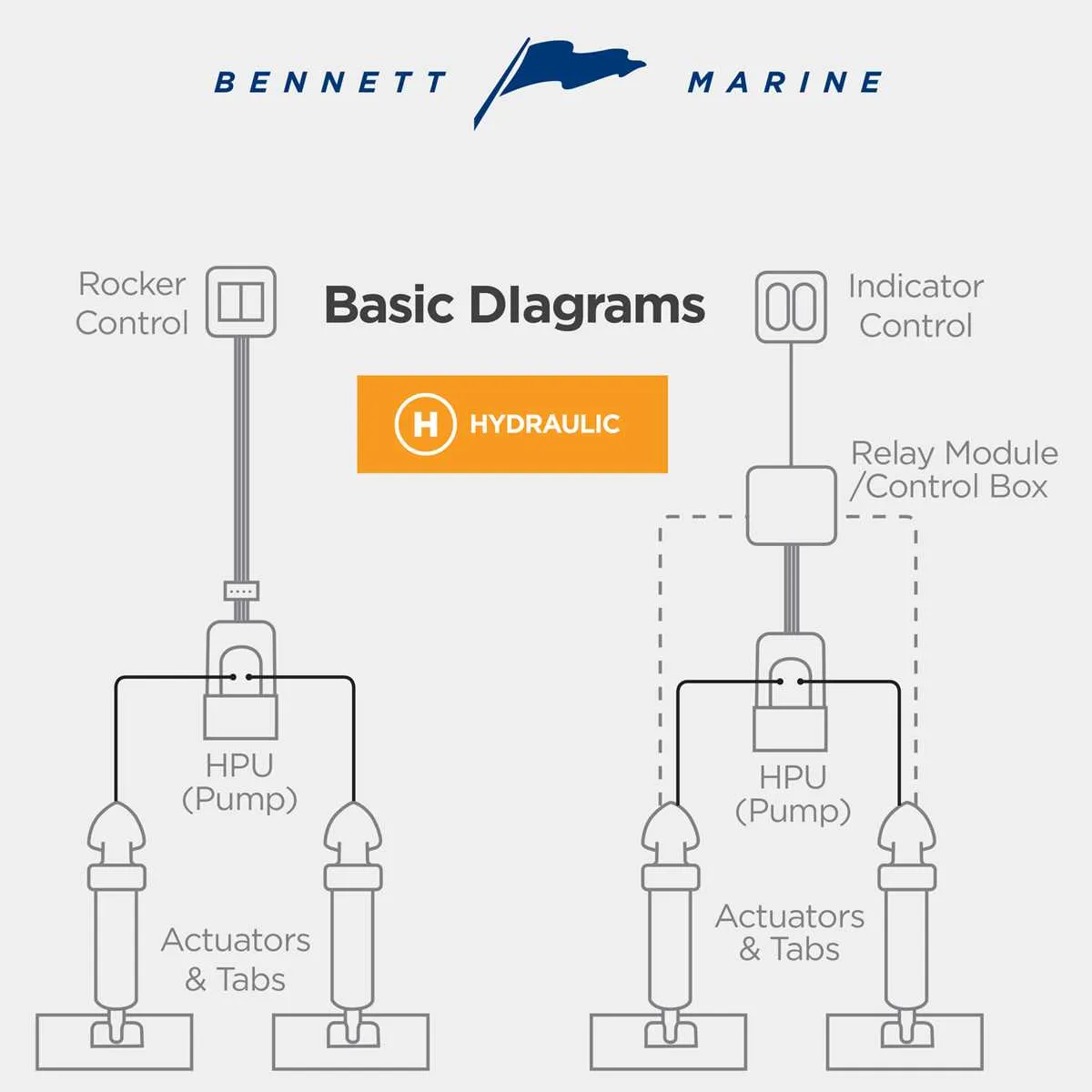
Ensure proper connections when setting up your boat’s steering adjustment system. Correctly wired components play a critical role in smooth operation, and any mistake in the setup can lead to malfunction or inefficiency. Begin by confirming that all connections between the control unit and the actuators are secure, avoiding any loose wires or incomplete contacts.
The control system should be linked to the hydraulic or electrical components depending on the model. If you’re using a system that operates with a hydraulic pump, check that the wires are securely fastened and that there is no possibility for short circuits. Use insulated connectors for any exposed wires to protect against corrosion.
For optimal performance, double-check the power source connections. This ensures that there is a steady flow of energy to the system, allowing smooth adjustments. Failure to connect the power source properly can lead to intermittent issues, affecting the responsiveness of the system when in use.
