The Big Muff is a legendary distortion pedal that has been used by countless guitarists to achieve a thick, saturated tone. First introduced in the late 1960s, it quickly became popular for its unique sound and versatility.
The Big Muff is known for its thick, fuzz-like distortion, which is achieved through a series of cascading gain stages. The pedal’s circuitry is based on a simple schematic, consisting of several key components that work together to shape the pedal’s tone.
One of the main components of the Big Muff schematic is the op-amp. The op-amp (operational amplifier) is responsible for amplifying the guitar’s signal and adding gain to create the distorted sound. It is a crucial part of the circuit, as it determines the overall tone and character of the pedal.
Another important component of the Big Muff schematic is the tone controls. These controls allow the guitarist to shape the pedal’s frequency response and tailor the sound to their preferences. The Big Muff typically has three tone controls: volume, tone, and sustain. The volume control adjusts the overall output level, while the tone control adjusts the high-end frequencies, and the sustain control adjusts the amount of distortion.
In addition to the op-amp and tone controls, the Big Muff schematic also includes various resistors, capacitors, and transistors. These components help to shape the pedal’s signal path and determine how the guitar’s signal is amplified and distorted. The values and configurations of these components can vary between different versions and variations of the Big Muff, resulting in different tonal characteristics.
Understanding the Big Muff schematic can provide valuable insight into how the pedal works and how to modify it to achieve different sounds. Many guitarists have used the schematic as a starting point for creating their own custom versions of the Big Muff, adding or changing components to achieve their desired tone.
Whether you’re a fan of the classic Big Muff tone or looking to experiment with its circuitry, delving into the schematic can be a fascinating journey into the world of guitar electronics.
Big Muff Schematic Explained
The Big Muff is a popular guitar distortion pedal known for its iconic fuzz tone. The circuitry behind the Big Muff is complex, but understanding the schematic can help you better understand how it works and make modifications if desired.
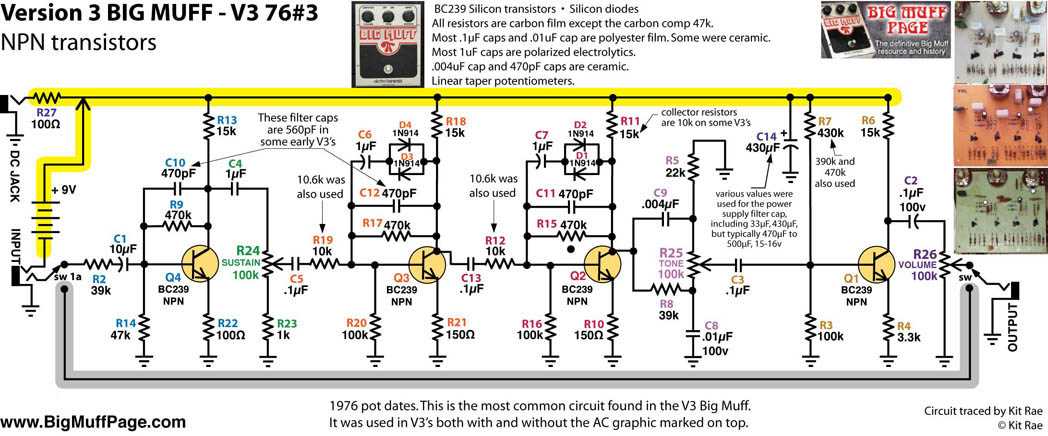
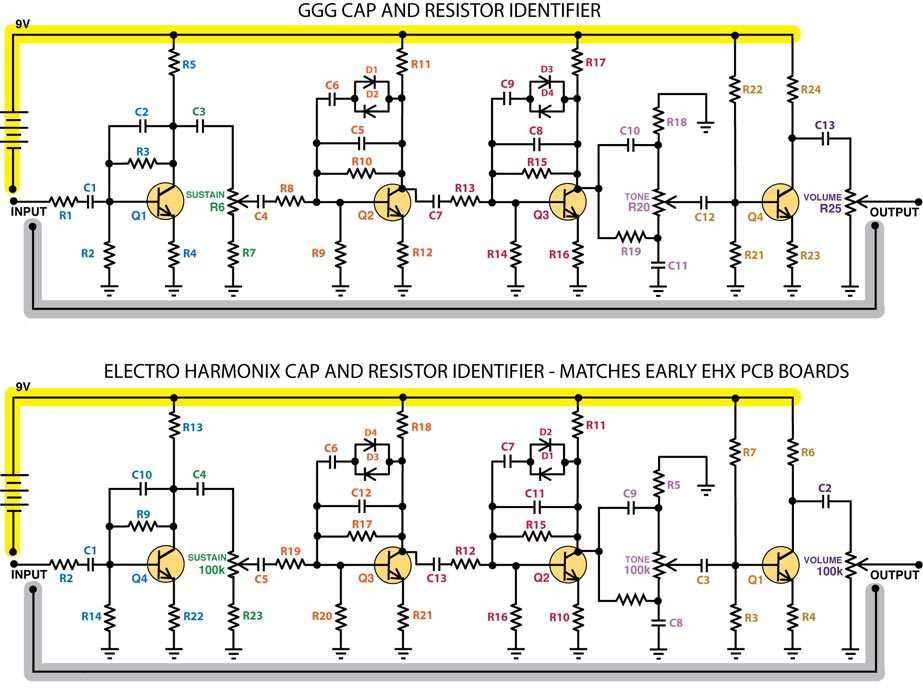
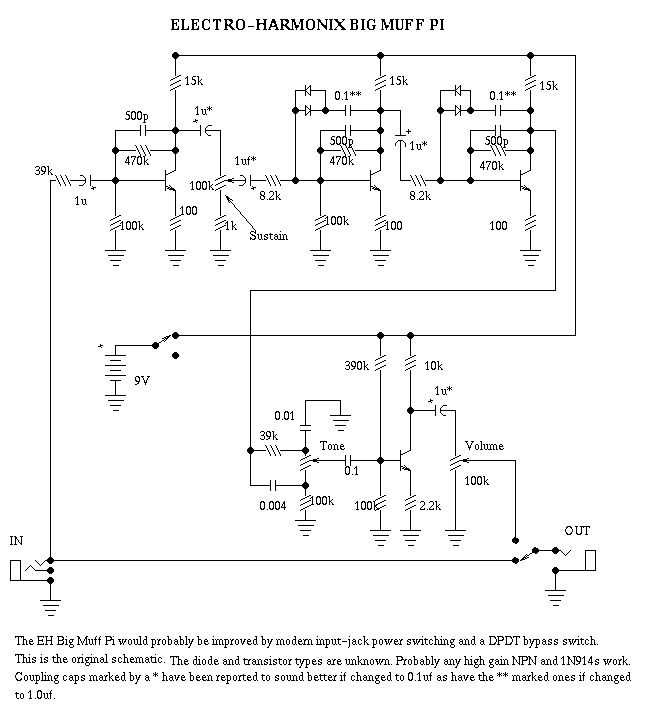
Transistors: The Big Muff uses a combination of three transistors to amplify the guitar signal and create the fuzzy distortion. The first two transistors are silicon NPN types, while the third transistor is a germanium PNP type. These transistors work together to shape the overall tone and character of the pedal.
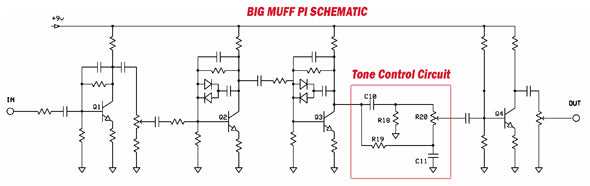
Tone Control: The Big Muff schematic includes a tone control circuit that allows you to adjust the bass and treble frequencies. This circuit uses a potentiometer to change the resistance, which in turn alters the frequency response. By turning the potentiometer, you can shape the tone to your preference, whether you want a darker, bass-heavy sound or a brighter, treble-focused sound.
