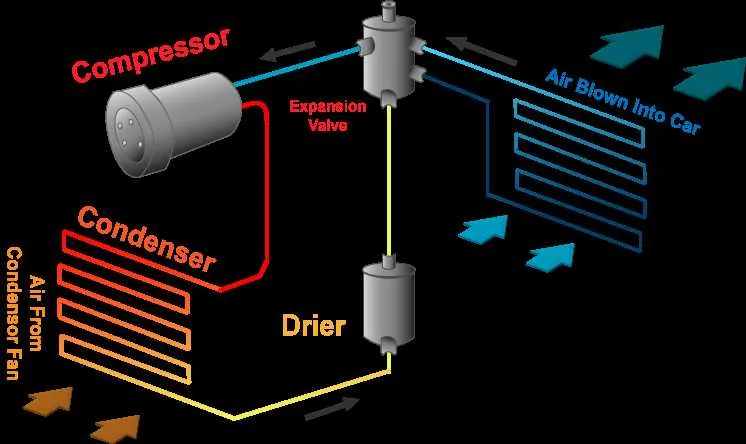
When it comes to maintaining a comfortable temperature within your vehicle, understanding the flow of refrigerant through the various components is crucial. The process involves a compressor, evaporator, condenser, and expansion valve working together to regulate cabin temperature. These parts are interconnected, ensuring the efficient transfer of heat from the interior to the outside environment.
Start with the compressor: This component is responsible for pressurizing the refrigerant and pushing it through the system. Once the refrigerant is compressed, it enters the condenser, where heat is released to the surrounding air. The refrigerant then travels to the expansion valve, which controls the flow of the substance, lowering its pressure and temperature as it moves towards the evaporator.
The evaporator’s role: As the refrigerant passes through the evaporator coil, it absorbs heat from the cabin air, lowering the overall temperature inside. The now heated refrigerant is then cycled back into the compressor to continue the process. Regular maintenance of these components ensures that your vehicle remains cool and comfortable, especially during the hotter months.
Proper care of the refrigerant level, cleaning the condenser and evaporator, and replacing any faulty components can significantly extend the lifespan and efficiency of this critical system.
Understanding the Climate Control Mechanism
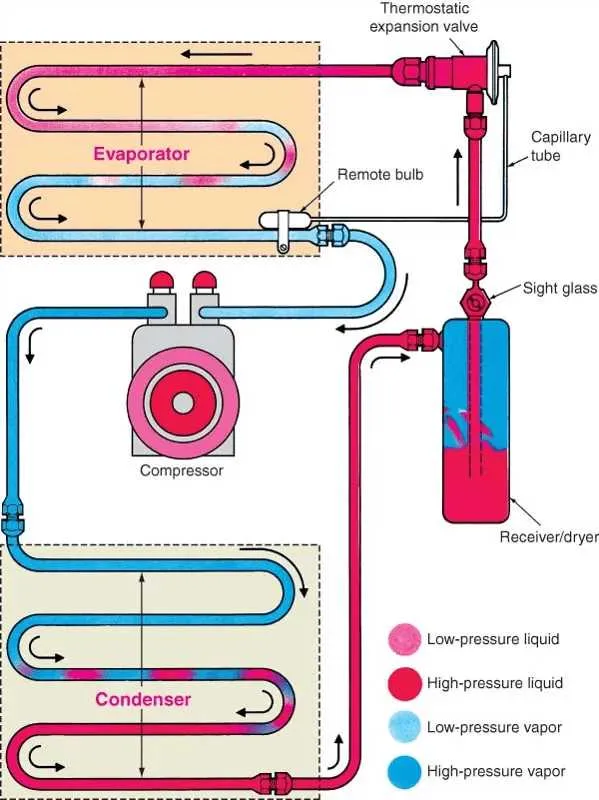
To effectively manage the cabin temperature, ensure regular checks of the refrigerant level. Low refrigerant can lead to poor performance and potential damage. Verify the compressor functionality–if it’s malfunctioning, cooling efficiency will drop significantly. Inspect the condenser for any blockages or dirt buildup, as this can impede heat dissipation and strain the entire setup.
The evaporator plays a critical role in maintaining comfort by absorbing heat and releasing cool air. Keep the airflow unobstructed and ensure the evaporator coils are free from mold or ice. Check the blower motor for any signs of wear and tear to maintain proper airflow throughout the cabin.
Don’t overlook the expansion valve; it controls refrigerant flow, and a clogged valve can disrupt temperature regulation. Keep an eye on hoses for leaks or cracks, as refrigerant loss can result in insufficient cooling. Also, inspect the compressor clutch and ensure it engages and disengages properly to maintain cycle efficiency.
Lastly, verify the cabin filter regularly. A clogged filter reduces airflow and can cause overheating, affecting the overall performance of the system. Routine maintenance is crucial for ensuring long-lasting functionality and energy efficiency.
