If you’re experiencing issues with electrical components in your 2001 Ford Ranger, pinpointing the precise location of each electrical component is crucial. Start by consulting the electrical circuit layout map, which will help you quickly identify which fuse controls which system. This map is a valuable tool for troubleshooting, ensuring that you can replace faulty components without causing damage to the vehicle’s wiring.
For example, if the lights or radio stop working, the relevant fuse might have blown. The layout will show you exactly which section to inspect. Refer to the panel for specifics, ensuring you match the fuse rating to avoid overloading the system. It’s a straightforward process, but understanding the layout will save you time and effort during maintenance or repairs.
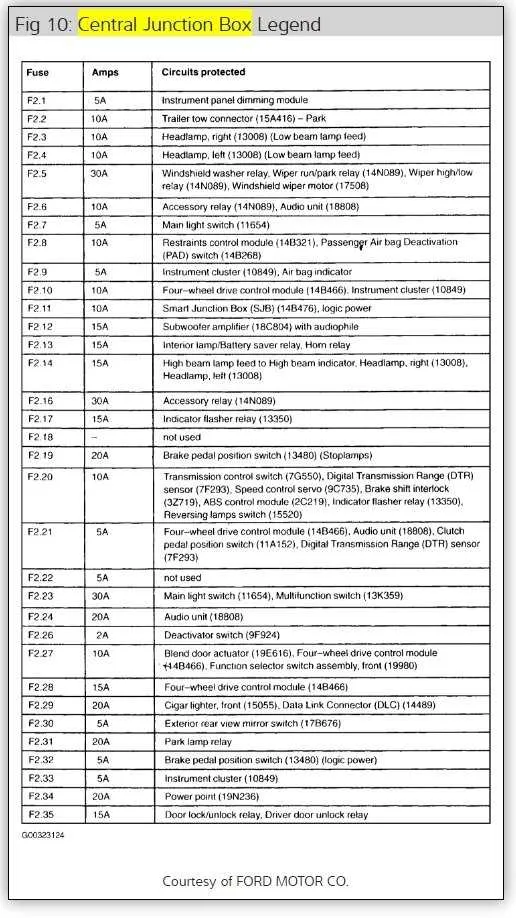
Understanding the different fuse groups is key to effective vehicle management. The electrical system of your vehicle is divided into sections, each handling specific functions like air conditioning, lights, or power windows. Take a moment to familiarize yourself with each circuit group to easily locate the faulty component when necessary.
Wiring Layout of Electrical Components
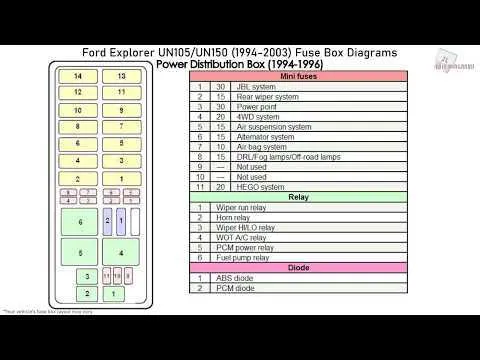
Locate the power distribution box under the hood, near the battery, and inspect the connections for proper functionality. Inside the cabin, there is a secondary panel under the dashboard. Make sure to check both areas when diagnosing electrical issues.
- Engine Control Module (ECM): Check the 10A fuse in position 3.
- Headlights: The 15A fuse in slot 7 should be monitored for any irregularities.
- Interior Lights: Position 8 contains a 20A fuse that affects all cabin illumination.
- Power Windows: Fuse 12 (30A) is responsible for window motor operation.
- Radio: Slot 5 includes a 5A fuse to protect the stereo system.
In case of malfunction, swap out the corresponding fuse. Always use the same amperage to avoid potential damage to the electrical circuits.
Key Areas to Inspect
- Engine Bay Fuse Block: Regularly check for corrosion around the connections.
- Cabin Fuse Box: Ensure proper seating of fuses to avoid loose contacts.
- Relays: Test the relays connected to critical systems like lighting and ignition.
Replacing blown components is straightforward, but make sure to address any underlying issues to prevent recurring failures.
How to Locate the Electrical Panel in a 2001 Ford Ranger

To find the electrical panel, begin by checking beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side, just to the left of the steering wheel. You may need to remove a small panel or cover to access the components. Alternatively, the engine compartment houses another box, which can be found near the battery. Both areas provide easy access to the fuses. Ensure that you identify the right panel depending on the component you need to check or replace.
Understanding the Electrical System and Its Components in the 2001 Ford Ranger
To ensure your vehicle’s electrical system is functioning properly, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the placement and role of each component within the circuit layout. Start by identifying the key areas in the cabin and engine bay where protection mechanisms are located. Pay attention to the capacity ratings printed near each fuse or relay to avoid overloading and damaging sensitive systems.
Engine Bay and Interior Distribution play a significant role in distributing power across various parts of the vehicle. Be sure to consult the service manual for exact locations of each protective element. These areas often include key components such as the air conditioning, headlights, and ignition system.
Relay Blocks are another critical part of the system, as they manage the flow of current between circuits. These units act as a switch, directing power to components only when required, thus preventing damage from constant electrical flow. Ensure you verify the type of relay used in each block and make any necessary replacements with the exact match.
Proper Maintenance involves regularly checking these parts for signs of wear or failure. When replacing any component, use the correct amperage rating. Under- or over-fusing can lead to system failures or potential electrical hazards.
Each electrical element in your vehicle works together to ensure that the complex network of components operates smoothly. Keeping this system in check will prevent costly repairs and ensure the longevity of your car’s electrical systems.
How to Replace Fuses Based on the Electrical Schematic
Start by locating the main electrical box under the dashboard or near the engine compartment, depending on the fuse placement. Open the cover carefully to access the internal components. Identify the specific element that needs replacing by referencing the markings that match the malfunctioning system.
Using a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers, gently extract the damaged component from its socket. Check the color coding or amperage on the side of the new part to ensure it matches the previous one. Avoid using a higher-rated component as it could lead to electrical damage or fire hazards.
Insert the new unit firmly into the empty slot. Ensure it is fully seated to maintain proper contact. After replacement, test the affected system, such as lights or power accessories, to verify the issue is resolved.
If the replacement part doesn’t fix the issue, double-check for any hidden electrical faults or a more severe malfunction in the system wiring that might require professional inspection.