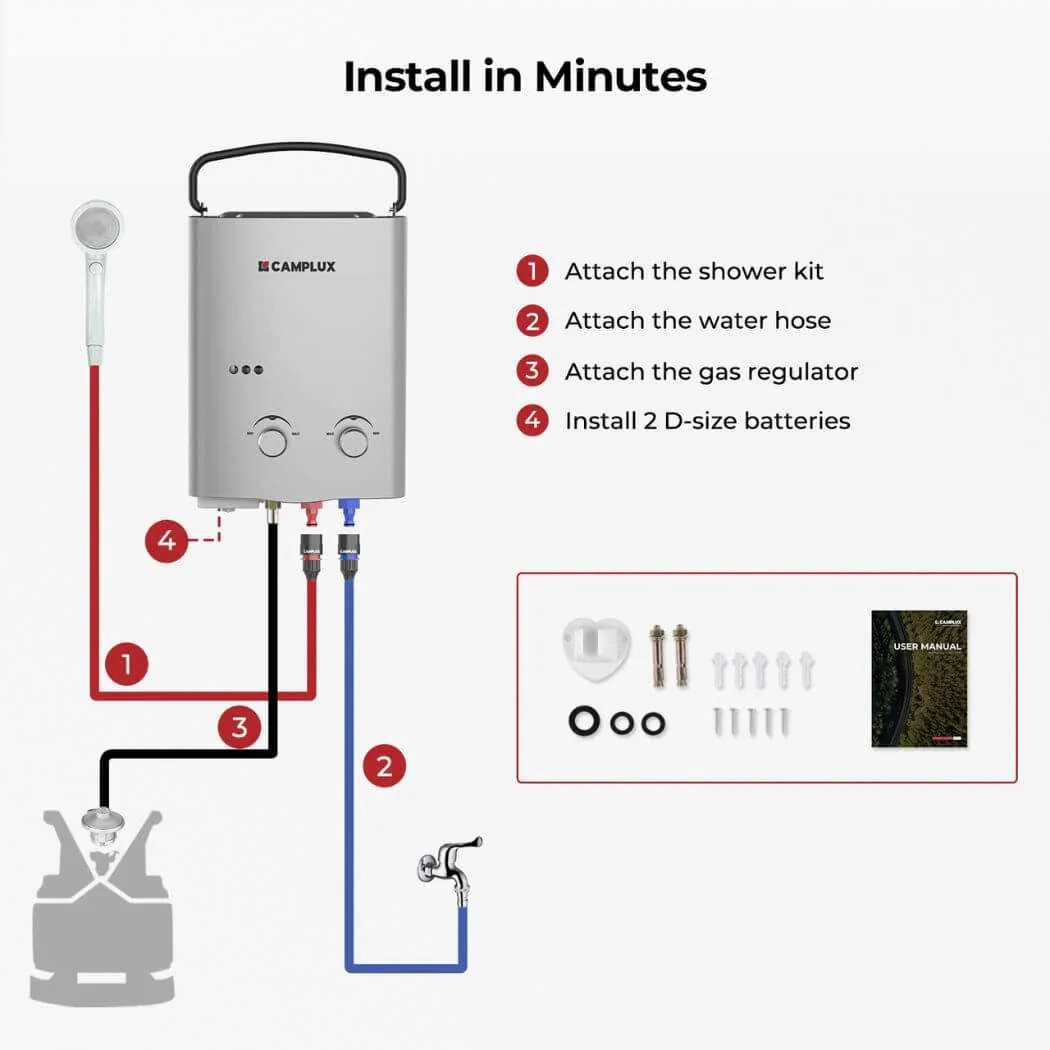
Ensure the location is properly ventilated before beginning setup. This is crucial for safe operation. The unit should be placed near an exhaust vent to allow for proper air circulation. Place the unit on a flat, non-combustible surface for stability.
1. Connect the fuel supply line: Ensure the pipe is tightly secured to prevent leaks. Use a wrench to ensure the connection is firm and leak-free. Always check the joints for any signs of potential issues.
2. Electrical connections: Connect the control system and ignition to the designated terminals. Follow the manufacturer’s guide for specific voltage requirements.
3. Water outlet and inlet connections: Attach the cold and hot pipes to their respective terminals. Ensure the seals are properly placed to prevent any leakage. Tighten all fittings using the correct tools, avoiding over-tightening, which could damage the connections.
4. Testing: Before finalizing the setup, conduct a thorough test to ensure that there are no leaks or malfunctions. Turn on the supply and check for any irregularities. If everything is functioning correctly, finish sealing and securing the appliance.
