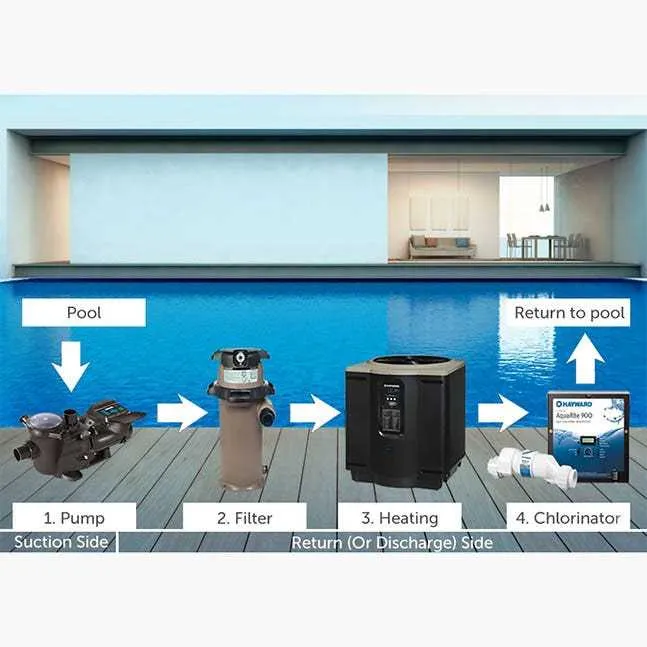

Ensure proper alignment of all equipment for maximum efficiency by understanding the key components of your system. The first step is ensuring that the filtration and circulation elements are correctly positioned to maintain consistent water movement. A well-designed layout ensures minimal resistance and optimizes flow, avoiding any potential bottlenecks that could reduce the performance of your system.
Next, focus on the connections between each part of the setup. Pay close attention to valves and piping sizes, as improper dimensions or installation can lead to inefficiencies. Avoid oversizing or undersizing any sections to ensure water is distributed evenly across all components. This will not only increase longevity but also prevent unnecessary strain on your equipment.
Finally, place emphasis on the maintenance access points. Accessibility is crucial for routine checks, repairs, or adjustments. Position your filtration unit and any related accessories where they can be easily reached without disturbing the flow or disrupting the overall structure.
A Practical Guide to Pool System Layouts
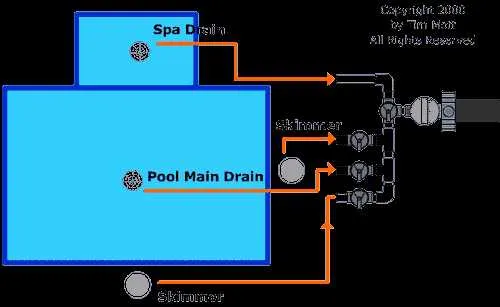
To ensure optimal water flow and efficiency in your system, it is crucial to follow a well-planned layout for the piping and filtration components. First, identify the placement of the pump relative to the filter–typically, the pump should be positioned near the intake to prevent strain on the motor. Proper alignment of the skimmer and drain lines is essential for smooth circulation. Always ensure the filter is located in such a way that debris is easily removed without obstruction.
Consider the flow rate when determining the size of the pipes. Larger diameter pipes reduce friction, allowing water to move through the system with less resistance, which improves overall performance. However, be mindful of the cost associated with oversizing. In most cases, 1.5-inch or 2-inch diameter pipes are sufficient for residential systems.
Incorporating a valve system at key junctions allows for better control over water flow and easy maintenance. Install a multi-port valve on the filter for more precise operation, ensuring the correct setting for filtration, backwashing, and rinsing. Use unions where connections are made for easy disassembly during repairs or upgrades.
For effective filtration, install a check valve on the return line to prevent backflow. This keeps contaminants out of the filtration system when the pump is off. Be sure to position the return jets at opposite ends of the tank, angled slightly downward, to promote efficient water movement and ensure even distribution of filtered water.
Lastly, always check for proper drainage and ensure there is no risk of backflow into the filtration unit, which could cause damage. Install a dedicated waste line to prevent flooding and ensure the system remains operational during heavy rains or unexpected water surges.