Clipping Diodes: The Big Muff uses clipping diodes to shape the distortion and create the characteristic fuzz sound. These diodes are responsible for clipping the peaks of the guitar signal and creating the distorted waveform. In the Big Muff schematic, you will find diodes connected to the output of the third transistor, which determines the amount and type of clipping. Swapping out these diodes with different types can alter the clipping characteristics and create different tonal variations.
Feedback Loop: The Big Muff features a feedback loop circuitry that helps to shape the sustain and overall tonal characteristics. The feedback loop consists of resistors and capacitors that control the amount of signal that gets fed back into the circuit. By adjusting the values of these components, you can alter the sustain and harmonic content, allowing for further customization of the pedal’s sound.
Footswitch and Controls: The Big Muff schematic includes the necessary components for the footswitch and controls. This includes a footswitch for turning the pedal on and off, as well as potentiometers for adjusting the volume, sustain, and tone. These controls allow you to fine-tune the pedal’s sound and tailor it to your specific playing style and musical genre.
Overview of the Big Muff Pedal
The Big Muff is a legendary distortion pedal that has become a staple in the world of guitar effects. It is known for its thick, rich tone and sustain, and is a favorite among many guitarists, from blues to rock to metal.
The Big Muff was first introduced in the late 1960s by Electro-Harmonix, and it has since gone through several different versions and variations. The most popular version is the Big Muff Pi, which has become synonymous with the name “Big Muff.”
The Big Muff Pi is a three-knob pedal that controls volume, sustain, and tone. The volume knob sets the overall output level of the pedal, while the sustain knob adjusts the amount of distortion or gain. The tone knob allows you to shape the EQ of the pedal, from a scooped sound to a more mid-range focused tone.
One of the defining characteristics of the Big Muff is its use of transistors in the circuit, which gives it a unique and distinctive sound. The pedal is known for its thick, saturated distortion, with plenty of sustain and harmonics. It can be used for both rhythm and lead playing, and can take your guitar tone from smooth and creamy to aggressive and biting.
- Thick, rich tone with plenty of sustain
- Three-knob control for volume, sustain, and tone
- Unique transistor-based circuit
- Versatile pedal for various styles of music
- Used by many famous guitarists
The Big Muff has been used by countless guitarists over the years, from David Gilmour of Pink Floyd to J Mascis of Dinosaur Jr. Its iconic sound and versatility have made it a go-to pedal for many musicians, and its schematic has been studied and replicated by pedal builders all over the world.
Whether you’re looking to add some crunch to your blues playing or unleash a wall of distortion for heavy metal riffs, the Big Muff is a pedal that delivers. Its unique circuitry and tone-shaping capabilities make it a must-have for any guitarist looking to add some character and depth to their sound.
Understanding the Schematic Diagram
When it comes to building or troubleshooting electronic circuits, one of the most important tools is the schematic diagram. This diagram provides a visual representation of the circuit, showing how different components are connected and how signals flow through the circuit. By understanding the schematic diagram, you can effectively analyze and modify circuits to meet your specific needs.
The schematic diagram uses a combination of symbols and lines to represent different components and interconnections. Each component is represented by a specific symbol, such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, or integrated circuits. These symbols make it easier to identify the components and understand their functions within the circuit. The lines connecting the components indicate the flow of signals, such as voltage or current, through the circuit.
One of the key aspects of understanding the schematic diagram is the ability to read component values and specifications. For example, resistors are labeled with their resistance value in ohms, capacitors with their capacitance value in farads, and transistors with their type and identification numbers. By being able to interpret these values, you can select the appropriate components for your circuit and ensure it functions as intended.
Additionally, understanding the schematic diagram allows you to identify potential issues or areas for improvement in a circuit. By analyzing the connections and component values, you can determine if the circuit is wired correctly and if each component is being used appropriately. If there are any errors or inefficiencies, you can make the necessary modifications to optimize the circuit’s performance.
In conclusion, the schematic diagram is an essential tool for anyone working with electronic circuits. By understanding how to read and interpret the diagram, you can effectively analyze, modify, and troubleshoot circuits to achieve your desired outcomes. Whether you are a hobbyist or a professional, mastering the art of understanding the schematic diagram will greatly enhance your electronics skills.
