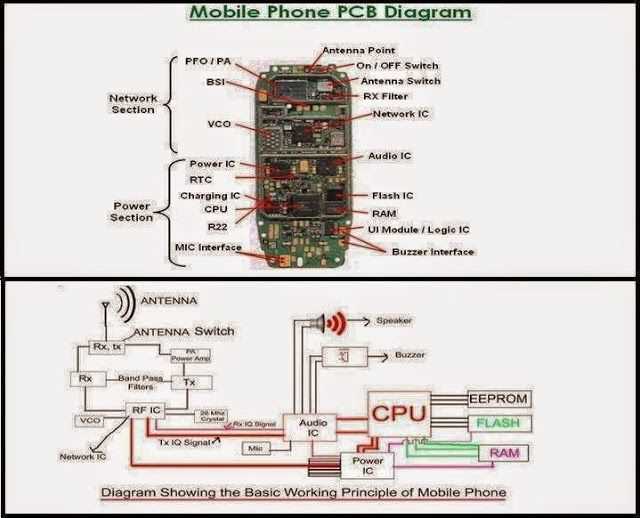
A mobile phone printed circuit board (PCB) diagram provides a visual representation of the different components and connections that make up a mobile phone. The PCB is one of the most important parts of a mobile phone as it houses the electronic circuitry that allows the device to function. From the processor to the memory, from the display to the camera, the PCB is responsible for connecting all these components together and ensuring their proper functioning.
Understanding the mobile phone PCB diagram is essential for mobile phone technicians and enthusiasts who want to repair or modify their devices. By studying the diagram, one can identify the various components and understand their interconnections. This knowledge is crucial for troubleshooting and diagnosing hardware problems that may arise in a mobile phone.
The mobile phone PCB diagram typically includes labels for the different components such as the processor, memory chips, power management IC, display connectors, camera module, and various sensors. It also shows the different pathways or “traces” that carry electrical signals between these components. These traces are usually made of copper and are etched onto the surface of the PCB. By following the traces, one can understand how the different components are connected and how they communicate with each other.
In conclusion, the mobile phone PCB diagram is a valuable tool for understanding the inner workings of a mobile phone. Whether you are a mobile phone technician or an enthusiast, studying the diagram can help you gain a deeper understanding of how a mobile phone functions and how to troubleshoot and repair any hardware issues that may arise.
What is a Mobile Phone PCB Diagram?
A mobile phone PCB diagram is a visual representation of the printed circuit board (PCB) of a mobile phone. The PCB is a crucial component of a mobile phone as it contains the electronic components and circuits that enable the device to function.
The PCB diagram provides a detailed layout of the various components on the board, including the processor, memory, power supply, and other essential parts. It also shows the interconnections between these components, allowing technicians and engineers to understand the flow of signals and data within the phone.
The PCB diagram is essential for diagnosing and repairing mobile phones. It helps technicians identify faulty components and trace the root cause of a problem. By referring to the diagram, they can identify the specific circuitry or component that needs attention and perform repairs or replacements accordingly.
The PCB diagram is also useful for mobile phone manufacturers and designers. It allows them to visualize and optimize the layout of components, ensuring efficient performance and maximizing the use of available space. Moreover, the diagram serves as a reference during production, making sure that each board is assembled correctly.
In summary, a mobile phone PCB diagram is a valuable tool for technicians, engineers, manufacturers, and designers. It provides an in-depth understanding of the internal structure and connections of a mobile phone, enabling efficient troubleshooting, repair, and optimization of the device.
Understanding the Basics of Mobile Phone PCB Diagrams
In the world of mobile phones, PCB diagrams play a crucial role in understanding the functionality and structure of the device. A PCB, or Printed Circuit Board, serves as the backbone of a mobile phone, providing a platform for the various electronic components to connect and communicate with each other.
What is a PCB diagram?
A PCB diagram is a visual representation of the layout and connections of the electronic components on a printed circuit board. It helps technicians and engineers understand the design and functionality of the mobile phone’s hardware components and their interconnections.
The key components of a mobile phone PCB diagram:
- Microprocessor: The brain of the mobile phone, responsible for processing and executing instructions.
