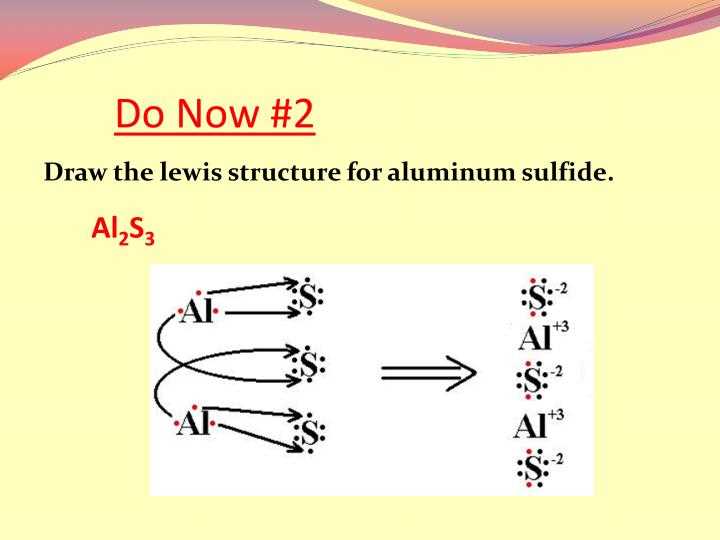
Aluminum is a widely used metal known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, malleability, and corrosion resistance. It is the third most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, making up approximately 8% of the planet’s total mass. Its atomic number is 13, and its symbol is Al.
One of the ways to represent the atom of aluminum is through a dot diagram. A dot diagram is a simplified representation of an atom, where the symbol of the element is surrounded by dots representing its valence electrons.
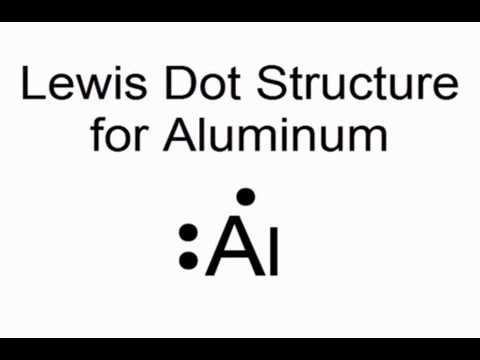
In the case of aluminum, it has three valence electrons, occupying the third energy level of the atom. The dot diagram for aluminum typically shows the symbol “Al” in the center, with three dots surrounding it.
The dot diagram is a useful tool for understanding the arrangement of electrons in an atom and predicting its chemical behavior. In the case of aluminum, its three valence electrons make it highly reactive and prone to forming bonds with other elements to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Dot Diagram of Aluminum
Aluminum is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. It is a silvery-white, soft, nonmagnetic, ductile metal in the boron group. Aluminum is the third most abundant element in the earth’s crust, making up about 8% of the crust by weight. It is known for its low density and ability to resist corrosion. These properties make aluminum a popular choice for a wide range of applications, from packaging materials to construction materials.