Components and Circuitry
The Big Muff is a popular effects pedal used by guitarists to create a distorted and sustain-heavy sound. Understanding its components and circuitry can help us better appreciate its unique sound and make modifications if desired.
The heart of the Big Muff is its circuit, which consists of various components working together to shape the sound. The basic design includes three key stages: input buffering, clipping, and output amplification. The input buffering stage ensures that the signal from the guitar remains clean and unaffected by the following stages. The clipping stage introduces distortion by limiting the peaks of the signal to create a clipped waveform. Finally, the output amplification stage boosts the signal to a desired level.
One of the key components in the Big Muff is the op-amp, or operational amplifier. This amplifier plays a crucial role in the circuit by amplifying the input signal and providing gain. The op-amp can be considered the “brain” of the Big Muff, as it determines the overall sound and character of the pedal. Various op-amp models and versions have been used in different iterations of the Big Muff, each contributing to its unique tonal qualities and characteristics.
Other important components in the circuit include resistors, capacitors, and diodes. Resistors are used to control the flow of current in the circuit and can affect the gain and frequency response. Capacitors, on the other hand, store and release electrical energy, shaping the tone and allowing for various filtering options. Diodes are responsible for the clipping of the signal, controlling the distortion and adding to the overall sound.
Understanding the components and circuitry of the Big Muff can give us insights into how the pedal works and how we can modify it to suit our preferences. By experimenting with different resistor and capacitor values, swapping out op-amps, or changing diode configurations, we can customize the Big Muff to achieve the desired tone and sound. It’s this versatility and flexibility that has made the Big Muff a favorite among guitarists seeking a distinct and powerful distortion effect.
Signal Flow and Operation
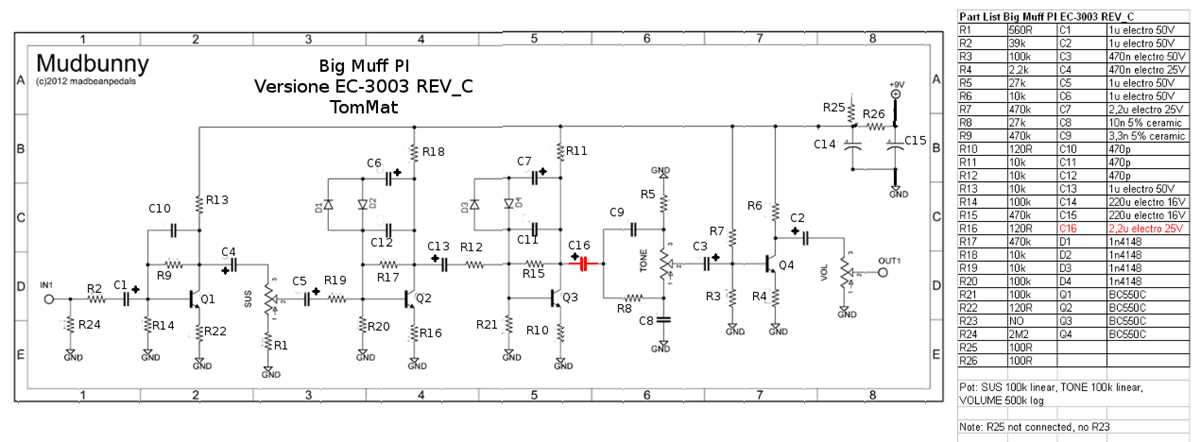
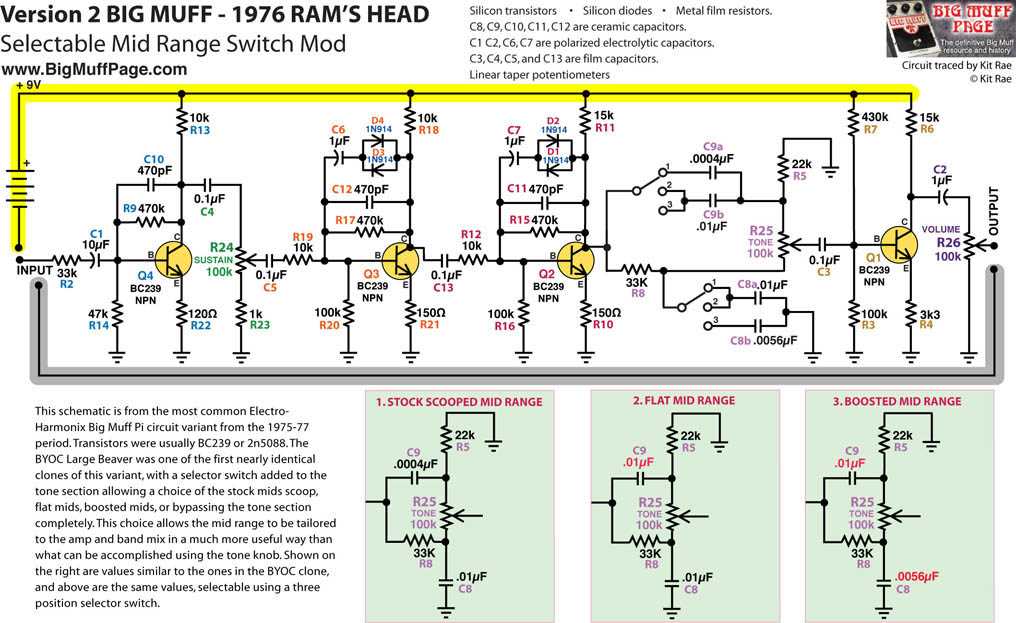
Understanding the signal flow and operation of the Big Muff schematic is crucial in order to fully comprehend how this iconic effect pedal works. The schematic consists of various stages and components that interact with each other to shape the sound. Let’s take a closer look at the signal flow and operation of the Big Muff.
Input Stage
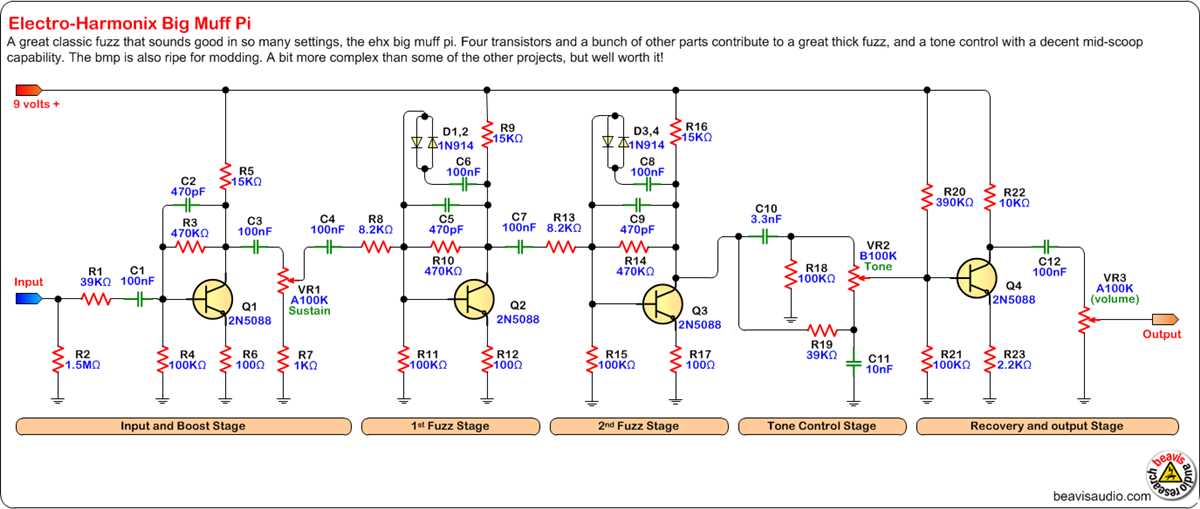
The signal flow starts at the input stage, where the audio signal enters the pedal. Here, the signal is first processed by a buffer circuit, which ensures that the impedance of the guitar signal remains consistent throughout the pedal. This helps to prevent any signal loss or deterioration.