- Memory: Storage units such as RAM and ROM, where data and instructions are stored.
- Power supply: The source of power for the mobile phone’s operations.
- Antenna: Provides wireless connectivity, allowing the device to communicate with other devices.
- Display: The screen that displays text, images, and videos.
- Camera module: Captures images and videos.
- Sensors: Various sensors, such as accelerometers and gyroscopes, that provide input for various functionalities.
- Connectivity components: USB ports, SIM card slots, and other connectors for data transfer and communication.
How to interpret a mobile phone PCB diagram?
Interpreting a PCB diagram requires a basic understanding of electronic components and their functions. Each component is labeled with a unique identifier, and lines or traces indicate the connections between the components. By following the traces, one can understand the flow of signals and data within the mobile phone.
The importance of mobile phone PCB diagrams:
Mobile phone PCB diagrams are indispensable for technicians, engineers, and repair professionals. They provide a blueprint for troubleshooting and diagnosing hardware issues, as well as for repairing and replacing faulty components. Understanding PCB diagrams helps ensure accurate repairs and proper functioning of mobile phones.
Summary:
In summary, mobile phone PCB diagrams are visual representations of the layout and connections of electronic components on a printed circuit board. These diagrams help technicians and engineers understand the design and functionality of a mobile phone’s hardware components, allowing them to diagnose and repair issues accurately. By deciphering the identifiers and connections on the PCB diagram, professionals can ensure the proper functioning of mobile phones.
Components of a Mobile Phone PCB Diagram
A mobile phone printed circuit board (PCB) diagram is a visual representation of the various components that make up a mobile phone’s circuit board. It shows how these components are connected and interact with one another to perform various functions.
1. Processor: The processor, also known as the central processing unit (CPU), is the brain of the mobile phone. It carries out the main processing tasks and controls the overall operation of the device.
2. Memory: Mobile phones have different types of memory components, including RAM (random access memory) and ROM (read-only memory). RAM is used for temporary storage and processing of data, while ROM stores permanent information like the phone’s firmware.
3. Power Management IC: The power management integrated circuit (IC) regulates the power supply to different components of the mobile phone, ensuring they receive the right amount of power and preventing overheating or damage.
4. Battery Connector: The battery connector allows the mobile phone’s PCB to connect with the battery, providing power to the device. It is usually a small socket or connector located on the circuit board.
5. Audio Components: Mobile phones have various audio components, including speakers, microphones, and audio codecs. These components allow users to hear and communicate with others during phone calls and multimedia playback.
6. Display Module: The display module includes the screen and related components such as the touchscreen digitizer and backlight. It displays the user interface and visual content on the mobile phone.
7. Camera Module: Mobile phone PCB diagrams often include a camera module, which consists of a camera sensor, lens, and related circuitry. It allows users to capture photos and record videos.
8. Connectivity Modules: Mobile phones typically include various connectivity modules, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular network modules. These modules enable wireless communication and internet connectivity.
9. Sensors: Mobile phones are equipped with various sensors, such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and ambient light sensors. These sensors provide input to the device, allowing it to detect motion, orientation, and adjust display brightness accordingly.
Overall, a mobile phone PCB diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the components and their connections within a mobile phone. It helps engineers and technicians understand the device’s internal structure and aids in troubleshooting and repairing mobile phones.
The Importance of Mobile Phone PCB Diagrams in Repair
In the world of technology, where mobile phones have become an essential part of our lives, it is important to understand the internal components that make up these devices. One crucial element is the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) diagram, which provides a visual representation of the phone’s circuitry and connections. These diagrams are instrumental in the repair and troubleshooting of mobile phones, as they serve as a guide for technicians to identify and fix any issues that may arise.
Identifying Components and Connections
Mobile phone PCB diagrams are incredibly helpful in identifying various components and their corresponding connections. With these diagrams, technicians can quickly locate the faulty component or connection, saving valuable time during the repair process. They provide a clear overview of the circuitry, allowing technicians to easily follow the flow of signals and pinpoint the exact problem area.
