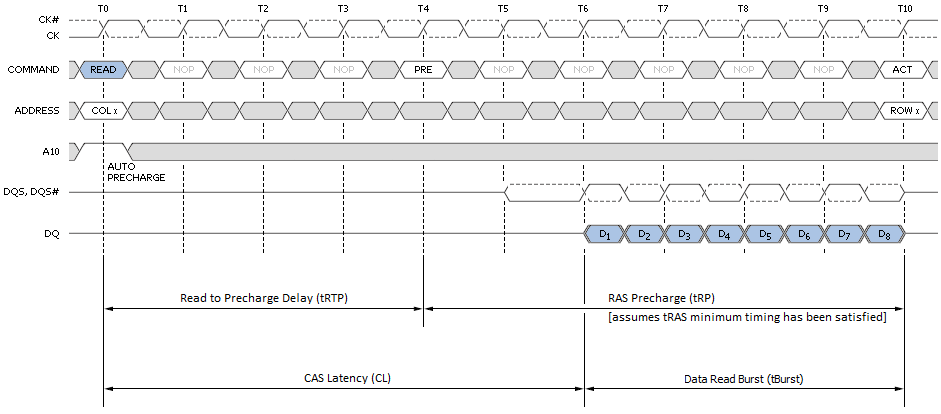
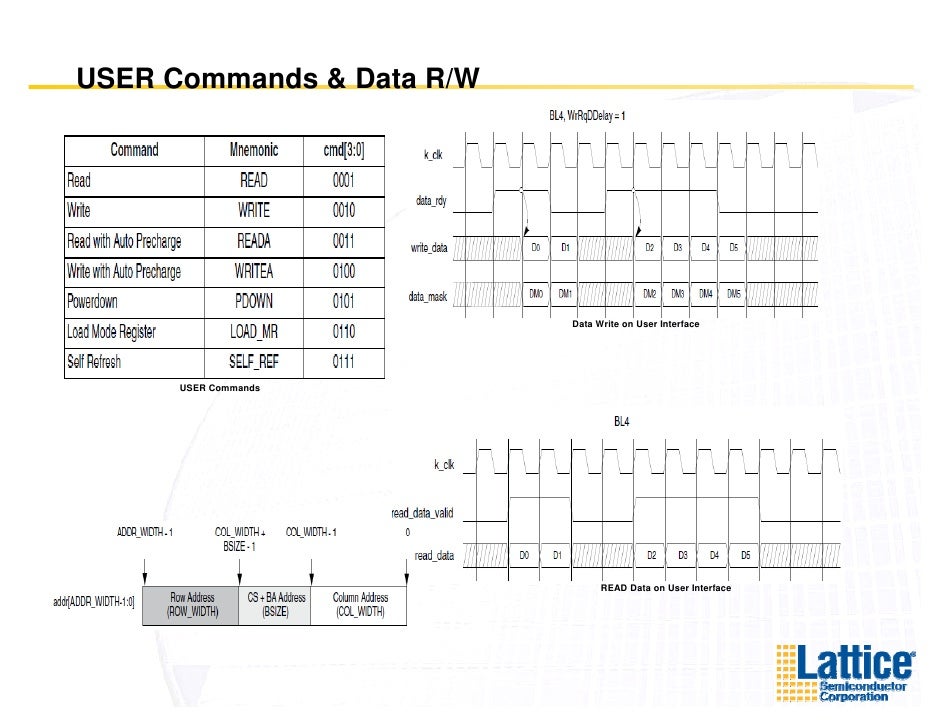
Basic Functionality. Read and write accesses to the DDR2 SDRAM are burst oriented; accesses start at a selected location and continue for a burst length of four. Implementing High-Speed DDR3 Memory Controllers in a Mid-Range FPGA.
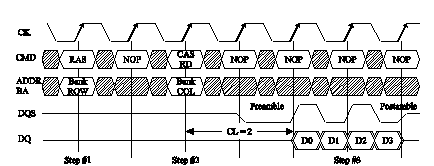
A Lattice Figure 2 – Timing Diagram for Write Leveling. 4.
Implementing. Electrical Characteristics & AC Timing for DDR to DDR This simplified State Diagram is intended to provide an overview of the possible state .
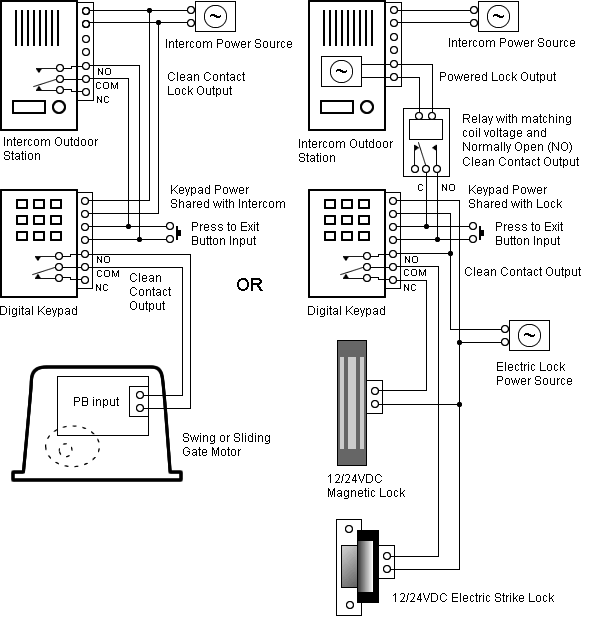
that DDR3 signaling is more critical, DDR3 point-to-point systems require an . do not require termination) or the DDR3 fly-by architecture (significant timing.
devices on the DIMM, and the DRAM controller must account for the timing skews . .
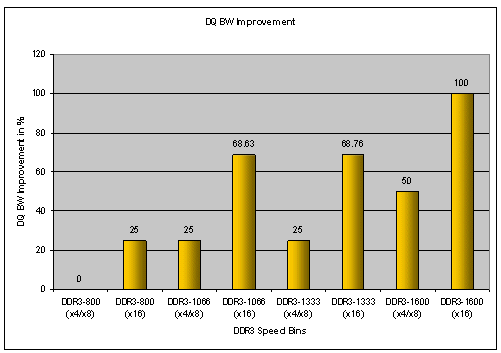
command 1T signal-group routing topology is shown in the block diagram.DDR3 Read/Write Eye diagram test 19 Eye Diagram Test (not required per JEDEC spec) • Allows measurement of Data eye height and eye width • User can also define own mask as per device specification Compliance app reports Fail status if eye diagram violates mask. Many engineers who have ever dealt with DDR SDRAM must have been intrigued by the various timing parameters of the DRAM.
This article explains the various timing parameters and its impact on the performance of the DRAM. To begin with, let’s first understand how different DDRs are rated or classified. For example, even though you may achieve 1, MHz ( MHz x2) with DDR/PC modules, on these modules it may be necessary to increase the memory timings, while on DDR/PC Double Data Rate means that this memory transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal.
This is why mhz DDR3 memory appears as MHz in cpuid. This is the current type of memory used in modern systems.
It is not backward compatible with any other type or memory. .
DDR3 timing interfaces are all differential. Built-in Timing Calibration Some of the most significant differences between DDR2 and DDR3, however, revolve around the memory interface’s ability to.Memory Design Considerations When Migrating to DDR3 Interfaces from DDR2DDR3 Memory Timings Explained | MSI HQ User-to-User FAQ