Tone Control
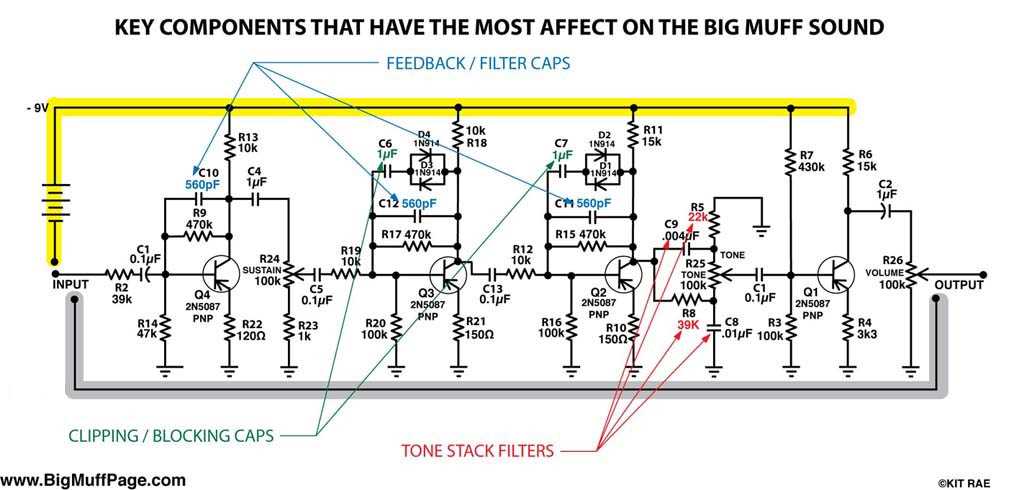
After passing through the input stage, the signal then reaches the tone control section. The tone control circuit is responsible for shaping the frequency response of the pedal. The Big Muff uses a simple passive tone control circuit, consisting of a potentiometer and capacitor. By adjusting the tone control knob, the user can boost or cut specific frequencies to achieve the desired tonal character.
Gain Stages
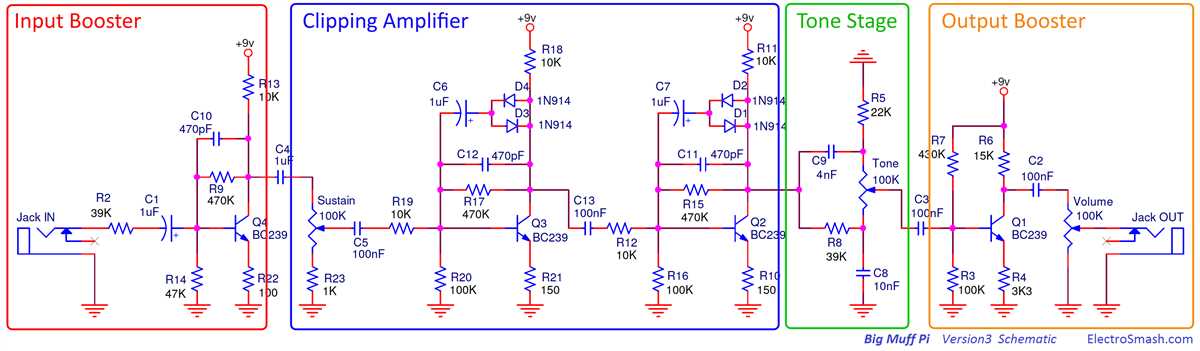
The next crucial part of the signal flow is the gain stages. The Big Muff employs multiple transistor stages to amplify the signal and introduce distortion. These gain stages are responsible for the characteristic overdriven and saturated tone that the Big Muff is known for. The gain control knob allows the user to adjust the amount of gain applied to the signal, ranging from mild overdrive to heavy distortion.
Output Stage
Finally, the signal reaches the output stage of the Big Muff, where it is prepared to be sent out to the amplifier or recording device. The output stage provides impedance matching and buffering to ensure that the signal is sent out properly without any impedance mismatch or signal degradation. It also includes a volume control knob, allowing the user to adjust the level of the output signal.
By understanding the signal flow and operation of the Big Muff schematic, guitarists can better appreciate the inner workings of this beloved effect pedal and make informed decisions when using it to shape their tone.