Understanding the Role of the Compressor in Vehicle Climate Control
The compressor is a critical component in managing temperature regulation inside the cabin. It performs the task of compressing refrigerant gas, transforming it into a high-pressure state that is then moved through the condenser for cooling. This process is essential for the entire temperature control mechanism to function properly.
The compressor operates by drawing in low-pressure refrigerant gas from the evaporator and compressing it to a higher pressure. This increase in pressure causes the refrigerant to heat up, and it is subsequently cooled down as it passes through the condenser coils. Without a properly functioning compressor, the system would fail to circulate the refrigerant, leading to ineffective cooling or heating.
Regular maintenance of the compressor ensures that it operates efficiently. Any leakage or malfunction in this component can cause a loss in refrigerant, leading to diminished performance. In the case of irregularities, it’s advisable to check for refrigerant levels and inspect the compressor for any signs of wear and tear, such as unusual noises or vibrations.
How the Evaporator and Condenser Work Together to Cool the Air
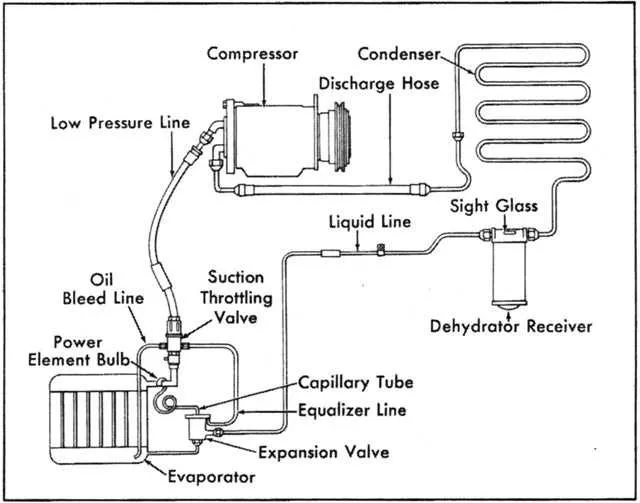
To effectively lower the temperature inside a vehicle cabin, the evaporator and condenser must operate in harmony. Each component plays a vital role in managing the refrigerant flow and phase changes that result in cool air. Here’s a breakdown of their interaction:
- Evaporator’s Role: The evaporator absorbs heat from the cabin. It contains refrigerant that has been expanded to a low pressure. As warm air passes over the evaporator coil, the refrigerant inside absorbs the heat, evaporating into a gas and cooling the air that flows into the cabin.
- Condenser’s Role: The condenser works to expel the absorbed heat. The refrigerant gas from the evaporator enters the condenser, where it is cooled by air flowing through the condenser fins. The refrigerant gas condenses back into a liquid state, releasing the heat it absorbed earlier.
- Heat Transfer: The process begins when the evaporator draws in warm air and removes its heat. The now-warmed refrigerant gas travels to the condenser. By passing through the condenser, the refrigerant releases heat to the surrounding environment and transforms back into a liquid. This liquid is then cycled back to the evaporator to repeat the process.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of this cycle is highly dependent on the flow of refrigerant, the temperature differential, and the capacity of the heat exchange surfaces in both the evaporator and condenser. Both components need to maintain proper flow rates to ensure effective heat absorption and expulsion.
Maintaining the balance between these components is crucial for ensuring that the cooling process remains consistent and efficient throughout use. Any disruption in refrigerant flow, leaks, or debris in the system can impact performance, making routine maintenance essential.
Diagnosing Common Issues in Vehicle Climate Control Units
If the unit is not cooling effectively, first check the refrigerant level. Low refrigerant could indicate a leak in the lines or a malfunctioning compressor. You can inspect the condenser coils for debris or damage that might impair airflow.
Another potential cause for poor performance is a faulty blower fan. When the fan is not functioning correctly, airflow will be compromised, resulting in inefficient cooling. Testing the fan motor and inspecting the associated wiring is essential in diagnosing this issue.
Compressor failure is another common issue. If you hear unusual noises or no sound at all from the compressor, it may have failed. Inspect the clutch and ensure it engages properly. If the compressor is not operating, cooling will be minimal or nonexistent.
If there’s no response when adjusting the temperature or fan speed, the control module or thermostat might be malfunctioning. A defective control board or sensor can prevent proper operation of temperature regulation and airflow settings.
Blocked or clogged evaporator can lead to improper cooling as well. Over time, dirt, dust, and moisture buildup can obstruct the coils, leading to frost or poor heat exchange. Regular cleaning of the evaporator ensures efficient cooling.
Regular inspection and maintenance are vital for ensuring the longevity of the unit. It’s important to replace worn-out parts like seals, hoses, and filters to maintain optimal performance over time.