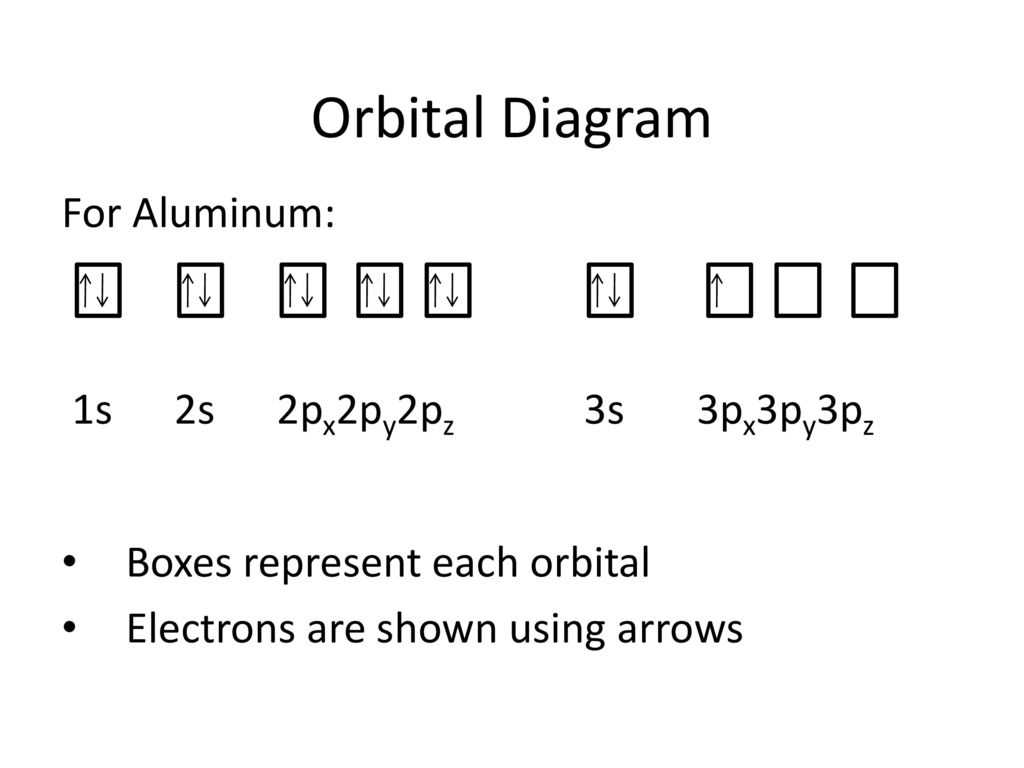
The dot diagram of aluminum represents the arrangement of its electrons in the atom. Aluminum has 13 electrons, arranged in three energy levels or shells around the nucleus. The first energy level can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, the second energy level can hold up to 8 electrons, and the third energy level can hold up to 3 electrons.
The dot diagram of aluminum can be represented as follows:
- Atomic symbol: Al
- Atomic number: 13
- Electron configuration: 2-8-3
- Dot diagram: Al . . . . . | . . . . .
Each dot in the diagram represents one electron in an energy level. The dots are placed around the symbol of the element in a way that represents the electron distribution in the atom.
In the case of aluminum, the dot diagram shows that there are 2 electrons in the first energy level, 8 electrons in the second energy level, and 3 electrons in the third energy level. This distribution of electrons gives aluminum its chemical and physical properties.
The dot diagram of aluminum provides a visual representation of the electron configuration, allowing scientists and students to better understand the structure and behavior of the element.
What is a Dot Diagram?
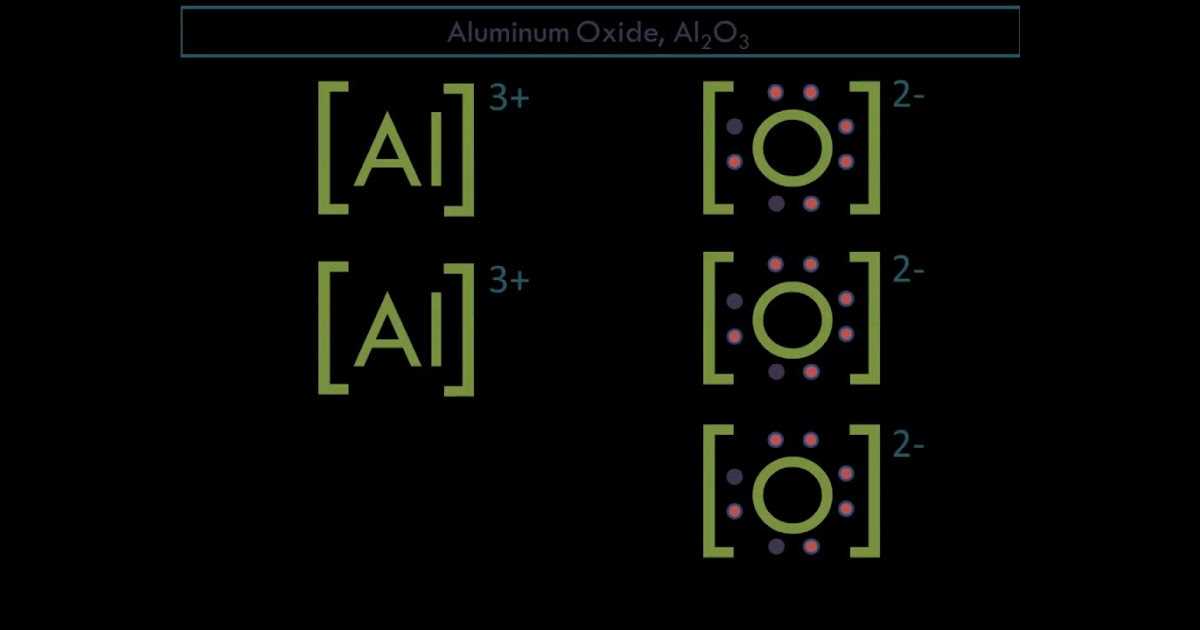
