
Ensure you follow these key steps when setting up a towing system to maintain proper functionality and safety. First, identify the appropriate power source from your vehicle, typically through the 12V auxiliary or a dedicated circuit. This is crucial for powering the electronic components involved in regulating force on the towed unit.
Next, establish a solid ground connection. The ground wire must be securely attached to the chassis of your towing vehicle, providing a stable return path for electrical current. Without this, performance issues are inevitable.
For the signal wire, it’s essential to link the vehicle’s braking system with the towing unit’s brake mechanism. This ensures that pressure applied to the vehicle’s pedal is accurately transmitted to the towed unit, enhancing braking efficiency and control.
Additionally, configure the adjustable output system. Depending on the weight and type of the towed unit, this will allow you to modify the force applied, optimizing braking power and improving overall safety during transport.
Be sure to follow all manufacturer specifications when choosing connectors, fuses, and wires to ensure maximum reliability and compliance with local regulations.
Setup Electrical Connections for Towing Equipment
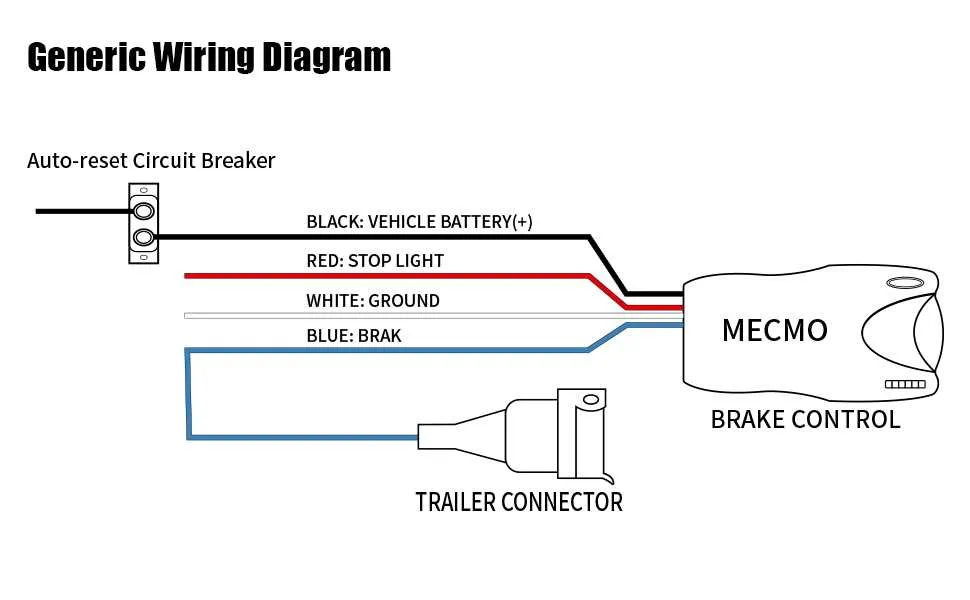
Start by connecting the power wire directly to the vehicle’s battery, ensuring it’s fused properly to avoid overload. A 12V power supply is necessary for optimal operation, with the fuse rated to match the vehicle’s capacity.
Next, link the output wire to the vehicle’s brake light system. This allows the towing device to react to braking signals from the car, enabling synchronized operation. A reliable connection ensures smooth interaction between the two systems, preventing overloading or failure during use.
The ground wire should be secured to a clean, bare metal surface on the vehicle to establish a stable circuit. This prevents electrical noise or interference, improving performance and safety.
Consider using an additional signal wire for quick communication between the two systems. This step is critical to ensure smooth responsiveness and prevent delayed actions when activating the towing equipment.
Ensure that all connections are properly insulated and free from corrosion. Proper sealing and insulation reduce the risk of damage due to environmental exposure, extending the longevity of the setup.
Finally, test the connections before use. Ensure the system is responsive and that the necessary components activate without delay or malfunction.
