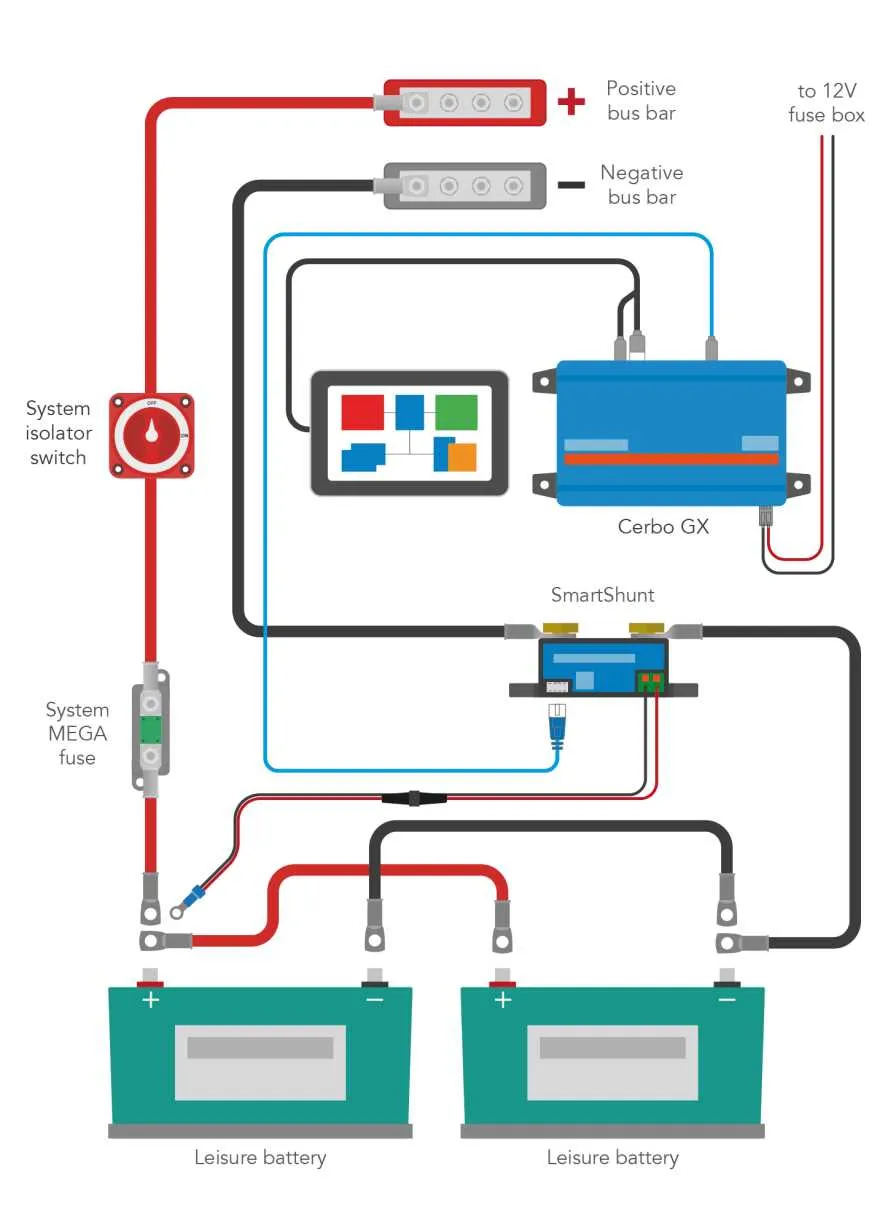
If you’re looking to enhance your RV’s electrical setup, implementing a second power source setup is one of the most effective ways to ensure reliable and long-lasting performance. This approach not only boosts your available energy storage but also helps in balancing the load across multiple energy cells, reducing strain on any single unit.
Begin by connecting both power sources through a system that allows them to charge simultaneously while being able to separate their energy for independent use. A dedicated isolator switch is key in managing the flow between the two, ensuring they do not drain each other under heavy load conditions.
