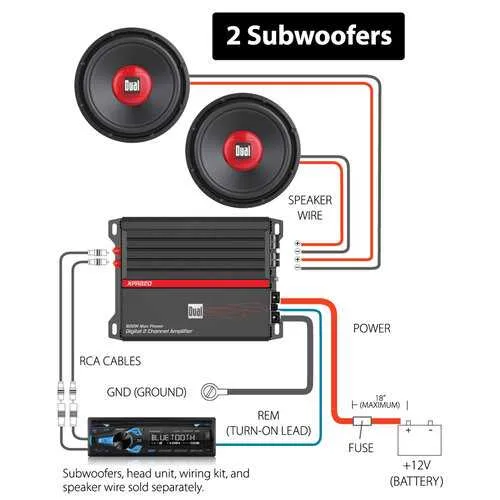
For optimal performance, ensure that your system’s power supply and speaker impedance match. Incorrect matching can lead to suboptimal sound quality or damage. Use high-quality cables for stable signal transmission, particularly for connections between the power source and the speaker.
Start by verifying the current rating of your setup, ensuring that the electrical components are rated for the intended load. Avoid using standard speaker wire if your system requires more robust options to handle higher currents.
When connecting the system to a power source, remember to connect the positive terminal of the power unit to the positive side of the speaker, and the negative terminal to the negative side. This will ensure proper phase alignment, which is critical for clear, undistorted sound reproduction.
Check all connections twice before powering up. A loose or improperly connected wire can result in poor sound quality or, in the worst case, equipment failure. If necessary, use a multimeter to test for continuity and make sure that no shorts are present.
Finally, after making all connections, perform a test to confirm everything is functioning as expected. Adjust the gain and other settings to fine-tune the output and ensure an ideal listening experience.
Wiring Setup for Single Channel Sound Systems
To correctly connect a single-channel sound system, begin by identifying the input and output terminals. The input connects to the source device, such as a head unit, and the output should be connected to the subwoofer or speaker. For power, use a suitable gauge wire to ensure minimal loss and optimal current flow.
Start by connecting the positive terminal from the source to the positive terminal of the output. Ensure that the negative terminal from the source connects securely to the negative terminal of the output as well. For grounding, use a dedicated ground wire, making sure it is attached to a metal surface in the vehicle for the best signal return.
If you are bridging multiple channels to increase power delivery, ensure the wiring matches the amplifier’s specifications. Properly fuse the power wire close to the battery to avoid potential shorts. Always check the voltage ratings of your components before connection to prevent damage from overvoltage.
Use high-quality cables for the best sound performance. Insulated cables reduce interference, while twisted-pair designs are recommended for power and ground connections. Additionally, ensure that any connectors used are rated for the expected current to avoid overheating or signal degradation.
Test all connections before final assembly. Ensure all contacts are tight, and there are no exposed wires that might cause short circuits. Once verified, secure all cables neatly to avoid any physical damage over time.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting a Single-Channel Power Unit to Speakers
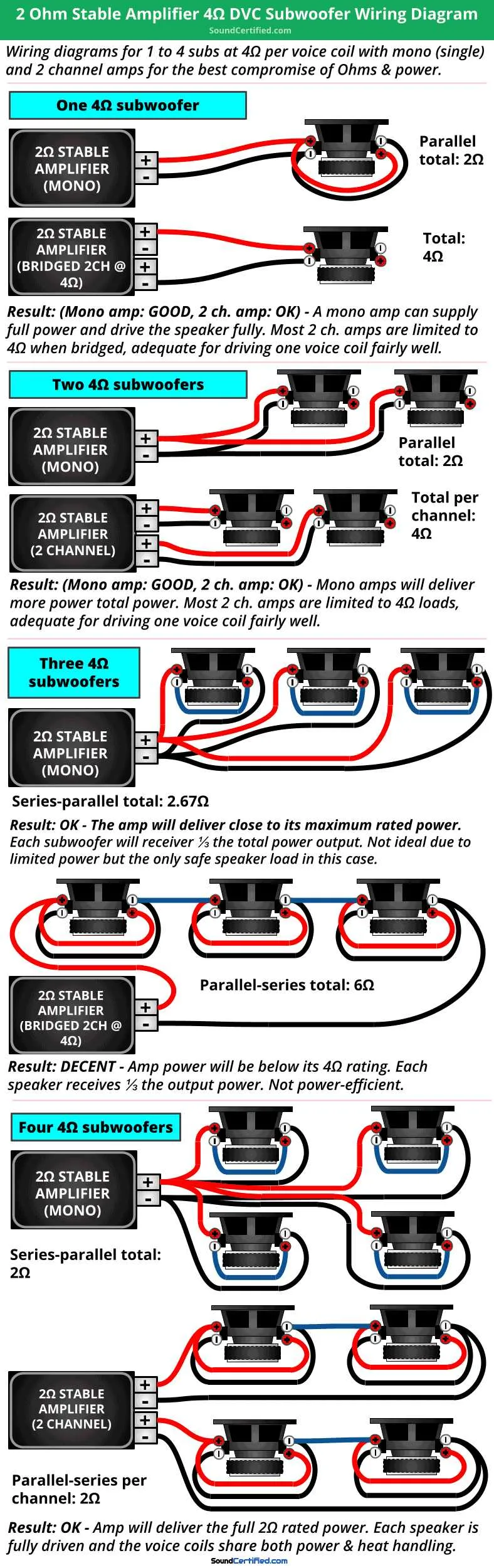
Start by ensuring that the power supply is switched off and that all components are disconnected. This prevents any accidental damage or electric shocks during the setup.
