
When it comes to understanding the structure and bonding of chemical compounds, dot diagrams are an essential tool. In the case of magnesium chloride, the dot diagram helps visualize the arrangement of atoms and the sharing or transfer of electrons.
Magnesium chloride is an ionic compound composed of one magnesium (Mg) atom and two chloride (Cl) atoms. The dot diagram represents the outermost energy level or valence shell of each atom. The valence shell is the most important when it comes to chemical bonding.
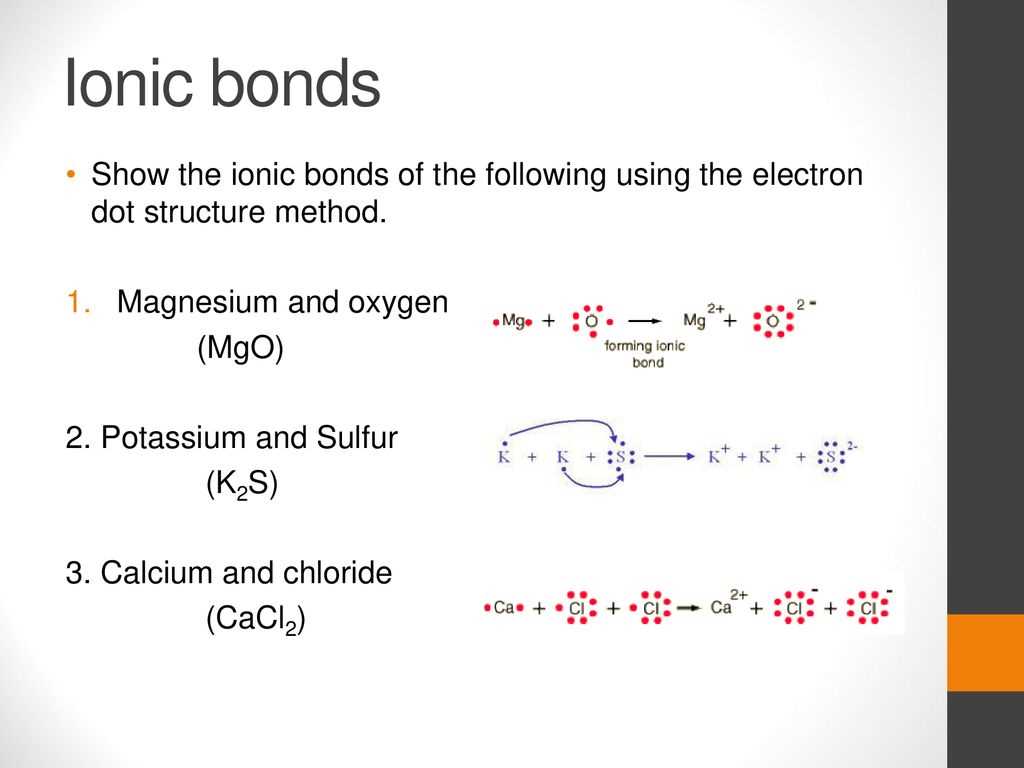
For magnesium, the electron dot diagram shows its valence shell with two electrons, symbolized by two dots. This indicates that magnesium has two valence electrons. Chlorine, on the other hand, has seven valence electrons. To achieve a stable electron configuration, chlorine needs one more electron. Thus, the chlorine atom will accept one electron from the magnesium atom to form an ionic bond.
In the dot diagram for magnesium chloride, the magnesium atom is represented by its symbol (Mg) with two dots around it, indicating its two valence electrons. The chloride ions, after accepting one electron each from the magnesium atom, are represented by the chlorine symbol (Cl) with eight dots around it, symbolizing its full octet of electrons.
Magnesium Chloride Dot Diagram: Explained
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) is a chemical compound composed of one magnesium atom and two chlorine atoms. The dot diagram of magnesium chloride depicts the arrangement of these atoms and their respective valence electrons.
To understand the dot diagram of magnesium chloride, it is important to first observe the electron configuration of each element. Magnesium (Mg) has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2, while chlorine (Cl) has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5.
The dot diagram represents the valence electrons of each element. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost energy level of an atom and are involved in chemical bonding. Magnesium has two valence electrons, while chlorine has seven. To form magnesium chloride, magnesium donates its two valence electrons to chlorine, resulting in the formation of ionic bonds.
The dot diagram of magnesium chloride would show magnesium with no dots around it, indicating the loss of its two valence electrons, and chlorine with seven dots around it, representing the gain of two electrons to complete its outer electron shell. The electron configuration of magnesium chloride can be represented as [Mg2+] [Cl–]. The brackets indicate the transfer of electrons between the elements.
