For an efficient installation, ensure the component holder is securely positioned to avoid any misalignment during operation. Proper placement of the hydraulic assist parts guarantees smooth functionality and reduces unnecessary wear. Begin by identifying the correct support points to connect the system to the engine bay. Utilize the mounting holes with precise measurements to avoid friction and vibrations that may affect performance.
First, check the alignment: Ensure the brackets are positioned in such a way that the drive belt can be attached without obstruction. Misalignment can cause stress on the pulleys, leading to premature damage. The angle of the mount plays a critical role in preventing any undue strain on the hoses or lines.
Next, secure the connection: Use robust, corrosion-resistant hardware to fasten the components. Check torque specifications to avoid over-tightening, which can cause damage to the aluminum or steel brackets. Always double-check for tightness before securing the hydraulic lines.
Lastly, double-check the clearance: Verify that the mounted system has enough space to operate freely without interfering with other engine components. This helps to prevent potential failures or leaks from contact with surrounding parts.
Essential Guide for Mounting Your Engine Fluid Pump Assembly
To ensure proper installation of the fluid pump mechanism in your engine, precise alignment and bracket placement are crucial. Here’s a detailed outline to help with the setup:
- Start by confirming the model of your engine to ensure compatibility with the pump and mounting hardware.
- Check if the assembly requires additional spacers or washers between the engine block and the pump mount.
- Ensure that the bolts used for securing the assembly are of the right length and material strength to prevent loosening under pressure.
- Measure the distance between the pump and the engine block to ensure the assembly sits correctly without strain on the mounting points.
- Align the fluid hoses and confirm the proper path for fluid circulation to avoid kinks or unnecessary bends.
Once the mount is positioned correctly, proceed by tightening all mounting points in a sequential manner. Begin with the top bolts, followed by the side fasteners, ensuring even distribution of force. Always torque the bolts to manufacturer specifications to avoid damaging the components.
If any misalignment occurs, double-check the position of the support bracket and adjust accordingly. Ensure the assembly moves freely without obstruction before completing the installation process.
Consult your engine’s manual for specific torque values and additional considerations for the fluid system to ensure optimal operation and longevity.
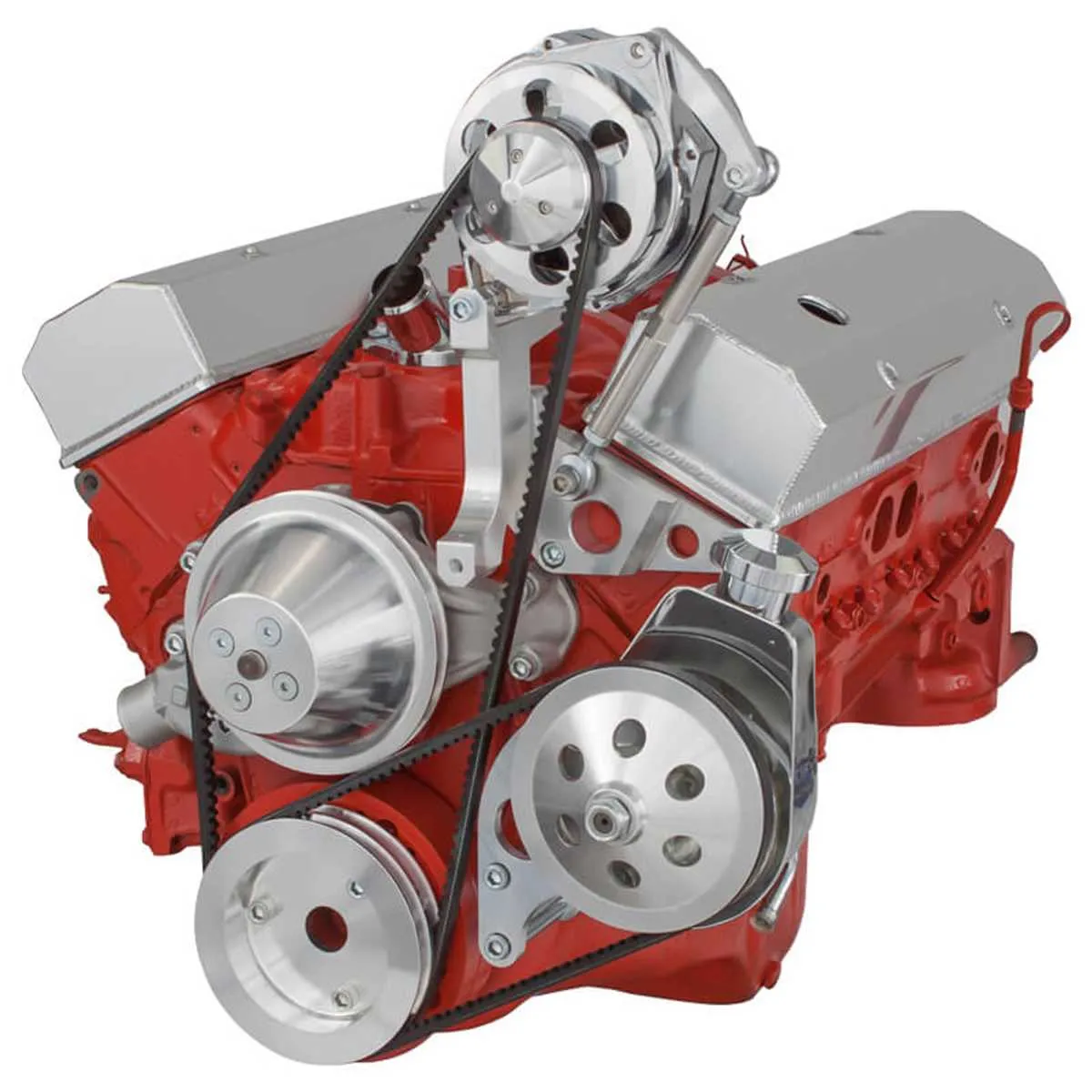
Identifying Key Components in the Chevy 350 Power Steering Pump Bracket
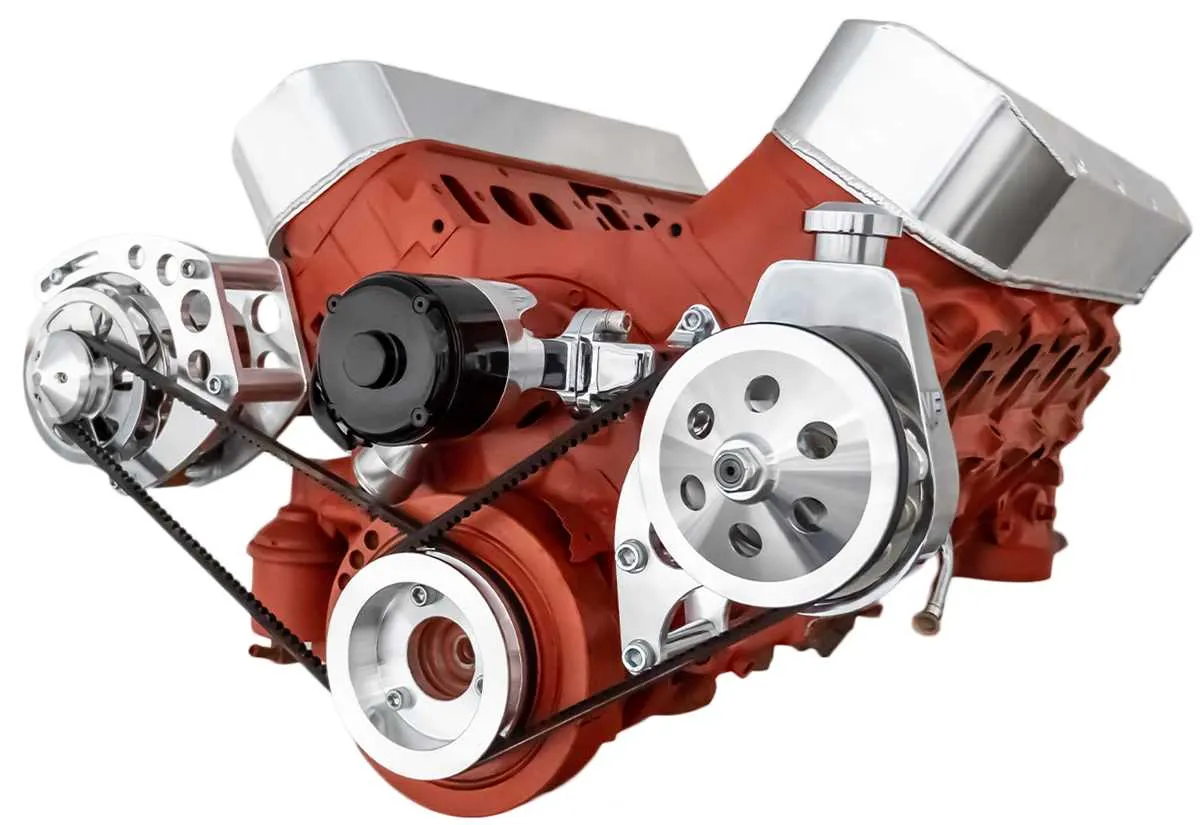

Start by locating the main support structure that holds the hydraulic fluid device in place. It typically has multiple fastening points to secure it firmly to the engine block. The mounting plate should be checked for corrosion or wear, which can compromise its strength and alignment.
