When servicing your grass-cutting machinery, ensure to follow the precise routing for the drive system. This guarantees both optimal performance and longevity of the components. If you are replacing the drive components, it’s essential to refer to the exact path of each piece. Fitting them in the wrong order or direction can result in poor operation or even damage to the motor.
Start by checking the pulleys that engage with the rotating elements. These parts are critical for transferring motion from the engine to the cutting blades. Misalignment of these parts can cause uneven cutting, excessive wear, or even failure to start. Always inspect the pulleys for wear and tear, and replace them if necessary.
Next, verify the position of the connection components that guide the energy from the engine to the active mechanisms. Each part must be routed according to the manufacturer’s instructions to maintain smooth operation. Double-check that the parts are securely fastened, as loose connections can create further issues.
Repairing the Tractor Drive System
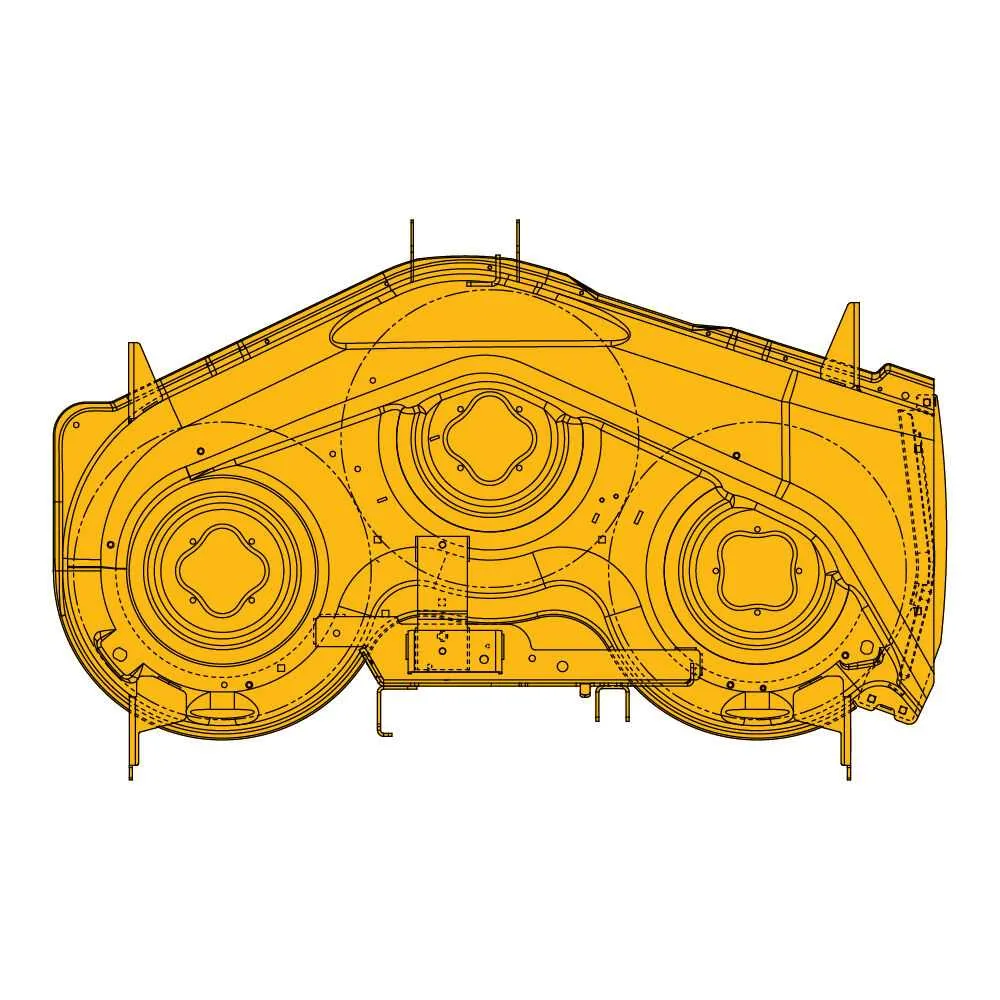
To ensure smooth operation, proper installation of the drive components is essential. Follow these steps to resolve any issues with the power transmission system:
- Start by verifying the path of the transmission parts. Ensure each part is correctly aligned with its corresponding pulley.