A dot diagram, also known as an electron dot diagram or Lewis dot diagram, is a visual representation of the electron arrangement in an atom or molecule. It uses dots to represent the valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. These valence electrons are responsible for the chemical behavior and bonding of an atom.
In a dot diagram, each dot represents one valence electron. The dots are placed around the atomic symbol to show the arrangement of electrons in a specific atom. The arrangement of the dots is determined by the electron configuration of the element. The positions of the dots can be thought of as the positions of the electrons in space around the nucleus of the atom.
Dot diagrams are a useful tool in chemistry as they provide a simple and visual way to understand the electron arrangement and bonding properties of an atom. They can be used to predict the type and number of bonds an atom can form, as well as to understand the overall structure of molecules and ions.
The Structure of Aluminum
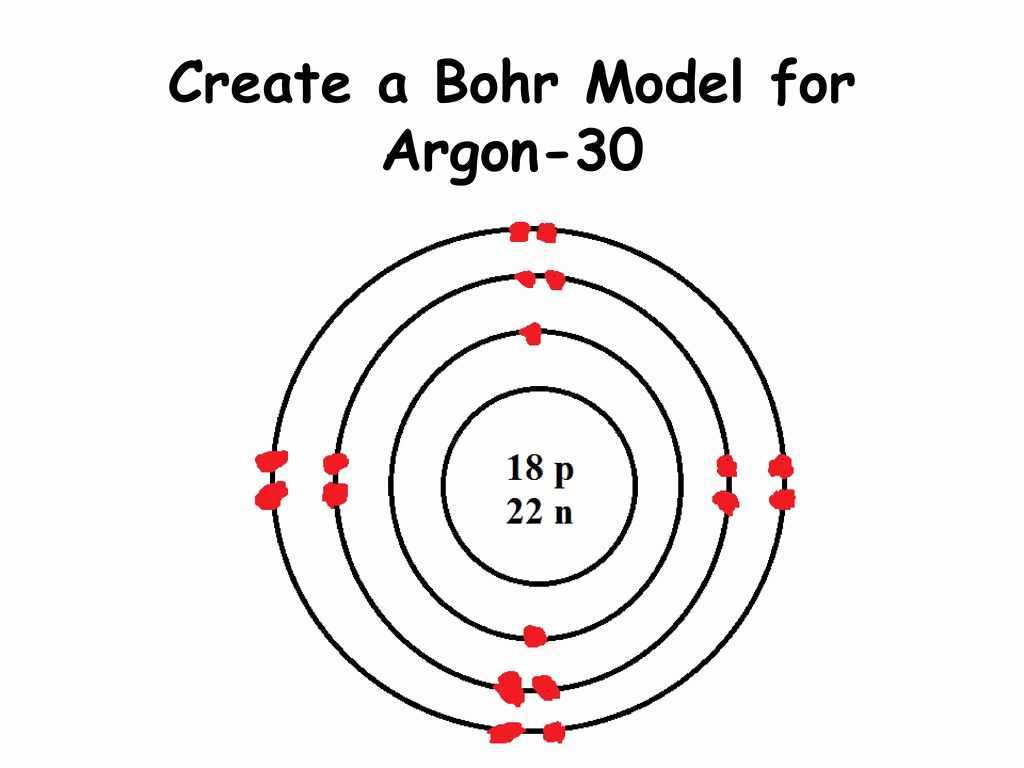
Aluminum is a metallic element that is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties. At an atomic level, aluminum is composed of a nucleus made up of protons and neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of electrons. The atomic number of aluminum is 13, which means it has 13 protons in its nucleus. This also determines its position in the periodic table.