Remember: Prioritize safety at every step. Always turn off the supply and follow the manufacturer’s manual for exact procedures.
Understanding the Key Components of a Gas-Fired Heating System
Ensure that the combustion chamber is properly sealed to prevent gas leaks and maximize efficiency. This component houses the burner, which ignites the fuel. A malfunctioning burner can lead to inefficient heating or safety risks.
The thermocouple is essential for detecting whether the pilot flame is lit. If it fails, the gas supply will automatically shut off to prevent dangerous conditions. Regular checks of this part are crucial for system reliability.
Inspect the venting system to ensure proper exhaust flow. Blockages in the flue can result in hazardous backdrafting, where harmful gases could be redirected into the living space. Keep the venting clear of debris and obstructions for optimal performance.
The expansion tank prevents excess pressure buildup within the system, which could cause premature failure of components. Make sure it’s installed at the highest point to effectively regulate internal pressure levels.
A temperature and pressure relief valve is a safety feature that should never be tampered with. It releases pressure if it rises beyond safe levels, preventing the risk of explosion. Test this valve regularly to ensure it functions properly.
Lastly, ensure that the gas control valve operates correctly. It regulates the amount of fuel being supplied to the burner. Any malfunction can result in inconsistent heating or, worse, an unregulated flow that poses a serious safety risk.
Step-by-Step Guide to Proper Fuel Line and Ventilation Setup
Ensure all connections are secure: The fuel supply must be tightly linked to the appliance using high-quality pipes. Use compression fittings or threaded connectors, ensuring there are no leaks. Test the connections using a soapy water solution to check for bubbles, indicating leaks.
Install a shutoff valve: A reliable shutoff valve should be placed near the appliance for emergency disconnections. This is essential for maintenance or in case of a malfunction. Ensure the valve is easily accessible and operational.
Position venting correctly: Proper exhaust piping is crucial for expelling harmful fumes. Select the correct diameter of vent pipes based on manufacturer guidelines. Use rigid pipes over flexible ducts for better durability and airflow. Ensure a vertical rise of at least 12 inches before any horizontal runs.
Ensure adequate ventilation: Install air intake systems in line with the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that the surrounding space is free from obstructions, allowing sufficient airflow for combustion. Avoid sealing vent openings or placing the appliance in tight, enclosed spaces without proper air exchange.
Check for correct pipe slope: Ensure that exhaust pipes slope at least 1/4 inch per foot towards the outside to allow proper drainage of condensation. Any horizontal pipes should be minimized to prevent backdrafts.
Test after setup: Once the connections are in place, perform a thorough testing procedure. Check for any leaks again and ensure that the system operates correctly by testing the exhaust function. The appliance should produce no visible emissions or signs of improper ventilation during operation.
Common Wiring Practices and Safety Measures During Setup
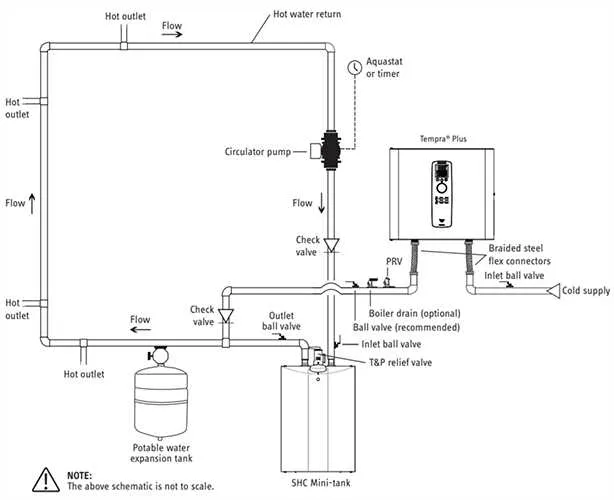
Ensure the power supply is disconnected before starting any work. This is crucial for preventing electric shocks and ensuring a secure connection. Always verify the absence of current using a voltage tester.
- Use high-quality, insulated wires to prevent short circuits and electrical fires.
- Choose the correct wire gauge based on the power requirements. For most systems, 12 AWG or 14 AWG wire is recommended.
- Properly ground all electrical components to avoid electrical surges.
- Ensure that the connections are tight and secure. Loose wires can lead to overheating and system failure.
- Keep all connections dry. Moisture exposure can result in corrosion and electrical faults.
Follow these grounding practices:
- Use a dedicated grounding rod for added protection.
- Ensure the grounding wire is connected to the system’s ground terminal and not to a water pipe, as it may not provide an adequate path for electric current.
Always check the local building codes for any specific electrical regulations and adhere to them strictly to ensure safety and compliance.