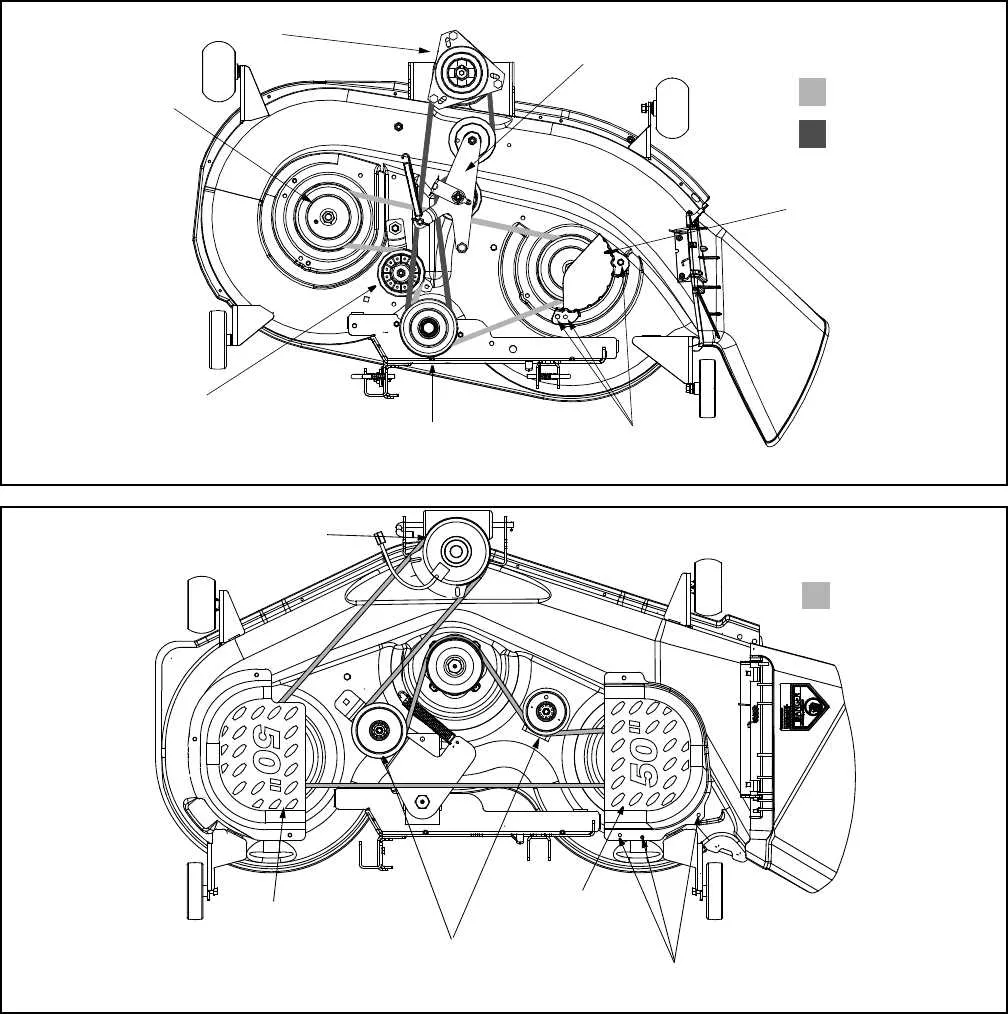
If you are troubleshooting or assembling a power drive system, it’s crucial to identify the correct parts and their arrangement. Focus on the actuator mechanism that engages the engine’s rotational force to external devices. A detailed understanding of how these parts interact can save you time and prevent errors during installation or repair.
The mechanism typically consists of a spring-loaded unit that connects to a pulley or other drive elements. Pay attention to the engagement spring, which plays a vital role in the smooth operation. If the spring is too tight or too loose, it may result in inefficient power transfer or mechanical failures.
For accurate assembly, refer to the correct component layout. Ensure that the engagement mechanism is correctly aligned with the driving components to avoid unnecessary wear. Proper tensioning is also critical, as an improperly adjusted spring may cause the system to malfunction.
Always verify the alignment of the sheave and the engaging parts. Any misalignment can lead to excessive strain on the engine or cause slippage, reducing the overall efficiency of the drive system. A well-maintained mechanism ensures that power is efficiently transferred to the required tools or implements, making your equipment more reliable in the long run.
Understanding the Drive Mechanism
When troubleshooting the engagement system of your lawn equipment, check the assembly carefully for wear and tear. If the connection between the engine and the deck is faulty, inspect the drive belt and the pulley system for any signs of damage. Ensure the springs are securely placed and the friction surfaces are smooth.
Key Component Checklist:
- Inspect the tensioner springs to ensure proper tension.
- Examine the flywheel and its grooves for any damage or excessive wear.
- Ensure the engagement lever or switch operates smoothly and is not obstructed.
In the case of malfunction, often the issue lies in the spring mechanism, which may require adjustment or replacement. Look out for any misalignment between the moving parts and correct them immediately. Also, pay attention to any excessive friction that might indicate a need for lubrication or part replacement.
Regular inspection of the drive components can save time and prevent more expensive repairs in the future.
How to Read and Interpret a PTO Mechanism Schematic
Focus on identifying the main components shown in the schematic. These usually include the pulley, springs, belts, and connectors. Understanding how they interact will help you troubleshoot or assemble the system effectively.
First, locate the drive components, which are typically positioned at the center. These are responsible for transferring power to the working parts. Make sure to follow the path from the power source to ensure a smooth flow of energy through the system.
Next, pay attention to the spring-loaded elements. These are essential for engagement and disengagement. Understanding their position and tension will assist you in adjusting or replacing them if necessary.