The electron configuration of aluminum is 2-8-3, indicating that it has two electrons in the innermost shell, eight electrons in the second shell, and three electrons in the outermost shell. This configuration gives aluminum its characteristic chemical behavior. It easily loses its three outermost electrons to form a positive ion, Al3+, which is why aluminum is commonly found in compounds with a 3+ charge.
In a dot diagram, also known as a Lewis structure, the symbol for aluminum is shown in the center, representing the nucleus and inner shells. The three valence electrons are represented as dots surrounding the symbol. This visual representation allows us to understand the arrangement of electrons in aluminum’s outermost shell and how it interacts with other elements in chemical reactions.
- Atomic number: 13
- Electron configuration: 2-8-3
- Dot diagram representation: Al • • •
The structure of aluminum plays a crucial role in its physical and chemical properties. It is a lightweight metal with a low density, making it useful in industries such as aerospace and automotive. Its ability to form strong bonds with other elements makes it an ideal material for construction and packaging. Understanding the structure of aluminum helps scientists and engineers harness its properties efficiently and develop innovative applications for this versatile metal.
How to Create a Dot Diagram
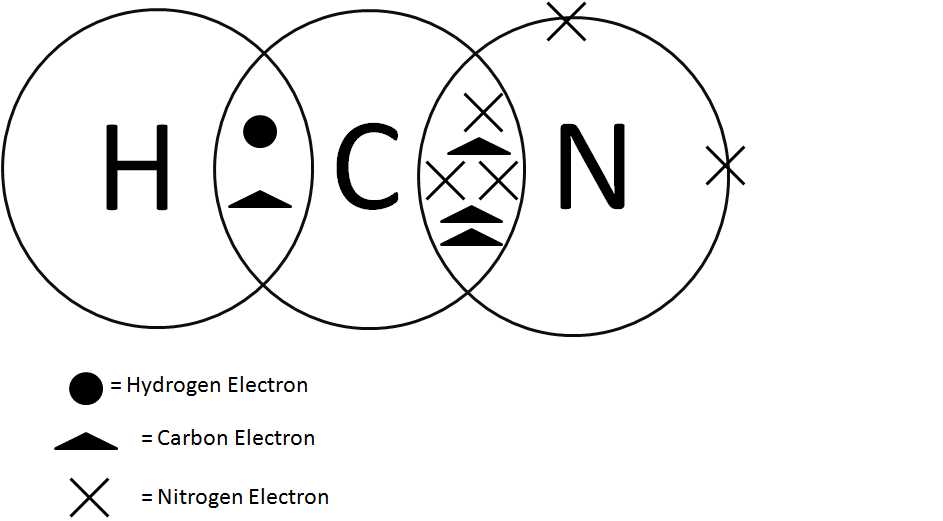
A dot diagram, also known as a Lewis dot diagram, is a visual representation of the valence electrons in an atom or ion. It is a simple way to depict the arrangement of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. Creating a dot diagram can be a useful tool in understanding the bonding and properties of elements.
To create a dot diagram, you will need to know the number of valence electrons an atom has. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom that are available for bonding. The number of valence electrons can be determined by looking at the group number of the element on the periodic table.