Modifications and Variations
While the original Big Muff circuit has remained largely unchanged since its inception, there have been many modifications and variations created by musicians, guitar technicians, and pedal manufacturers over the years. These modifications and variations can alter the tone, gain, and overall character of the pedal, providing players with a wide range of options to explore.
One popular modification is the addition of a tone control, which allows players to adjust the high-frequency response of the pedal. This can be useful for tailoring the tone to different guitars and amplifiers, or for achieving a specific desired sound. Another common modification is the addition of a mid-range control, which can help cut through the mix and add more clarity to the guitar sound.
Some players also like to experiment with different transistor and capacitor options in the circuit, which can significantly change the overall tone and voicing of the pedal. For example, using a different type of transistor can result in a smoother or more aggressive distortion, while changing the capacitor values can affect the bass response or the amount of gain. These modifications can help players achieve their desired sound and make the Big Muff circuit truly their own.
In addition to modifications, there are also many variations of the Big Muff circuit available from different pedal manufacturers. These variations may include additional features, such as a built-in boost or fuzz switch, or different voicing options to suit different musical styles. Some variations may also have a smaller footprint or be housed in a different enclosure, making them more pedalboard-friendly. These variations provide players with even more options to explore and find the perfect Big Muff for their needs.
In conclusion, modifications and variations of the Big Muff circuit have allowed players to customize and fine-tune the pedal to suit their individual preferences and musical styles. Whether it’s adding a tone control, experimenting with different components, or exploring different variations from pedal manufacturers, the possibilities for shaping the Big Muff’s sound are virtually limitless.