In conclusion, the dot diagram of magnesium chloride illustrates the transfer of two valence electrons from magnesium to chlorine, resulting in the formation of an ionic compound. Understanding the dot diagram helps visualize the electron arrangement and bonding in magnesium chloride.
What is a Dot Diagram?
A dot diagram, also known as an electron dot diagram or Lewis dot diagram, is a representation of the valence electrons in an atom or ion. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, and they play a crucial role in determining an atom’s chemical properties and its ability to form bonds with other atoms.
In a dot diagram, a dot is used to represent each valence electron. The dots are placed around the element symbol in a way that reflects the arrangement of electrons in the atom’s energy levels. Each side of the symbol represents an orbital, and each dot represents an electron.
The dot diagram helps visualize the configuration of electrons in an atom and provides information about the number and types of bonds an atom can form. It also aids in understanding the chemical properties and reactivity of elements. Dot diagrams are often used to depict the formation of chemical bonds and the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms.
For example, in a dot diagram of magnesium chloride (MgCl2), the symbol “Mg” would have two dots on one side, representing its two valence electrons in the 3s orbital. The symbol “Cl” would have seven dots surrounding it, representing its seven valence electrons in the 3s and 3p orbitals. The dots on each atom would be arranged to show the sharing of electrons and the formation of the ionic compound.
The Structure of Magnesium Chloride
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) is a compound composed of one magnesium ion (Mg2+) and two chlorine ions (Cl–). This compound is commonly used in various applications, including medicine, food additives, and industrial processes.
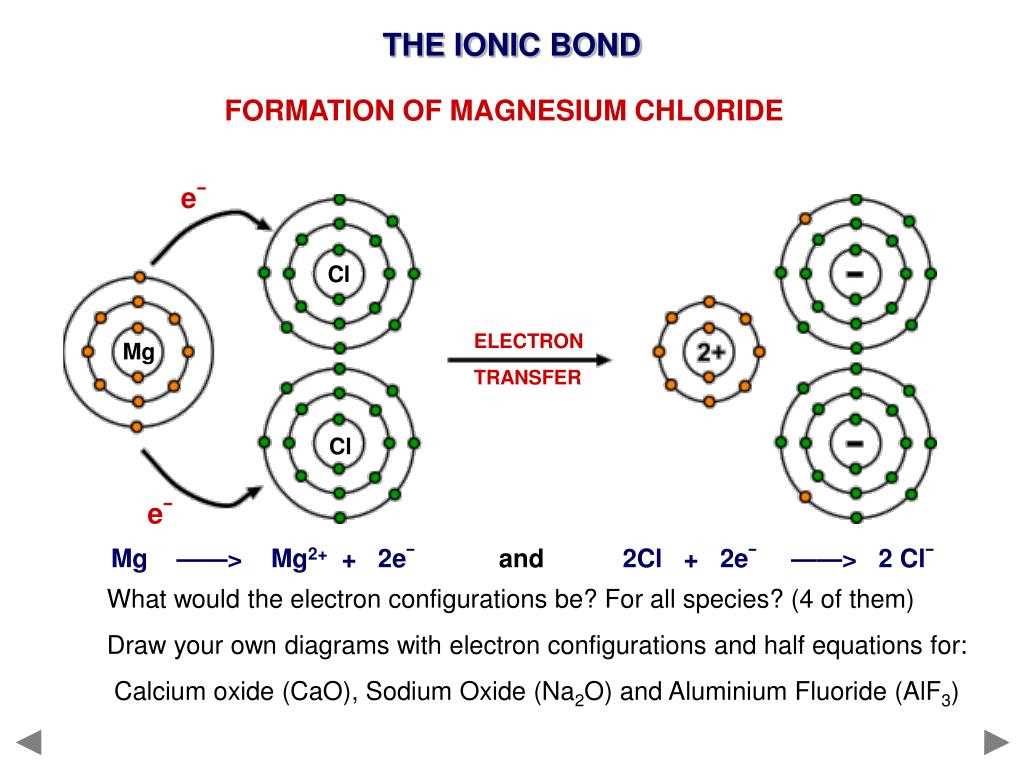
The structure of magnesium chloride is characterized by the arrangement of its constituent ions. The magnesium ion has a 2+ charge and is smaller in size compared to the chlorine ion, which has a 1- charge. As a result, the magnesium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions in a octahedral arrangement, with each chloride ion being bonded to the magnesium ion through ionic bonding.