Once you have determined the number of valence electrons, you can begin creating the dot diagram. Start by drawing the symbol of the element in the center of your paper. Each valence electron is represented by a dot. Place the first two dots on opposite sides of the element symbol. Then, continue placing dots around the symbol, one at a time, until you have used all the valence electrons.
If there are more than four valence electrons, start pairing them up. Each side of the element symbol can hold a maximum of two dots. Once all the valence electrons are accounted for, you can add brackets and charges if necessary to represent ions.
Creating a dot diagram can help you visualize the electron configuration of an atom and better understand its reactivity and bonding capabilities. It is a useful tool in chemistry and can be used to predict how elements will interact with each other to form compounds.
The Importance of Dot Diagrams
Dot diagrams, also known as Lewis dot diagrams or electron dot diagrams, are a powerful tool in chemistry for representing the valence electrons of an atom. These diagrams are essential for understanding and predicting the chemical behavior of elements and compounds.
By using dot diagrams, scientists can easily determine the number of valence electrons an atom has. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom and are responsible for the element’s chemical properties. Dot diagrams represent the valence electrons as dots placed around the atomic symbol, with one dot representing each valence electron.
Dot diagrams are particularly important for understanding the bonding behavior of atoms. They provide a visual representation of how atoms form chemical bonds by sharing or transferring electrons. By analyzing the dot diagrams of two or more atoms, scientists can determine whether a bond will be formed and what type of bond it will be.
Furthermore, dot diagrams help in understanding the concept of octet rule, which states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight valence electrons. Dot diagrams clearly illustrate how atoms satisfy the octet rule by either gaining or losing electrons or by forming covalent bonds.
In conclusion, dot diagrams are crucial for understanding the electron configuration, bonding behavior, and chemical properties of elements and compounds. They provide a simple and visual representation of the valence electrons and aid in predicting the formation of chemical bonds. Dot diagrams are an essential tool in chemistry and play a vital role in the study of atomic and molecular structures.
Applications of Aluminum Dot Diagram
Aluminum is a versatile metal that finds its application in various industries. The dot diagram of aluminum, representing its electron configuration, helps us understand its chemical and physical properties, which in turn, determine its applications.
1. Construction: Aluminum is widely used in the construction industry due to its lightweight, durability, and corrosion resistance. It is used in the form of alloys to construct buildings, bridges, and various structural components. The dot diagram of aluminum helps us understand its ability to form strong metallic bonds, making it ideal for structural applications.
2. Transportation: The dot diagram of aluminum shows that it has three valence electrons, which makes it highly conductive. This property, along with its lightweight nature, makes aluminum an ideal choice for the transportation industry. It is used to manufacture vehicle bodies, aircraft parts, and even bicycles. Aluminum’s excellent thermal conductivity also makes it suitable for cooling systems in vehicles.
3. Packaging: Aluminum’s ability to resist corrosion and its low weight make it a popular choice for packaging materials. It is commonly used in the form of foils and cans for food and beverage packaging. The dot diagram of aluminum shows its stability, which ensures the preservation of the packaged products.
4. Electrical and Electronic Equipment: Aluminum’s high electrical conductivity makes it useful in the production of electrical wires and cables. It is also used in the manufacturing of electronic equipment such as smartphones, laptops, and audio devices. The dot diagram of aluminum explains its ability to donate and accept electrons, making it a good conductor.
5. Consumer Goods: Aluminum’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties make it widely used in the production of consumer goods. It is used to manufacture kitchen utensils, furniture, appliances, and even cosmetic packaging. The dot diagram of aluminum indicates its stability and resistance to chemical reactions, ensuring the longevity of these consumer goods.
In conclusion,
the dot diagram of aluminum helps us understand the electron configuration, which determines its chemical and physical properties. These properties, such as lightweight, conductivity, and corrosion resistance, make aluminum suitable for various applications, including construction, transportation, packaging, electrical and electronic equipment, and consumer goods. The versatility of aluminum makes it a valuable and highly sought-after material in multiple industries.