- Prepare the Power Unit: Check the input terminals. You’ll find either RCA or speaker-level inputs for the signal source. Ensure you have the correct cables for your setup.
- Speaker Selection: Choose a speaker with the correct impedance rating, matching the unit’s output. Most systems work with 4 to 8 ohms, but confirm the specs to avoid mismatched impedance.
- Connect the Signal Input: For RCA inputs, use RCA cables from the signal source (e.g., receiver or preamp). If you’re using speaker-level inputs, connect the speaker wire directly from the source.
- Attach the Speaker Wires: Strip about half an inch of insulation from the ends of the speaker wires. Insert the stripped ends into the output terminals, ensuring the positive and negative connections are correctly aligned. Tighten the terminal screws to secure the wires.
- Verify the Grounding: If necessary, connect the ground terminal of the power unit to a suitable grounding point on the chassis or power source to prevent hum or interference.
- Check the Cables: Double-check all connections for secure fittings. Loose cables can lead to poor sound quality or even damage the equipment.
- Power On: Once the connections are secure, power up the system. Adjust the volume gradually to test the signal output to the speaker.
Ensure that the system operates correctly by listening for clear sound without distortion. If the unit overheats or you notice issues, power off and recheck all connections, especially the impedance settings and wire integrity.
Understanding Grounding and Power Connections
For optimal performance, always connect the ground terminal of the system to a solid, unpainted metal part of the vehicle or chassis. This minimizes the risk of ground loop interference and ensures consistent audio quality. Ensure the power supply cable is thick enough to handle the current draw without causing voltage drop. Use at least 8 AWG cable for standard systems, but consider 4 AWG or thicker for higher power setups.
When connecting the power wire to the positive terminal, make sure it is secure and the connection is free from corrosion. The power cable should ideally be routed away from sensitive signal lines to prevent interference. Use fuse protection near the power source to safeguard against electrical surges or shorts.
For ground connections, keep the wire as short as possible. A long ground wire can introduce noise and reduce efficiency. If possible, run the ground wire directly to the battery’s negative terminal or the chassis, avoiding intermediate connections that could increase resistance.
Pay close attention to the power and ground cables’ gauge, as undersized cables will lead to inefficiencies and potential overheating. Properly securing cables with zip ties or clips prevents any movement that could cause wear over time.
Common Wiring Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

Ensure you always double-check connections to avoid shorts or incorrect polarities. Inaccurate connections can cause damage to components or even lead to system failure.
Incorrect Grounding is one of the most frequent issues. A poor or missing ground connection can lead to electrical hums or interference. Make sure the ground is securely attached to a metal surface with proper conductivity.
Overloading the System happens when the total impedance is not considered. Connecting too many speakers or mismatched units can draw excessive current. Always check the specifications to ensure the system can handle the load.
Wrong Speaker Polarity often causes phase issues, resulting in poor sound quality. Connect the positive and negative terminals of the speaker to their corresponding terminals on the device. Use color-coded wires to simplify the process.
Loose Connections can lead to unreliable performance and noise. Always tighten terminals properly and double-check them before powering on the system.
Using Inadequate Cables is another common mistake. Low-quality or undersized cables can restrict power flow, reducing system performance. Use cables rated for the required voltage and current.
Over-tightening Screws can damage connections and cause poor conductivity. Tighten connections firmly but avoid excessive force, which can strip threads or damage the components.
Lastly, testing the system after completing any setup is crucial. This ensures that all connections are functioning properly and no mistakes have been made during the assembly process.