This octahedral arrangement creates a crystal lattice structure for magnesium chloride. In this structure, the chloride ions form a cubic close-packed arrangement, with a chloride ion at each corner of the cube and one in the center of each face. The magnesium ions occupy the octahedral voids (empty spaces) between the chloride ions, with one magnesium ion in the center of each edge of the cube.
The crystal lattice structure of magnesium chloride gives it its characteristic properties. It has a high melting and boiling point, indicating strong ionic bonds between the ions. It is also a highly soluble compound in water, as the polar water molecules can easily interact with the charged ions and break the ionic bonds. Furthermore, magnesium chloride exhibits good conductivity when dissolved in water or molten form, as the ions are free to move and carry electrical charge.
How to Represent Magnesium Chloride using Dot Diagram?
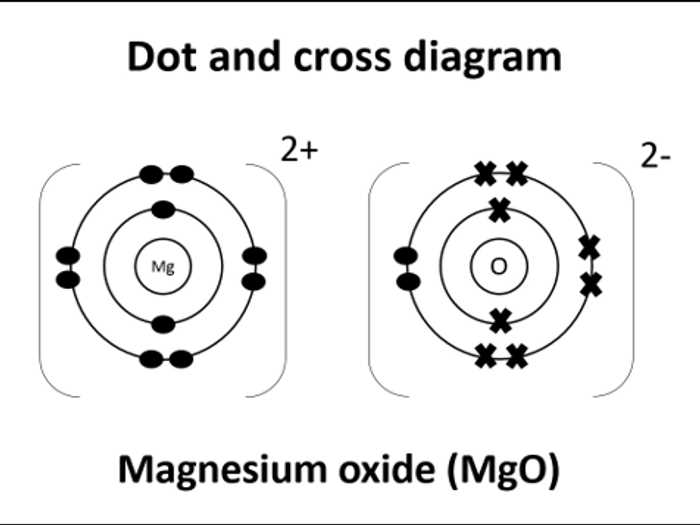
Magnesium chloride is an ionic compound composed of magnesium (Mg) and chloride (Cl) ions. In a dot diagram, the valence electrons of each atom are represented as dots around the atomic symbol. This helps us visualize the transfer of electrons between atoms and understand the bonding in the compound.
To represent magnesium chloride using a dot diagram, we first need to determine the number of valence electrons for each atom. Magnesium is in group 2 of the periodic table, so it has 2 valence electrons. Chlorine is in group 17, so it has 7 valence electrons.
We start by representing the magnesium atom, placing two dots around the atomic symbol to represent its two valence electrons. Next, we represent the chloride ions by placing one dot around each atomic symbol to represent the single valence electron. The aim is to achieve a stable electron configuration by transferring or sharing electrons between atoms.
Dot Diagram Representation of Magnesium Chloride:
Magnesium: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
Chloride: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
Magnesium (Mg): • •
Chlorine (Cl): •
In the dot diagram, the electrons are represented by dots outside the atomic symbol. The magnesium atom “loses” its two valence electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration like the noble gas neon (Ne). Each chlorine atom “gains” one electron from magnesium to achieve a stable octet configuration like the noble gas argon (Ar).
Overall, the dot diagram of magnesium chloride represents the transfer of electrons from magnesium to chlorine, resulting in the formation of Mg2+ and 2Cl– ions. These ions then bond together through their opposite charges to form the ionic compound, magnesium chloride.
Understanding the Bonding in Magnesium Chloride Dot Diagram

Magnesium chloride is a chemical compound composed of one magnesium atom bonded to two chloride atoms. It is an ionic compound, which means the bonding occurs through the transfer of electrons between the atoms. In order to understand the bonding in magnesium chloride, it is helpful to use a dot diagram.
In a dot diagram, the symbol for each element is surrounded by dots that represent the valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom and are involved in the formation of chemical bonds. Magnesium has a configuration of 2,8,2, meaning it has two valence electrons. Chlorine, on the other hand, has a configuration of 2,8,7, meaning it has seven valence electrons.
When magnesium and chlorine come together to form magnesium chloride, magnesium donates its two valence electrons to chlorine. This transfer of electrons results in both atoms achieving a full outer energy level, which is a more stable configuration. The two chlorine atoms each receive one electron from magnesium, giving them a total of eight valence electrons, and the magnesium ion that forms loses its two electrons, leaving it with a stable octet.