Look for the belt routing, which is usually depicted as a series of lines or arrows. The way the belts are arranged will determine the efficiency and functionality of the mechanism. Ensure that the belts follow the correct path, as any deviation could cause malfunctions or excessive wear.
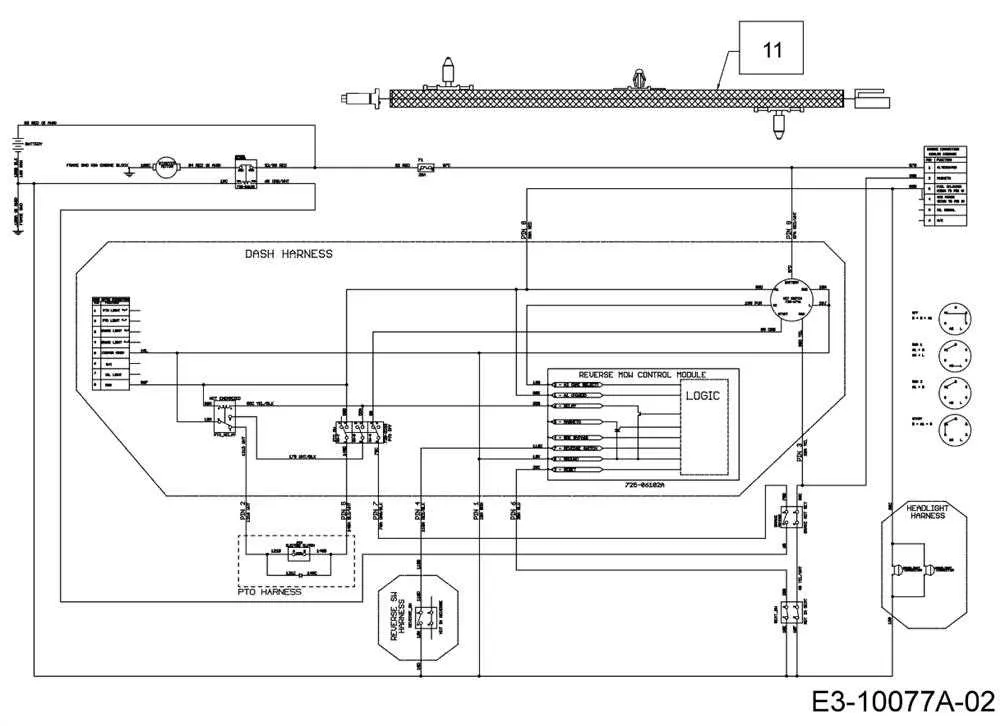
Examine the electrical connections if present. These will typically be shown with dashed lines or symbols. Ensure that all connections are intact, as electrical failure can prevent proper operation.
Finally, check for any alignment markers that may indicate whether the system is functioning correctly. Misalignment can often lead to mechanical failures or inefficient performance. Aligning the components according to the schematic ensures smooth operation and longevity of the system.
Common Issues with Power Take-Off Systems in Lawn Mowers
Regularly check the engagement mechanism for issues with smooth operation. If the system fails to engage properly, it may be due to a malfunctioning actuator or worn-out springs. These components should be inspected and replaced as necessary to maintain proper functionality.
- Worn-out Actuator: The actuator can become sluggish or fail over time. If the system doesn’t engage, inspect the actuator for wear and replace it if needed.
- Spring Damage: A stretched or broken spring is one of the most common causes of failure. Check the tension and integrity of the spring regularly.
- Faulty Electrical Connections: Power issues may stem from faulty wiring or corroded connectors. Ensure all connections are clean and secure to avoid unreliable operation.
- Engagement Lever Issues: A stiff or broken lever can prevent the system from engaging. Check the mechanism and lubricate or replace parts if necessary.
If you notice excessive vibration or noise during operation, the bearings or mounting points may need attention. These components wear out over time, leading to increased friction and noise. Replace them as part of routine maintenance.
- Worn Bearings: Inspect the bearings regularly for signs of wear or damage. Replace them if they are noisy or loose to prevent further damage.
- Loose Mounting Points: Ensure all mounting points are secure. Loose connections can lead to improper alignment, causing increased vibration.
Finally, ensure that the drive belt remains tight and in good condition. A worn or loose belt can prevent the system from transferring power efficiently, leading to underperformance or failure.
- Belt Tension: Regularly check the tension on the drive belt. A loose or overly tight belt can affect the efficiency of the system.
- Belt Condition: Inspect the belt for fraying or cracks. Replace it if necessary to maintain smooth power transmission.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the Power Take-Off Mechanism in Lawn Mowers
Start by ensuring the mower’s engine is off and the spark plug is disconnected to prevent accidental starts. Raise the mower deck to provide sufficient space for work. Use a jack or lifting equipment to elevate the mower if needed.
Next, locate the drive mechanism, which connects to the engine. Carefully remove any fasteners securing the old assembly in place. You may need to detach the belt from the pulley system, which is usually done by loosening the tension or removing a guide bolt.
Once the old unit is free, examine the mounting area for any wear or damage. Clean the surface thoroughly before installing the new component. Align the new part with the mounting brackets, ensuring it fits properly into the pulley system.
Secure the assembly using the appropriate fasteners. Tighten them according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Ensure the new part is correctly aligned and spins freely without obstruction.
Reattach the belt to the newly installed mechanism, ensuring it is seated correctly on all pulleys. Check for proper tension by pressing gently on the belt–there should be no slack, but it shouldn’t be overly tight either.
Reconnect the spark plug, lower the deck, and perform a test run to verify the new assembly is functioning as expected. Monitor for unusual noises or vibrations that might indicate improper installation or alignment.