Understanding the Key Components of Pool System Setup
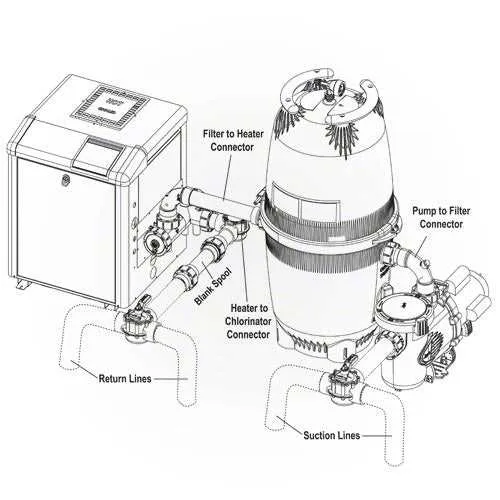
When assembling the water circulation system, it is crucial to prioritize the following elements to ensure smooth operation and efficient filtration:
- Pump: The heart of the setup, responsible for moving water through the entire system. Choose a pump with the appropriate flow rate to avoid strain on other components.
- Filter: This removes debris and contaminants from the water. The size and type of filter (sand, cartridge, or DE) should match the volume of the body of water to maintain cleanliness.
- Heater: For maintaining the ideal temperature, ensure the heater is compatible with the pump and filter to avoid overworking the system.
- Valves: Used to control the flow direction, these elements allow easy adjustment of the water flow for maintenance or for redirecting water to different areas of the setup.
- Return Lines: These pipes direct filtered water back to the structure, usually located near the bottom to prevent surface water stagnation.
- Skimmer: Positioned at the water’s surface, this device collects floating debris before it sinks to the bottom, ensuring cleaner water throughout.
- Drainage System: Proper drainage is essential to avoid water stagnation and ensure efficient removal of excess water during backwashing or maintenance.
Each of these components plays a critical role in the overall system performance. To achieve optimal results, consider upgrading each part based on the system’s demands and the frequency of use.
How to Read and Interpret Hayward Pool Plumbing Diagrams
Start by identifying the key components: filter, pump, skimmer, return lines, and valve system. Each is represented by specific symbols or shapes. The filter, usually a rectangular or cylindrical shape, plays a central role in water circulation. The pump is often depicted with an arrow to indicate water flow direction. Pay attention to line thickness; larger lines typically indicate higher flow, while thinner lines represent lower flow areas.
Examine the flow paths indicated by arrows or lines. These show the direction of water movement through the system, from intake to filtration and back to the system. The return lines often curve or extend outward to indicate water being sent back to the structure. It’s essential to verify if any components, such as valves, are placed to control this flow, as they will often have different symbols, like a triangle or circle, to show their open or closed positions.
When interpreting the pump’s operation, check for details like suction and return connections. Suction lines often have smaller arrows indicating water being pulled in, while return lines have larger arrows showing the water being expelled back. Pay attention to any notes or labels that specify valve settings, as these indicate how water flow is being adjusted for different system modes like filtering or heating.
Ensure you understand the legend or key if included; this will explain any abbreviations or unique symbols. The legend can clarify whether a specific valve is a multi-port valve or a bypass, and if any components have filters or check valves integrated into their design.
Finally, take note of the overall configuration. Some systems use parallel setups, where multiple lines perform the same function simultaneously. This is particularly important when analyzing the flow distribution for energy efficiency or troubleshooting a system malfunction.
Common Issues and Solutions for Pool Systems
If your filtration system is losing pressure, inspect the filter and pump for blockages. A clogged skimmer or pump basket can significantly reduce the water flow. Clean these components thoroughly, ensuring there are no debris or dirt obstructing the system.
Leaks are often caused by worn or cracked seals. Check connections around the pump and filter, especially the O-rings and gaskets. Replacing these seals can prevent water from escaping and maintain efficient operation.
If the water circulation seems weak, verify that the impeller isn’t obstructed by debris or calcium buildup. Cleaning the impeller can restore the optimal flow rate, ensuring proper water turnover and chemical balance.
A common issue is air entering the system, which can cause priming problems. This is typically due to a loose valve or a cracked pipe. Inspect all fittings and ensure they are tight and sealed. If the problem persists, look for leaks in the suction lines that may be allowing air in.
Water levels that drop too quickly may indicate a leak in the structure. Perform a bucket test by filling the system to a certain level and marking the waterline. If the water drops faster than expected, the leak could be in the plumbing beneath the surface. Consider hiring a professional to conduct a pressure test to locate and repair hidden leaks.
If your pump is running loudly or making unusual noises, check for debris stuck in the motor or impeller. Sometimes, air trapped in the system can cause cavitation, leading to noisy operation. Bleeding the system to release any trapped air can solve this issue.