
When working with heavy-duty engines, having a detailed understanding of the fuel distribution process is crucial for troubleshooting and efficient maintenance. The injector setup plays a pivotal role in ensuring that each cylinder receives the optimal amount of fuel at the correct time, preventing any performance issues such as incomplete combustion or fuel wastage.
The primary components in this network include the high-pressure pump, fuel lines, and injectors. The pump is responsible for drawing fuel from the tank and pressurizing it, while the lines carry the pressurized liquid to the injectors, which atomize the fuel for efficient combustion. To avoid poor engine performance, these parts must be regularly inspected for blockages, leaks, or wear.
For accurate diagnosis, it’s essential to know how each part interacts within the network. A proper breakdown of each component’s function allows for quick identification of any irregularities that may impact engine efficiency, whether it’s poor acceleration, rough idle, or excessive exhaust emissions. By familiarizing yourself with the exact placement and function of these elements, you’ll be able to conduct targeted repairs and ensure that the engine operates at its peak capacity.
Understanding the Diesel Engine’s Power Supply Layout
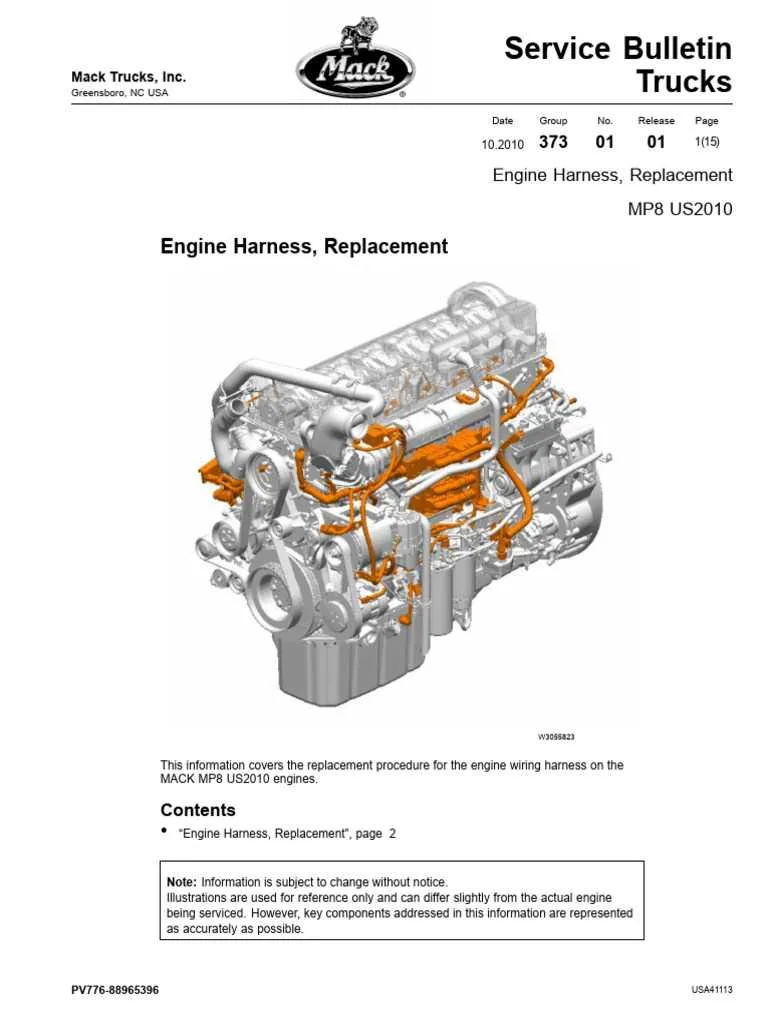
To ensure optimal performance, always start with checking the primary components: high-pressure pumps, injectors, and filters. The fuel intake pathway should be regularly inspected for blockages, wear, and leaks, especially in the hoses that carry pressurized liquid to the combustion chamber. A detailed examination of the injector nozzles and seals will prevent uneven distribution of the injected liquid, which can lead to misfires and excessive emissions.
One essential part to monitor is the electronic control unit (ECU), which regulates the fuel delivery timing and volume. If there is a delay or malfunction in signal transmission to the injector solenoids, you may notice issues such as power loss or irregular engine running. Ensure that all electrical connections are free from corrosion or damage, particularly the wiring harness attached to the ECU.
The intake and return lines play a crucial role in maintaining fuel pressure, and must be checked for any signs of clogging or air intrusion. Any disruption in these lines can result in inefficient engine operation and higher consumption rates. A visual inspection of fuel tanks and associated valves is also vital for identifying potential contamination or leaks.