Also, pay attention to the control switches placement. They should be easily accessible while ensuring safety during operation. Make sure the installation follows the manufacturer’s guidelines for wire placement to avoid interference with other boat systems. A clean and organized setup will contribute to both reliability and longevity of the system.
Electrical Setup for Adjustable Hull Fins
Ensure a clear and organized connection layout when installing the electrical components for the hull fins system. Follow these steps for a reliable installation:
- Start by connecting the power supply to the control unit, ensuring the voltage matches the device requirements.
- Install the circuit breakers to prevent any overcurrent situations during operation.
- Use marine-grade wires to connect the motor terminals to the control mechanism.
- Ensure proper grounding to avoid electrical interference and maintain safety.
- Test all connections before securing them in place, checking for any loose fittings.
- If installing a dual-system, connect both motors to the primary switch, using a parallel configuration for synchronization.
Double-check polarity when attaching wires to the motor terminals. Incorrect polarity could result in the system malfunctioning. Ensure that the control switch is positioned in an accessible location, within easy reach of the pilot.
After confirming the electrical connections, run a test to verify the motors’ responsiveness and proper operation of the hull fins system. Adjust the system as needed based on performance.
Understanding the Electrical Connections for Adjustable Hull Flaps
Ensure correct polarity when connecting the power leads to the actuator system, as reversing these can lead to malfunction. The positive wire should be connected to the red terminal, while the negative wire should go to the black terminal on the control unit. Always use properly rated fuses to protect against electrical surges, typically a 10-amp fuse for most systems.
For control switch installation, choose a location that allows easy access while operating. The switch should be wired in parallel with the actuator and connected to the power source. Ensure that the switch terminals are securely connected to prevent accidental disconnections.
When routing the cables, avoid placing them near sharp edges or hot surfaces to prevent damage. It’s advisable to use marine-grade cables with a good insulation rating to ensure durability in a saltwater environment. Insulate all exposed connectors to prevent corrosion over time.
Grounding is crucial for safe operation. A proper ground connection should be made from the control unit to the boat’s common ground, typically the negative terminal of the battery. Ensure the ground wire is short and well-secured to prevent signal interference and reduce the risk of electrical faults.
Testing the system after installation is key. Power the system on, and operate the controls in both directions. If the unit fails to respond or operates incorrectly, double-check all connections, especially the polarity and ground connections, as these are common causes of issues.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting the Electrical System
Ensure that the battery is disconnected before starting any installation. Begin by preparing the necessary cables and connectors for the motor and control system. Verify that all components are rated for the appropriate voltage and amperage to prevent overloading the system.
Next, connect the positive terminal of the power source to the input terminal of the actuator using a thick gauge wire. Secure the connection with a high-quality terminal lug, ensuring a tight fit to prevent any loose contacts that could lead to malfunction.
Attach the ground wire to the negative terminal of the power source. Connect the other end to the grounding point on the frame or any metal surface that ensures a solid electrical return. Make sure the connection is free from corrosion to avoid resistance in the circuit.
For the control switch, wire the positive lead from the actuator to one terminal on the switch. Use a durable wire for this connection, ensuring it’s long enough to comfortably reach the switch location.
The other terminal of the switch should be connected to the positive side of the power source. This will allow you to control the direction of the actuator when toggling the switch.
Finally, check all wiring for secure and insulated connections, making sure no exposed wires could short circuit. Test the system by reconnecting the battery and activating the switch to confirm proper operation. If any issues arise, recheck the connections, particularly the power and ground points.
Common Electrical Issues and How to Troubleshoot
Faulty connections are often the primary cause of electrical malfunctions. Ensure all terminals are securely fastened, and inspect for any signs of corrosion or wear. If you notice loose connectors, tighten them properly or replace if needed.
Power loss can stem from a number of factors, including blown fuses or faulty relays. Test the voltage at the control unit and check the integrity of the fuse box. If a fuse is blown, replace it with the correct amperage rating.
Short circuits may occur if wires are damaged or improperly routed. Inspect each wire for visible damage, including frays or cuts, and ensure that all wires are well-insulated. Pay attention to areas where wires are near sharp edges or exposed to excessive movement.
Erratic behavior can be linked to issues with the ground connection. A poor or missing ground can cause intermittent power surges. Verify that the grounding point is clean, secure, and free of any debris or corrosion.
Overheating components can be a result of insufficient power supply or overloaded circuits. Ensure that the system is not drawing more power than it’s designed to handle. If overheating persists, consider checking the amperage specifications for compatibility.
Interference from nearby electronic devices may cause fluctuations in performance. To troubleshoot this, try moving or isolating wires from sources of electromagnetic interference, such as large motors or communication equipment.