
For accurate troubleshooting and maintenance, refer to the electrical system layout of the 98 model. A clear map of the components’ arrangement is essential for identifying malfunctioning parts. Be sure to locate the main and secondary distribution units, as well as the auxiliary connections that handle critical functions such as lights, ignition, and control modules.
Key Areas to Check: Ensure that the primary box located under the dashboard is examined for any blown components. This box handles most internal electrical circuits. Additionally, inspect the engine compartment for the external module that powers the engine’s auxiliary systems. Double-check both locations for damage or wear, as these can disrupt vehicle operations.
Common Issues: Often, components within these blocks may wear out or fail due to age. Symptoms include non-functioning accessories, engine misfires, or irregular behavior of lights and signals. Always replace faulty units with high-quality alternatives to avoid further damage and maintain the system’s integrity.
Tip: For an easy check, use a multimeter to test each connection for continuity. This will allow you to pinpoint which part needs replacing without unnecessary disassembly.
98 Model Fuse Layout
If you’re experiencing electrical issues, refer to the following layout for precise identification of the components within the system. Check each location thoroughly for blown units. The primary block inside the engine bay handles the most essential connections for the vehicle’s operation.
Engine Compartment Block: Located near the driver’s side, this unit controls critical components like the ignition, lights, and cooling system. Common problems include a malfunctioning relay for the radiator fan or starter issues.
Interior Power Distribution Panel: Found beneath the dashboard, this panel regulates the power flow to interior functions such as the stereo, air conditioning, and dashboard lights. If any of these features fail, inspect this area first.
Relay Check: Pay close attention to the relays, as they often cause power interruptions when faulty. The relay for the fuel pump is one of the most common failures in this setup.
Consult the label near each block for the exact amp ratings and their corresponding components. Always use a multimeter to verify any irregularities in electrical flow.
Maintenance Tip: When replacing any unit, ensure that the replacements match the specifications outlined for your vehicle’s model year. Using incorrect replacements may lead to further issues down the road.
Identifying Fuse Locations in the 1998 Honda Civic
To locate the electrical protection components in the 1998 vehicle, first check the under-hood box, typically positioned near the engine. This compartment houses high-amp items like the main relay and the alternator circuit. Another essential area is inside the cabin, under the dashboard near the driver’s side. Here, you’ll find components responsible for lights, radio, and interior functions.
The engine compartment houses larger units, while the cabin section includes smaller, more specific units for accessories and critical systems. If a certain function like power windows or airbags isn’t operating, begin by inspecting these areas. Consult the vehicle’s manual for the precise layout and amperage ratings of each element.
Understanding the Function of Each Fuse in the 98 Honda Civic
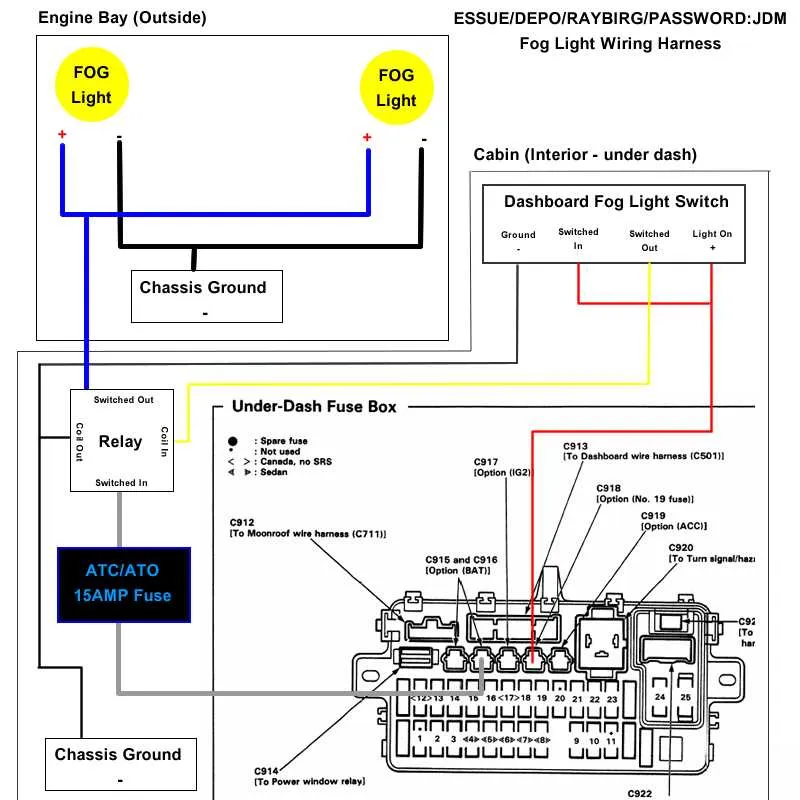
Check the 15A fuses located in the under-hood box for components like the alternator and ignition system. If the engine stalls or doesn’t start, inspect these first. In the cabin, the 10A fuses power critical systems like the radio, power windows, and interior lights. For issues with these features, these fuses are the most likely culprit.
The 30A fuse controls the air conditioning system. If there’s no cooling or heating, a blown fuse could be the cause. Another key fuse is the 20A one that handles the electric cooling fan; if the engine temperature rises too high, it might be due to a malfunction here.
For safety systems, such as the airbags, the 10A fuses are crucial. These should be regularly checked to ensure the airbag system is ready in case of an accident. Additionally, check the 7.5A fuse for dashboard electronics–without it, the instrument cluster won’t function properly.
Always replace any fuse with one of the same rating to avoid overloading the circuits and damaging the components. If problems persist even after replacing fuses, inspect the wiring for short circuits or damage.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues in the 1998 Honda Vehicle

Start by inspecting the main power distribution panel located under the dashboard and the engine compartment. If an electrical component stops working, the first step is to check the appropriate relays and connections.
- No Power to the Radio or Interior Lights: Check the 15A fuse in the interior fuse box. If blown, replace it with one of the same amperage. If the issue persists, verify the integrity of the wiring.
- Headlights Not Functioning: Inspect the 30A headlamp relay and the 10A fuse linked to the lighting system. Also, check the ground connections near the battery.
- Engine Cranks, But Won’t Start: Often caused by a faulty fuel pump relay or a blown ignition fuse. Test the relay and replace if necessary.
- Power Windows Not Responding: The 30A window motor fuse in the fuse box near the driver’s seat should be examined. If there’s no power, consider testing the switch mechanism for faults.
- Air Conditioning Not Cooling: The 10A A/C fuse in the engine compartment should be checked. If it’s intact, inspect the refrigerant levels and compressor function.
If any circuit consistently blows after replacement, inspect for wiring short circuits or defective components that could be causing the overload.