- Inspect the wear of the components. If any part is worn, it’s crucial to replace it to avoid malfunction.
- When reinstalling, make sure to route the parts exactly as specified by the machine’s specifications. Incorrect routing can cause premature damage or inefficient operation.
Below are the key elements to examine when working on the system:
- Check that all pulleys are firmly in place and properly aligned.
- Ensure the system is free from debris or obstructions that could impair function.
- Make sure each part is in good condition to avoid unnecessary strain on other components.
Regular maintenance is essential. Clean and check all parts periodically to prolong the life of the machine and ensure consistent performance. Replace any worn components immediately.
How to Identify and Interpret the Belt Layout
Start by locating the manual or service guide specific to your machine model. This will provide the most accurate configuration for the drive components. Carefully observe the routing of each part within the system, noting how they interact with pulleys and tensioners. Focus on the direction in which the parts are aligned, paying particular attention to the method of attachment and any notable turns or loops.
Examine the pulleys to understand their function in directing the movement. The smaller pulleys typically serve as guides, while larger ones often handle the power transfer. Look for wear patterns on both the pulleys and the components to identify any misalignment or potential issues. Ensure that each part moves smoothly and does not exhibit excessive resistance or slippage during operation.
It’s important to verify that all parts are securely in place. Misplaced components can cause unnecessary strain, leading to faster wear and potential failure. Double-check the path to ensure no twists or crossovers that could interfere with the system’s efficiency.
If you’re replacing any parts, ensure that the new components are compatible in size and function. Using parts not suited to your system may lead to malfunctions or reduced performance. Always follow the provided guide closely to avoid errors in assembly.
Common Issues with Belt Alignment and Fixes
Check pulley parallelism first–misaligned pulleys are a leading cause of premature drive wear. Use a straightedge across the faces of both pulleys to confirm they’re in the same plane. Adjust brackets or mounting bolts until alignment is precise.
If the tensioner arm doesn’t return smoothly, inspect the pivot point for debris or corrosion. Lubricate with lithium grease or replace the spring if resistance persists. Weak tensioning leads to slippage and excessive vibration.
Worn idler wheels often create tracking problems. Rotate each guide by hand and listen for grinding. Replace any unit showing play, noise, or surface damage. Use OEM parts to preserve proper tension ratios.
Verify the routing path follows the manufacturer’s specification exactly. A single misrouted loop causes uneven tension and increases heat. Reference the model-specific routing chart before reassembly.
If edge fraying or glazing appears, examine each spindle for wobble or uneven rotation. Replace bent shafts or cracked housings. Balance all rotating components to reduce lateral stress on the drive loop.
After correction, run the system under load for ten minutes and recheck alignment. Thermal expansion can shift positions, especially if housing bolts weren’t torqued uniformly. Retighten all fasteners to spec with a calibrated wrench.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the Lawn Mower Belt
Disconnect the spark plug wire to prevent accidental starting. Position the machine on a flat, stable surface and engage the parking brake.
Remove the deck by detaching the hanger arms and support pins. Slide the assembly out from under the frame.
Use a wrench to loosen the tensioning pulley. Carefully slip the worn-out loop off all pulleys, noting the routing path for reference.
Inspect spindles, pulleys, and the tensioner for damage or debris. Replace any seized or worn components before installing the new drive strap.
Fit the replacement around the engine pulley first, then route it around the idler and spindle pulleys according to the manufacturer’s configuration.
Reapply tension using the idler arm. Ensure the new part sits flush in all grooves and doesn’t twist or bind when rotated by hand.
Reattach the cutting deck, secure all pins and arms, and reconnect the spark plug. Test run the system briefly to verify proper tracking and tension.