Troubleshooting and Repairs
When it comes to troubleshooting and repairs, mobile phone PCB diagrams are essential tools for technicians. They provide a visual representation of the electrical paths and connections, enabling technicians to trace the source of a problem. Whether it’s a faulty capacitor, resistor, or IC chip, these diagrams help technicians identify the specific component that needs repair or replacement.
Assisting with Advanced Repairs and Modifications
Mobile phone PCB diagrams also play a crucial role in advanced repairs and modifications. They allow technicians to understand the layout and design of the circuitry, making it easier to implement modifications or upgrades. By referring to these diagrams, technicians can add new components, replace existing ones, or even modify the circuit to improve performance or add new features to the mobile phone.
Overall Efficiency and Accuracy in Repair
The availability of mobile phone PCB diagrams greatly enhances the efficiency and accuracy of repairs. Technicians can work more effectively, as they have a clear visual guide to reference throughout the repair process. This reduces the risk of errors and ensures that repairs are conducted in a timely manner. Whether it’s a cracked screen, a malfunctioning camera, or a faulty charging port, having access to the PCB diagram ensures that technicians can quickly diagnose and fix the problem, restoring the mobile phone to its full functionality.
Conclusion
In summary, mobile phone PCB diagrams are essential tools for technicians in the repair and troubleshooting of mobile phones. They provide a visual representation of the circuitry, aiding in the identification of faulty components and connections. These diagrams assist in advanced repairs and modifications, improving overall efficiency and accuracy. With the help of PCB diagrams, technicians can ensure that mobile phone repairs are conducted effectively and efficiently.
How to Read and Interpret a Mobile Phone PCB Diagram
Mobile phone PCB diagrams are essential tools for repairing and troubleshooting mobile phones. They provide a detailed graphical representation of the phone’s printed circuit board (PCB), which contains all the electronic components and their interconnections. To effectively read and interpret these diagrams, it is important to understand the various elements and symbols used.
Components and Symbols: The PCB diagram includes symbols to represent different components such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, microprocessors, connectors, and more. Each component symbol is labeled with a unique identifier or value, which helps in identifying and locating the corresponding component on the actual PCB.
Traces and Connections: Traces are thin lines on the diagram that represent the conductive paths on the PCB. These lines depict the connections between different components and help understand the flow of current and signals. It is important to carefully follow the traces and connections to identify any potential issues or faults.
Power and Ground: The PCB diagram also indicates the power and ground connections. These are represented by specific symbols or labels such as Vcc (power supply), GND (ground), and various voltage levels. Understanding the power and ground connections is crucial for diagnosing power-related issues and ensuring proper functioning of the phone.
Layout and Placement: The PCB diagram provides a visual representation of the physical layout of components on the PCB. It helps in understanding the spatial arrangement and placement of different parts, which can be useful for identifying faulty components, making repairs, or performing modifications. Paying attention to the component layout is important for efficient troubleshooting.
Additional Information: In addition to the basic components and connections, PCB diagrams may also include additional information such as test points, jumpers, switches, and more. These details provide further insights into the phone’s circuitry and can be helpful during repairs or modifications.
References: While interpreting a mobile phone PCB diagram, it is important to refer to the manufacturer’s documentation or schematic diagrams whenever available. These references provide detailed information about specific components, circuitry, and signal paths, which can greatly aid in understanding and troubleshooting the PCB diagram.
- Understanding the components, symbols, traces, and connections used in the PCB diagram is crucial for effective troubleshooting and repair.
- Carefully following the traces and connections helps identify potential faults or issues.
- Understanding the power and ground connections is important for diagnosing power-related problems.
- Examining the layout and placement of components helps identify faulty parts and perform repairs or modifications.
- Referring to manufacturer’s documentation or schematic diagrams provides additional information and clarification.
Common Problems and Solutions in Mobile Phone PCB Diagrams
Mobile phone PCB diagrams play a crucial role in understanding the internal circuitry and components of a mobile phone. However, like any electronic device, mobile phones can encounter various problems that may require troubleshooting and repairs. Here, we will discuss some common problems that can be identified using PCB diagrams and their potential solutions.