Finally, always refer to the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule to replace filters on time. Dirty filters can cause inadequate supply to the injectors, leading to poor combustion and possible engine stalling. Regularly monitor fuel pressure with an appropriate gauge to detect any abnormalities early on.
Understanding the Components of the Engine’s Fuel Management

The key to optimal performance lies in understanding the core elements of the engine’s liquid delivery mechanism. Start with the primary pump, which ensures pressurized flow to the injectors. It is crucial to regularly inspect its operation, as any failure in this component will directly affect engine efficiency.
Next, the fuel rail serves as a conduit, directing the pressurized liquid to individual injectors. It’s important to check for blockages or leaks, as these can cause irregular distribution, resulting in engine misfires or reduced power output. Ensure the fuel filter is changed on schedule, as its clogging can lead to restricted flow and potential damage to the system.
The injectors themselves are responsible for precise atomization of the liquid, delivering the correct amount of fuel into the combustion chamber. Clogged or malfunctioning injectors can disrupt this process, leading to uneven combustion and increased emissions. Cleaning or replacing them is essential for maintaining fuel efficiency.
The pressure regulator controls the amount of liquid entering the system by maintaining a consistent pressure. If the regulator is faulty, it can lead to excessive or insufficient flow, negatively impacting engine performance. Regular testing and recalibration of this component are recommended.
Lastly, the return lines are vital for directing excess liquid back to the tank. Inspect these lines for leaks or cracks, as fuel loss through them can compromise overall system efficiency.
Common Issues in Diesel Engine Fuel Delivery
When diagnosing problems with engine power or efficiency, the root cause often lies in the fuel delivery components. Several critical areas should be checked first to identify potential issues quickly.
- Clogged Filters: Fuel filters can easily become clogged by debris or contaminants. This restricts the flow of diesel and causes the engine to lose power or stall. Replacing the filter regularly prevents this issue.
- Poor Injector Performance: If the injectors are worn or malfunctioning, they may fail to deliver the proper amount of fuel into the combustion chamber. Symptoms of injector issues include rough idling, poor fuel economy, and excess black smoke.
- Fuel Pump Failures: A faulty pump can lead to inconsistent fuel pressure, resulting in engine misfires or poor performance. Ensure that the pump is providing adequate pressure for optimal combustion. Check for any leaks or signs of wear.
- Air in the Lines: Air bubbles within the lines can prevent proper fuel flow, leading to starting issues or engine stalling. Bleeding the lines to remove trapped air is necessary to restore smooth operation.
- Water Contamination: Water in the diesel can corrode components and cause engine knock or hesitation. Ensure the water separator is functioning properly, and check for water buildup that needs to be drained regularly.
- Failed Sensors: Sensors that monitor fuel temperature or pressure can fail, sending incorrect signals to the engine control unit (ECU). This can result in fuel mixture problems, affecting performance and emissions.
- Worn Fuel Lines: Fuel lines are subject to cracking and wear over time. Inspect them for leaks or deterioration, especially in high-pressure areas, as fuel leaks are a significant fire hazard.
Regular maintenance and prompt attention to these issues can significantly improve the engine’s longevity and efficiency. Always use quality diesel and adhere to the recommended service intervals to avoid these common problems.
Troubleshooting Delivery Issues in Diesel Engines
Start by checking the primary and secondary filters for blockages or contamination. A clogged filter restricts the flow of pressurized liquid to the injectors, leading to engine performance issues. Replace them if necessary and ensure they are properly seated.
Inspect the high-pressure pump for any signs of wear or failure. If the pump is not generating adequate pressure, fuel delivery to the injectors will be insufficient, causing misfires or stalling. Check for leaks around the pump seals and connections.
Examine the injectors for clogging or improper spray patterns. If the nozzle is blocked or the injector is malfunctioning, it will not deliver the correct amount of liquid into the combustion chamber. Cleaning or replacing the injectors may resolve the issue.
Verify the condition of the fuel lines for cracks or air leaks. Air entering the lines can cause inconsistent pressure, leading to irregular engine performance. Tighten or replace any loose or damaged hoses and ensure all connections are secure.
Test the pressure regulator to ensure it maintains consistent output. A faulty regulator can cause fluctuating pressures, leading to poor engine operation. If necessary, replace the regulator with a properly calibrated one.
Inspect the electronic control module (ECM) for error codes related to fuel delivery. The ECM controls various components such as the pump and injectors, and a malfunction could prevent proper operation. Reset or replace the ECM if it is found to be faulty.
Check the air intake system for obstructions or leaks. An inadequate air supply will affect the combustion process, which in turn impacts the performance of the engine. Replace any air filters and seals that are damaged or clogged.
Finally, test the entire setup with a fuel pressure gauge to verify that all components are functioning within specified parameters. This ensures that the delivery pressure is optimal and consistent for reliable engine performance.