Overall, the bonding in magnesium chloride is an example of ionic bonding, where electrons are transferred between atoms. In the dot diagram, this is represented by the arrows showing the transfer of electrons from magnesium to chlorine. The resulting ionic compound, magnesium chloride, has an electrically neutral charge due to the equal number of positive and negative charges.
Summary:
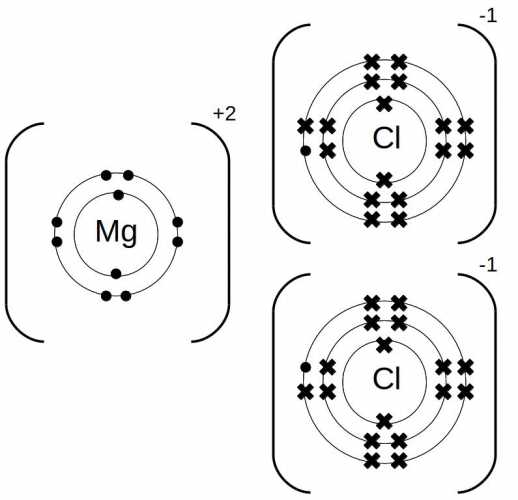
- Magnesium chloride is an ionic compound.
- Dot diagrams can be used to understand the bonding in magnesium chloride.
- In the dot diagram, magnesium donates its two valence electrons to chlorine.
- The transfer of electrons results in a stable octet for both atoms.
- The bonding in magnesium chloride is an example of ionic bonding.
Electron Distribution in Magnesium Chloride
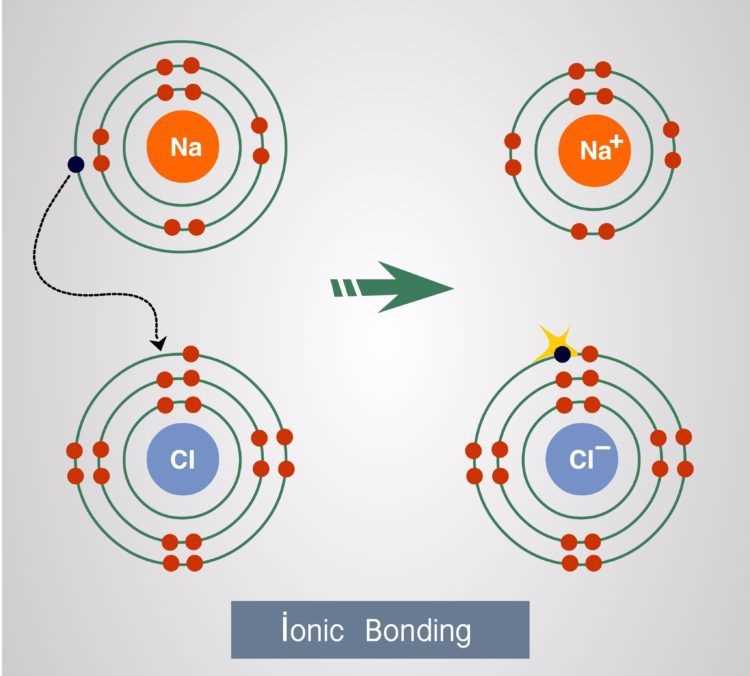
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) is an ionic compound composed of one magnesium cation (Mg2+) and two chloride anions (Cl-). As an ionic compound, magnesium chloride forms a crystal lattice structure in its solid state, with the magnesium cations attracted to the chloride anions through electrostatic forces. This arrangement allows for the transfer of electrons between the magnesium and chloride ions.
In the electron distribution of magnesium chloride, the magnesium atom loses two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, resulting in the formation of a Mg2+ cation. The two electrons lost by magnesium are transferred to the two chloride atoms, which then each gain one electron to achieve stable electron configurations as Cl- anions. This transfer of electrons allows both the magnesium and chloride ions to achieve full outer electron shells, resembling the electron configurations of the noble gases.
The electron distribution in magnesium chloride can be represented using a Lewis dot diagram. In this diagram, the magnesium cation is represented by the symbol for magnesium (Mg) surrounded by dots or crosses to indicate that it has lost two electrons. The chloride anions are represented by the symbol for chlorine (Cl) surrounded by dots or crosses to indicate that they have gained one electron each. The diagram visually illustrates the transfer of electrons between the magnesium and chloride ions, highlighting the formation of the ionic bond.
In summary, the electron distribution in magnesium chloride involves the transfer of two electrons from the magnesium atom to two chlorine atoms. This transfer results in the formation of a magnesium cation and two chloride anions, allowing both ions to achieve stable electron configurations. The Lewis dot diagram provides a visual representation of this electron transfer and the resulting ionic bond in magnesium chloride.