1. Power-related issues:
- No power: If the mobile phone does not power on, the first step is to check the battery and make sure it is properly connected. Additionally, inspecting the power supply circuit on the PCB diagram can help identify any damaged components or loose connections. Replacing faulty components or re-soldering loose connections can resolve the issue.
- Power fluctuations: If the mobile phone experiences power fluctuations or sudden shutdowns, it could indicate a problem with the power management circuit. Checking the PCB diagram for any damaged capacitors or voltage regulators can help pinpoint the issue. Replacing faulty components or conducting proper power management circuit repairs may solve the problem.
2. Network-related issues:
- No signal: When a mobile phone fails to find or maintain a signal, it could be due to antenna or network-related problems. Referring to the PCB diagram can help locate the antenna and associated circuitry. Ensuring a proper connection between the antenna and the PCB, and replacing any damaged components if necessary, can improve the phone’s reception.
- Weak signal: If the mobile phone experiences weak signal strength or frequent call drops, it may indicate an issue with the RF circuit. Examining the PCB diagram for the RF section and checking for damaged or disconnected components can help identify the problem. Replacing faulty components or re-soldering loose connections can improve signal quality.
3. Display-related issues:
- No display: If the mobile phone’s screen remains blank or shows no display, examining the PCB diagram can help identify faults in the display circuit. Checking for damaged connectors, ICs, or other display-related components and repairing or replacing them can restore the display functionality.
- Touchscreen problems: Unresponsive or malfunctioning touchscreens can be attributed to issues with the touch IC or the touchscreen connector. Inspecting the relevant sections on the PCB diagram and replacing faulty components or re-soldering loose connections may resolve the problem.
These are just a few examples of the common problems that can be detected using mobile phone PCB diagrams. These diagrams serve as valuable resources for technicians and repair professionals, enabling them to diagnose and fix various issues in mobile phone circuitry.
Tips for Troubleshooting and Repairing Mobile Phone PCBs
When it comes to troubleshooting and repairing mobile phone PCBs, it is important to have a systematic approach and the right tools. Here are some tips to help you in the process:
1. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Having the right tools and equipment is crucial for repairing mobile phone PCBs. Invest in a good quality soldering iron, tweezers, multimeter, and other necessary tools. These tools will help you in diagnosing and fixing the issues with the PCB more efficiently.
2. Understand the Circuit Diagram:
Before starting the troubleshooting process, make sure you have a clear understanding of the mobile phone PCB’s circuit diagram. This will help you in identifying the components, their connections, and finding potential faults. Refer to the manufacturer’s documentation or online resources for the circuit diagram.
3. Visual Inspection:
Perform a visual inspection of the PCB for any physical damage or signs of burnt components. Look for components that are cracked, discolored, or have loose connections. This will give you an initial idea of the possible issues.
4. Test the Power Supply:
Check the power supply to ensure it is delivering the correct voltage. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at different points on the PCB. A faulty power supply can cause various issues, including a non-functional mobile phone.
5. Check for Short Circuits:
Look for any short circuits on the PCB, which can be caused by components touching each other or damaged tracks. Use a multimeter in the continuity mode to check for shorts between different points on the PCB. Repair any short circuits by removing the faulty components or fixing the damaged tracks.
6. Identify Faulty Components:
If you have identified a specific area or component that is causing the issue, focus on that particular section. Check the individual components in that section for any faults. Remove and replace any faulty components using proper soldering techniques.
7. Follow Proper Soldering Techniques:
When replacing components on the PCB, make sure to follow proper soldering techniques. Use the right amount of solder, avoid overheating the components, and ensure proper connections. Improper soldering can lead to further damage and potentially cause more issues.
8. Test and Verify:
After making the necessary repairs or replacements, test the PCB to ensure the issue has been resolved. Connect the mobile phone to a power source and check its functionality. Test all the features and functionalities to make sure everything is working properly.
Conclusion:
Repairing mobile phone PCBs can be a challenging task, but with the right tools, knowledge, and systematic approach, it can be accomplished successfully. By following these tips, you will be able to troubleshoot and repair mobile phone PCBs efficiently and effectively. Remember to take necessary precautions and refer to professional help if needed.