How to Connect a Towing System to Your Vehicle
Start by locating the correct connection points on your vehicle’s electrical system. These are usually found beneath the dashboard or near the towing hitch area, depending on the model. You’ll need a power source, ground connection, and a signal wire that activates the braking function when engaged.
Ensure that the power feed is connected to a 12V supply from your vehicle’s battery or fuse box. This will ensure that the towing system receives sufficient power to operate. Use a fuse rated for the appropriate amperage to protect the electrical components from overloads.
Next, connect the ground wire to a solid metal part of the vehicle’s chassis to ensure a stable return for the electrical current. It’s important to ensure the ground connection is clean and free from rust or paint for proper conductivity.
The signal wire from the vehicle’s brake system should be routed to the input terminal. This wire will send a signal whenever the vehicle’s brakes are applied, activating the towing system accordingly. Ensure that this connection is secure and properly insulated to prevent shorts or malfunctions.
For smooth operation, connect the output wire to the corresponding terminals on your towing unit. This wire will transmit the necessary current to engage the braking mechanism. Double-check all connections for tightness and stability before testing.
Test the system thoroughly by activating the brakes and observing the response. If any issues arise, inspect each connection point for potential issues such as corrosion, loose wires, or faulty connectors.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting for Trailer Brake Systems
If the system isn’t engaging, check the connection between the power supply and the unit. Loose or corroded terminals can prevent a steady flow of current. Tighten any loose connections and clean off any rust or oxidation.
Inconsistent braking response is often linked to a faulty ground. Ensure the negative lead is securely connected to the chassis, with no corrosion or rust. A poor ground can cause erratic behavior and delayed braking responses.
Excessive or weak activation could be due to incorrect voltage output. Use a multimeter to confirm that the unit is receiving the correct voltage from the power source. Voltage fluctuations can be indicative of issues with the source or the unit itself.
When there’s no response, even after checking connections and voltage, inspect the internal fuse. A blown fuse is a common reason for complete failure and can be replaced easily. Ensure the fuse rating is correct for the system to prevent future failures.
If you experience intermittent operation, inspect the control unit’s internal components. Overheating or faulty relays may cause temporary failures. Make sure the system is operating within its temperature range to avoid internal damage.
For inconsistent or weak performance, verify that all electrical components are receiving the proper amperage. Insufficient current can impair the operation of the unit, leading to slower or unresponsive actions when braking.
Finally, ensure that all wires are appropriately sized and rated for the load. Under or oversized wires can lead to overheating, poor functionality, or even damage to the system over time. Reassess the wire gauge if there are any signs of wear or malfunction.
Choosing the Right Wire Gauge and Fuses for Brake Controller Installation
Use 10 AWG wire for optimal current flow between the vehicle’s power source and the electric braking system. This gauge minimizes voltage drop and ensures efficient operation of the system under high load conditions.
For connections to the towing vehicle’s battery, a 10 AWG wire is recommended. For secondary wiring, such as to the trailer brakes, 12 AWG will suffice in most cases. If unsure, always opt for the thicker wire to avoid overheating issues and potential system failure.
Fuses are a critical component in protecting both the electrical components and wiring from overloads. Always choose a fuse rated for 20 to 30 amps, depending on the total amperage required by the brake system. The fuse should match or slightly exceed the amperage rating of the system to ensure safety.
- 20-amp fuse: Ideal for lower current systems.
- 30-amp fuse: Used for higher current demands, typically for heavy-duty braking applications.
Position fuses as close to the power source as possible to minimize risks in case of short circuits. Ensure proper fuse sizing to avoid unnecessary interruptions while providing adequate protection.
For wire insulation, use high-temperature resistant materials like PVC or Teflon, which can withstand heat generated by prolonged braking operations without deteriorating.
Consider installing an inline fuse holder for easier replacement and maintenance. This also allows for quick identification of any issues during troubleshooting.
Do not rely on a single fuse or gauge; always test your system for load and functionality before finalizing installation. Regularly check connections for corrosion or wear that could affect the performance of the entire setup.