The Significance of Magnesium Chloride Dot Diagram in Chemistry
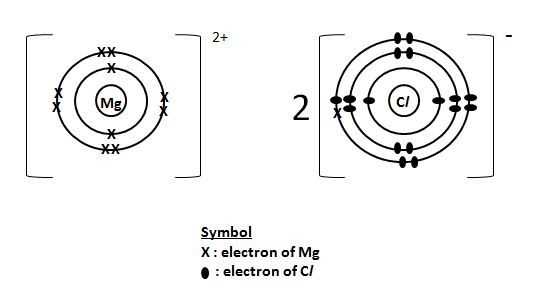
Magnesium chloride dot diagram is an important tool in the field of chemistry. It helps chemists understand the bonding and structure of magnesium chloride, which is a highly useful compound.
The dot diagram of magnesium chloride shows the arrangement of atoms and the distribution of electrons in the compound. Each dot represents an electron, and the lines between the dots represent chemical bonds. By analyzing the dot diagram, chemists can determine the number of valence electrons, the type of chemical bond, and the overall structure of the compound.
Magnesium chloride, with the chemical formula MgCl2, consists of one magnesium atom and two chlorine atoms. The dot diagram for this compound shows two chlorine atoms surrounding the magnesium atom, with each chlorine atom sharing one electron with the magnesium atom. This arrangement forms an ionic bond, where the magnesium atom loses two electrons and becomes positively charged, while the chlorine atoms gain one electron each and become negatively charged. The resulting compound is a crystalline solid with a high melting point and good conductivity in the molten state.
Understanding the dot diagram of magnesium chloride is crucial for various applications in chemistry. For example, it helps chemists predict the chemical reactivity of magnesium chloride and its ability to form other compounds. It also aids in the study of chemical reactions involving magnesium chloride and the design of new materials with specific properties.
In conclusion, the magnesium chloride dot diagram is a powerful tool in chemistry that provides valuable insights into the bonding and structure of the compound. It serves as a foundation for understanding the properties and behavior of magnesium chloride, as well as its applications in various fields of chemistry.
Q&A:
What is the significance of magnesium chloride dot diagram in chemistry?
The dot diagram for magnesium chloride shows the arrangement of atoms in the compound. It helps to illustrate the sharing or transfer of electrons between the magnesium and chlorine atoms, which ultimately determines the chemical properties of magnesium chloride.
How is the dot diagram of magnesium chloride constructed?
The dot diagram of magnesium chloride is constructed by representing the valence electrons of each atom as dots around the symbol of the element. Magnesium has two valence electrons, while chlorine has seven. The dots are placed around the symbols to show the electron configuration of the compound.
What does the dot diagram of magnesium chloride indicate about the bonding between magnesium and chlorine?
The dot diagram of magnesium chloride indicates that magnesium has donated two electrons to chlorine, resulting in the formation of an ionic bond between the two elements. This transfer of electrons creates positively charged magnesium ions and negatively charged chloride ions, which are attracted to each other.
Why is the dot diagram of magnesium chloride important in understanding its properties?
The dot diagram of magnesium chloride is important in understanding its properties because it provides a visual representation of the bonding and electron configuration in the compound. This information helps to explain why magnesium chloride has certain chemical and physical properties, such as its high melting and boiling points, as well as its ability to conduct electricity when dissolved in water.
What can be inferred from the dot diagram of magnesium chloride?
From the dot diagram of magnesium chloride, it can be inferred that magnesium has a tendency to lose two electrons, while chlorine has a tendency to gain one electron. This indicates that magnesium is more electropositive and chlorine is more electronegative. It also suggests that magnesium chloride has a crystalline structure due to the strong electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative ions.
What is the significance of magnesium chloride dot diagram in chemistry?
The dot diagram represents the valence electrons of the elements in a compound. Magnesium chloride dot diagram shows that magnesium has two valence electrons and chlorine has seven valence electrons. This allows us to see the electron transfer that occurs between magnesium and chlorine to form magnesium chloride, which is a stable ionic compound.
How does the magnesium chloride dot diagram help in understanding chemical bonding?
The magnesium chloride dot diagram helps in understanding chemical bonding by showing the electron transfer between magnesium and chlorine. This transfer of electrons creates ions with opposite charges, which then attract each other to form the ionic bond in magnesium chloride. It also helps to determine the ratio of ions in the compound, as the dot diagram shows that one magnesium ion is balanced by two chlorine ions.