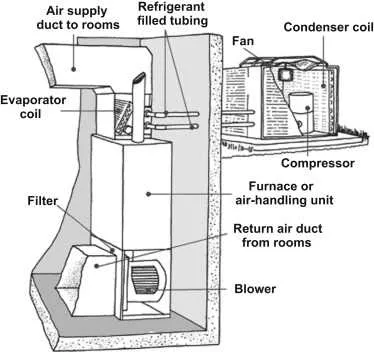
To optimize the performance of an air conditioning unit, it’s crucial to understand its essential components and their interconnection. A well-designed setup can enhance airflow, energy efficiency, and the overall comfort of your living space. Begin by examining the core elements like the compressor, evaporator, and condenser, each playing a vital role in regulating temperature.
The compressor is the powerhouse of any cooling device, compressing the refrigerant to initiate the cooling cycle. It’s typically located outside to expel heat. Meanwhile, the evaporator, found indoors, absorbs heat from the air to lower the temperature. To ensure optimal airflow, install ducts and vents strategically to distribute cool air efficiently across all rooms.
Maximizing energy savings involves more than choosing the right unit; the configuration of the components also matters. Positioning the condenser in a shaded, open space helps it operate more efficiently. Additionally, regular maintenance and checks for air leaks can prevent energy loss, ensuring the unit remains effective for longer periods without unnecessary power consumption.
AC Cooling Setup Overview
To ensure optimal cooling, place the air handler or furnace in a centrally located area of your home. This minimizes the ductwork length and improves airflow efficiency. Use insulated ducts to prevent energy loss. Direct return ducts to the central air handler for consistent air circulation.
Install an appropriately sized condenser unit outside. Ensure it’s placed on a solid, level surface, and keep it clear of debris to maximize airflow. The distance between the condenser and the evaporator coil should be minimized to reduce cooling loss during the refrigerant transfer process.
Ensure all refrigerant lines are insulated. This reduces heat gain during transfer and maintains efficiency. Properly seal all joints and connections to avoid leaks, which can lead to a decrease in cooling performance.
Integrate a programmable thermostat to adjust temperature settings automatically. Place the thermostat in a location free from drafts, direct sunlight, and other heat sources. This will help maintain accurate temperature control and prevent unnecessary energy use.
Ensure that air returns are placed at low points in rooms, and supply vents at higher levels. This promotes efficient airflow and even temperature distribution throughout your living spaces.
Understanding the Role of the Air Handler in Home AC Units
The air handler is a critical component in cooling equipment, responsible for circulating conditioned air throughout the living space. It houses essential parts like the blower, coil, and filter, which work in unison to ensure efficient air distribution. When selecting an air handler, it’s vital to choose one with the correct airflow capacity to match the cooling load of your home. Over-sized units can lead to short cycling, while undersized ones strain the system, reducing efficiency.
Ensure that the blower motor is powerful enough to move air through the ducts without creating excessive noise or energy consumption. Additionally, regular maintenance, such as replacing filters and checking the evaporator coils, is essential to keep the handler operating at peak efficiency. A clogged filter can impede airflow, reducing cooling performance and energy efficiency.
Another important factor is the integration of the air handler with the rest of the cooling setup. A mismatched handler can cause improper pressure in the ducts, resulting in uneven cooling and potential wear on other parts. To optimize performance, have an HVAC professional verify that the air handler is correctly sized and installed in relation to the rest of the components.
In some setups, advanced handlers include features like variable-speed motors that adjust the airflow based on the demand, contributing to better energy efficiency and comfort. Consider upgrading to these models for improved temperature control and quieter operation.
How Ductwork Layout Affects Airflow and Cooling Performance
A well-designed duct network directly influences airflow efficiency and the overall cooling effectiveness. A layout that minimizes sharp bends, excessive lengths, and constrictions can reduce air resistance, improving the distribution of cool air throughout the living space. To enhance performance, ducts should be sized correctly according to the required airflow, considering room dimensions and heat loads. Keep ducts as short and direct as possible to prevent energy loss and avoid turbulence that can lead to inconsistent cooling.
Inadequate insulation or poorly sealed joints increase air leakage, reducing the system’s efficiency and raising energy costs. Sealing all connections and using high-quality materials ensures better air control and consistent temperatures. Additionally, placing ducts in conditioned spaces instead of uninsulated attics or basements helps prevent thermal losses.
Balancing air distribution is key. Too many branches from a single duct can restrict airflow, causing uneven cooling. Implementing zone control or using dampers allows for customized airflow, improving comfort in different areas of the building. Finally, periodic maintenance, including duct cleaning and checking for obstructions, ensures optimal operation and avoids performance drops over time.
Common Troubleshooting Tips for Your Home AC Unit
If your air conditioning unit is not cooling effectively, try these steps to pinpoint the issue:
- Check the thermostat: Ensure it is set to “cool” mode and the temperature is below the current room temperature. Replace the batteries if necessary.
- Inspect air filters: Clogged filters restrict airflow, leading to poor performance. Clean or replace filters every 1-3 months.
- Examine the condenser unit: Remove debris, such as leaves or dirt, from around the outdoor unit. This improves airflow and helps prevent overheating.
- Ensure proper refrigerant levels: Low refrigerant may indicate a leak. Call a professional for recharging or leak detection.
- Check the evaporator coil: If the coil is frozen, turn off the unit to allow it to thaw. A dirty coil can cause freezing, so clean it regularly.
- Inspect the ductwork: Leaky or disconnected ducts can waste energy and reduce cooling efficiency. Seal any visible gaps and check for airflow blockages.
For more complex issues, such as electrical malfunctions or compressor failure, contact a qualified technician for repairs.