Next, focus on using a quality switch for both charge and discharge cycles. This setup ensures that each power unit is charged evenly and does not compromise the overall system when one of the cells is low on charge. Make sure to include an inline fuse to protect the system from short circuits or overloads.
In addition, consider using a monitoring system that tracks both energy sources’ status in real-time. This allows you to avoid overcharging or undercharging, which can shorten the lifespan of the cells and reduce their efficiency over time. With this setup, your RV will have a much more reliable power source, even during extended off-grid stays.
Setting Up Two-Power Source System for Your RV
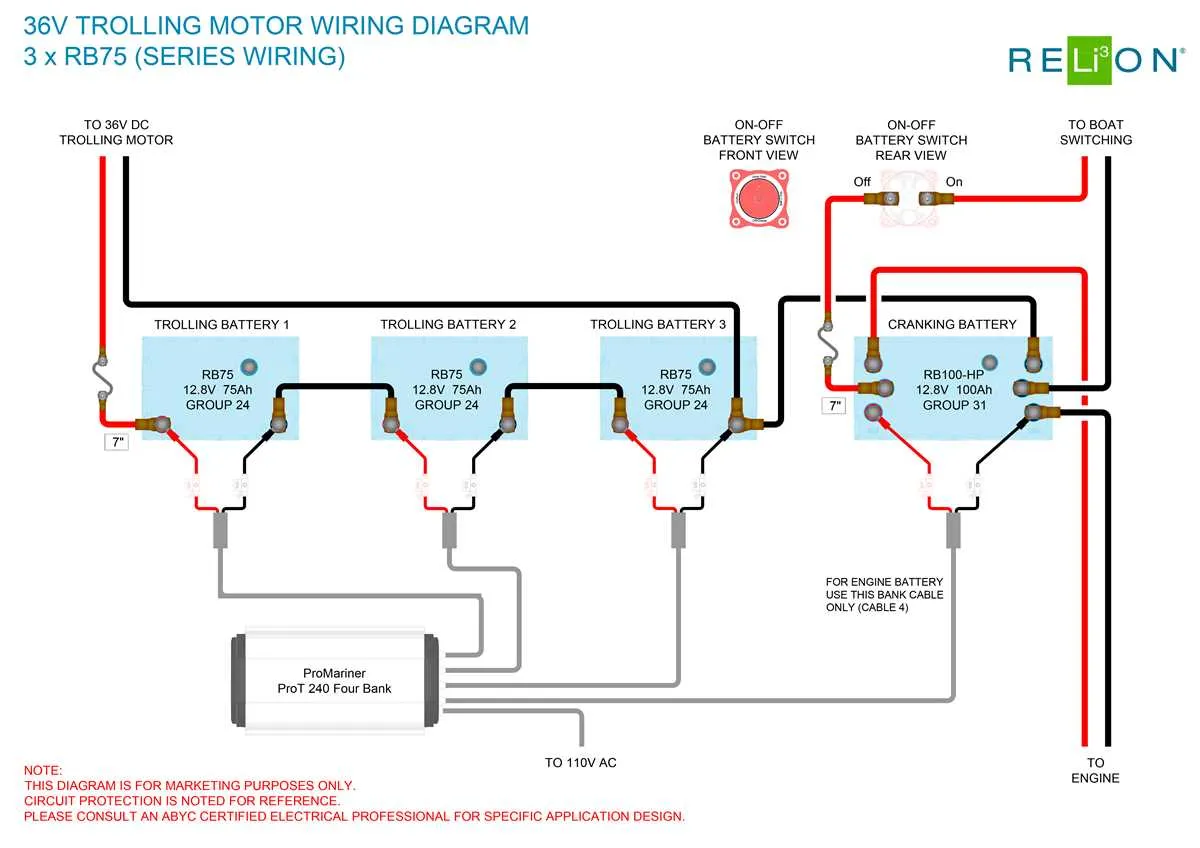
For an efficient setup with two power sources in your RV, follow these key steps to ensure reliable energy storage and distribution:
- Install a high-quality isolator to manage the flow of current between both power sources, ensuring the primary unit is not drained when parked.