Next, examine the pulley attachment area. The part that connects the rotational mechanism to the assembly will often show signs of wear from constant movement. Ensure it is properly aligned and securely fastened to prevent any malfunction in the drive system.
The bracket should feature a tension adjustment mechanism, usually in the form of a bolt or threaded rod. This mechanism allows you to adjust the distance between the component and the engine, ensuring the correct tension on the drive belt. Pay attention to any wear on the adjustment mechanism, as failure to maintain proper tension can lead to ineffective operation.
Check for any support arms or braces that reinforce the structure. These components prevent flexing and ensure stability under load. Over time, they may loosen or crack, requiring replacement or tightening. These supports are critical for maintaining the alignment of the assembly, especially under heavy use.
Inspect the fluid line connections that integrate with the assembly. Look for any signs of leakage or corrosion on the fittings. Proper sealing is vital to prevent hydraulic fluid loss, which can lead to decreased performance. Ensure that all hoses are securely connected to avoid any disconnections during operation.
How to Install the Pump Mounting System Correctly
Start by positioning the mounting component against the engine block, aligning the holes with the threaded inserts. Ensure the component is oriented in the correct direction for the pulley alignment. Use a torque wrench to fasten the bolts, tightening them to the manufacturer’s specified torque value to avoid over-tightening and damaging the threads.
Before securing everything completely, check that the mounting piece sits flush with the engine block. This step is crucial to ensure proper pulley alignment. If there’s any misalignment, adjust the component’s position slightly before tightening it fully.
Next, install the adjustment mechanism. Attach it to the mounting piece and secure it to the designated bracket. This allows you to adjust tension when the system is installed and helps maintain the proper angle for smooth operation.
For best results, use the appropriate washers between the bolts and the bracket to ensure a secure fit and prevent vibration over time. Avoid using worn or damaged bolts, as they may not secure the bracket tightly, leading to potential issues with system performance.
Once everything is tightened and secured, double-check that the alignment of the belts is correct. Misalignment can cause excessive wear and inefficient functioning of the system. Finally, test the unit by rotating the pulley by hand to make sure it turns smoothly without any resistance or unusual noise.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with Power Assistance Setup
If you’re encountering issues with the hydraulic support mechanism, focus on the following common problems and fixes:
1. Leaking Hydraulic Lines
Leaks in the system can cause significant drops in fluid levels, leading to reduced assistance or erratic performance. Inspect all hoses, fittings, and connections for visible damage or wear. A common area for leaks is where the lines attach to the pump or gearbox. If you find a crack or rupture, replace the affected component and ensure all fittings are tightened to manufacturer specifications.
2. Misalignment of Mounting Components
Improper alignment of the mounting points for the components can lead to excess vibration and premature wear. Verify that the pump assembly is securely mounted and that the pulley is aligned with the other drive components. Use a straight edge to check alignment and adjust accordingly. A misaligned pulley can result in noise or slipping.
3. Excessive Belt Tension
An overly tight belt can put undue stress on the bearings, leading to premature failure of the pump. Adjust the belt tension to the manufacturer’s recommended setting. Use a belt tension gauge to ensure the correct force is applied, preventing further issues.
4. Air in the System
Air pockets within the hydraulic system can cause intermittent failure or inconsistent operation. Bleed the system following the proper procedure, making sure to purge any trapped air from the lines. This will restore smooth fluid flow and reduce noise.
5. Pump Noise
A whining or growling noise often indicates insufficient fluid levels or a failing pump. Check fluid levels and top up if necessary. If the noise persists, inspect the pump for signs of internal wear, such as bearing damage or an irregular rotational pattern.
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Leak | Damaged hose or fitting | Replace the damaged component and check for proper fitment |
| Misalignment | Improper installation | Use a straight edge to align the components properly |
| Excessive noise | Low fluid or internal wear | Top up fluid and check for wear; replace if necessary |
| Air in system | Improper bleeding | Follow the correct bleeding procedure to remove air |
| Excessive belt tension | Incorrect tension setting | Adjust belt to correct tension using a gauge |