Tips for Building Your Own Big Muff
Building your own Big Muff can be a rewarding and fun experience. Here are some tips to help you along the way:
1. Gather all the necessary components
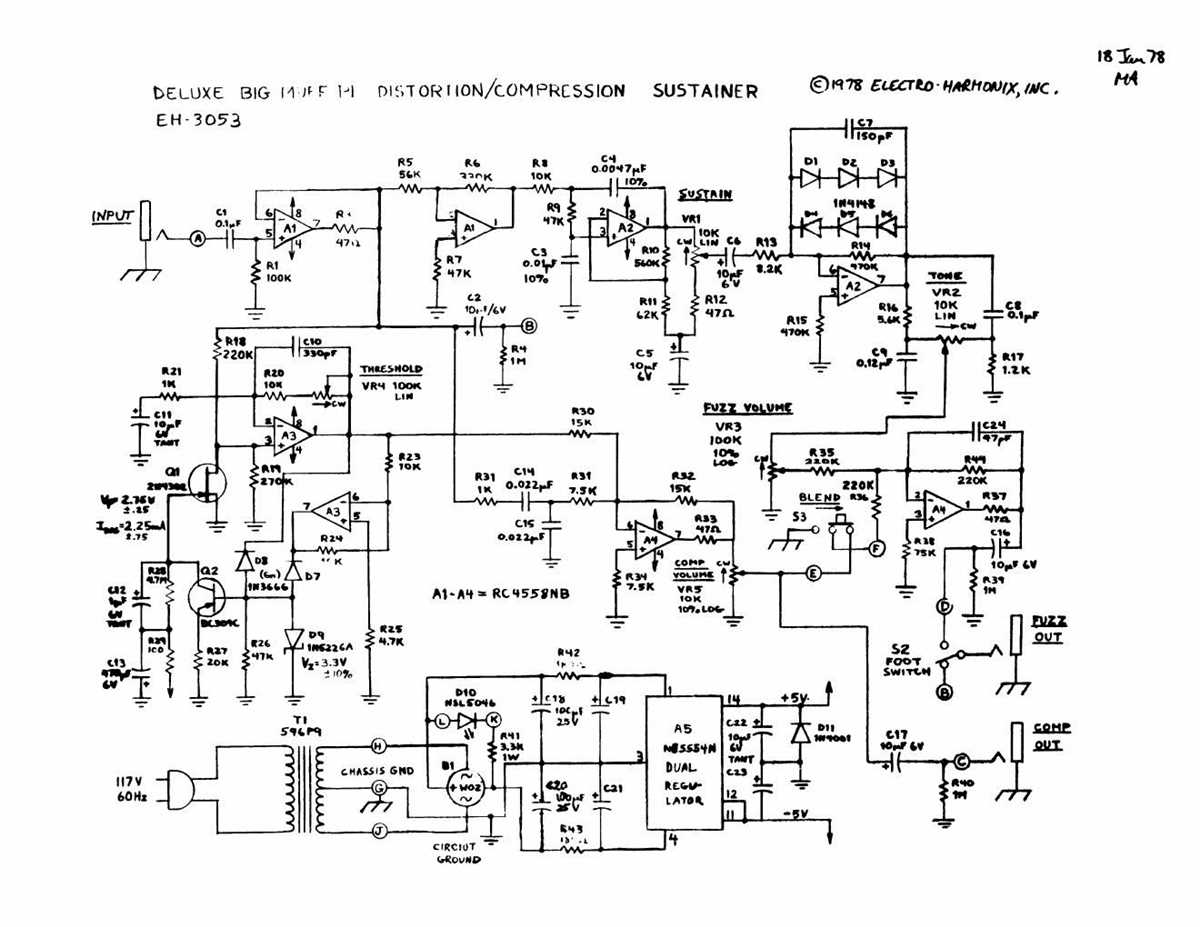
Before you start building, make sure you have all the necessary components. This includes resistors, capacitors, transistors, potentiometers, and other small electronic parts. You will also need a soldering iron, solder, and a breadboard or PCB to assemble the circuit.
2. Double-check the schematic
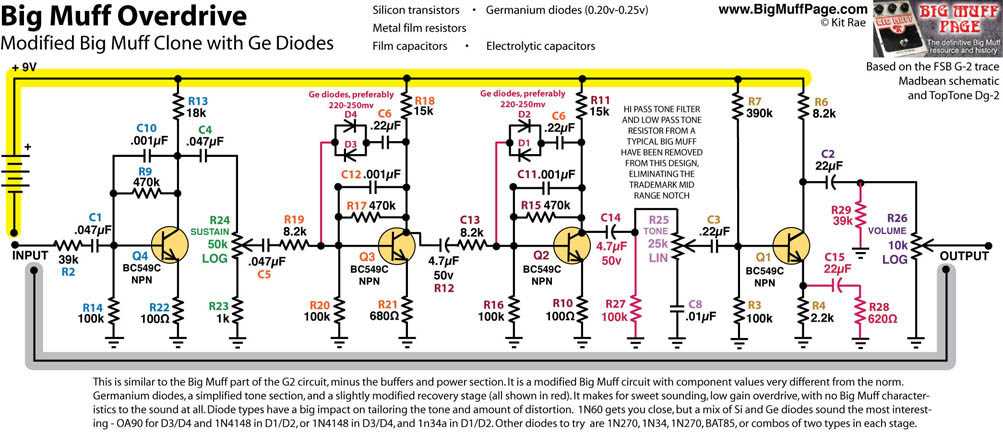
Before you start soldering, double-check the schematic and make sure you understand how the circuit works. This will help you troubleshoot any issues that may arise during the building process.
3. Take your time
Building a Big Muff takes time and patience. Take your time with each solder joint and make sure it is clean and secure before moving on to the next one. Rushing through the process can lead to mistakes and potentially damage the circuit.
4. Test as you go
As you build the Big Muff, test each section of the circuit to ensure everything is working as it should. This will help you identify any errors or faulty components early on and make troubleshooting easier.
5. Use proper safety precautions
When working with electronic components, it is important to take proper safety precautions. Always work in a well-ventilated area, wear safety goggles, and avoid touching hot solder or components. Additionally, make sure to unplug your soldering iron when not in use.
6. Ask for help if needed
If you are new to building electronics or encounter any difficulties during the process, don’t hesitate to ask for help. There are plenty of online forums and communities where experienced builders are willing to offer guidance and assistance.
Building your own Big Muff can be a rewarding experience. By following these tips and taking your time, you can create a unique and customized effect pedal that suits your needs and preferences.