- Use properly rated cables for each connection, keeping them short and free of sharp bends to reduce resistance and loss.
- Place the charge controller near the power intake point to prevent voltage drop during energy conversion from external sources.
- Choose a transfer switch that can automatically connect the backup system when the main one reaches low levels.
- Ensure both power sources are of the same type and capacity to avoid mismatched charging rates and imbalanced usage.
By incorporating these elements, your RV will maintain a consistent power supply even during extended trips, enhancing your experience on the road.
Understanding the Basic Components of a Dual Power Setup
To ensure efficient power management in recreational vehicles (RVs), two energy storage units are typically installed. The key components to understand include the isolator, the connections, and the energy management system. The isolator, often a smart relay or diode, separates the two units to prevent overcharging or depletion. It allows for charging one unit while the other remains in reserve. Proper gauge cables and robust connectors are essential to handle high currents, minimizing resistance and ensuring safety during operation.
Another critical component is the fuse or circuit breaker, providing protection against overcurrent situations. These protect the wiring and the power units from damage in case of a short or overload. The charge controller regulates the flow of energy from the RV’s charging source to the storage units, optimizing efficiency and preventing damage. The voltage regulator, if used, ensures that each unit receives the proper charge levels, preventing undercharging or overcharging, which can reduce lifespan.
Lastly, the energy monitoring system allows users to track the charge status of each unit. It helps prevent unintended depletion of the main energy source, ensuring that there is always power available when needed. Proper installation of these elements enhances the overall performance and reliability of the setup, making the RV more self-sufficient and minimizing the risk of power failure.
Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring a Dual Power System in Your RV
Start by selecting the appropriate power sources. Choose deep cycle units with sufficient amp-hour capacity for your needs, ensuring they can handle the energy draw from your appliances and accessories.
Install the isolator between the two units. This component prevents one from draining the other when the RV is not in use, allowing you to keep both fully charged during long trips. Mount it close to the main power unit, ideally in an accessible location for maintenance.
Connect the first unit to the isolator’s primary terminal. Use heavy-duty cables, typically 4 AWG or thicker, to ensure minimal voltage loss. Secure the connection with crimp connectors and tighten them properly to avoid any loose connections.
Next, link the secondary unit to the isolator’s auxiliary terminal using the same gauge of wire. Be sure to route the cable neatly to prevent wear and tear. Ensure both power sources are in parallel, so they work together without overloading either one.
Ground both units to the RV’s chassis. The grounding wire should be as short as possible to minimize resistance, using the same heavy-duty wire. Ensure a solid, corrosion-resistant connection to prevent voltage drop.
Once the connections are made, double-check for correct polarity to avoid damage. Ensure that the positive terminals from both units connect to the isolator, and the negative terminals go to the chassis ground.
Finally, test the system. Turn on the RV and monitor the voltage readings of both power sources to confirm that the isolator is functioning properly. The units should charge independently while preserving their individual charge when not in use.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Dual Power System Connections
If your RV’s power system isn’t performing as expected, check for improper connections or faulty components. The most common issue is poor contact between the terminals and cables. Ensure all terminals are clean, free of corrosion, and tightly connected. A multimeter can be used to check for voltage drops at critical points.
Next, inspect the isolator or relay that manages power distribution between the units. If this component malfunctions, it can prevent efficient charging or cause one unit to discharge faster than the other. Replace any faulty relay or isolator and test with a voltage meter.
If there’s no charge despite correct wiring, the issue may lie with the charging source–whether it’s the RV’s alternator or a solar setup. Verify that the charging system is providing the correct output voltage. If there’s a noticeable discrepancy, inspect the alternator or solar charge controller settings.
For systems that include inverters, be mindful of overloading. Inverters that are too small for the power demands of your RV can cause drops in performance. Ensure that your inverter is rated for the total wattage required by the devices it’s powering. You may need to upgrade if your power needs exceed the inverter’s capacity.
Finally, keep an eye on overall system maintenance. Regularly check for signs of wear, such as fraying wires or loose connectors, and replace any damaged components promptly. A neglected setup can cause long-term inefficiencies, reducing overall performance and lifespan.