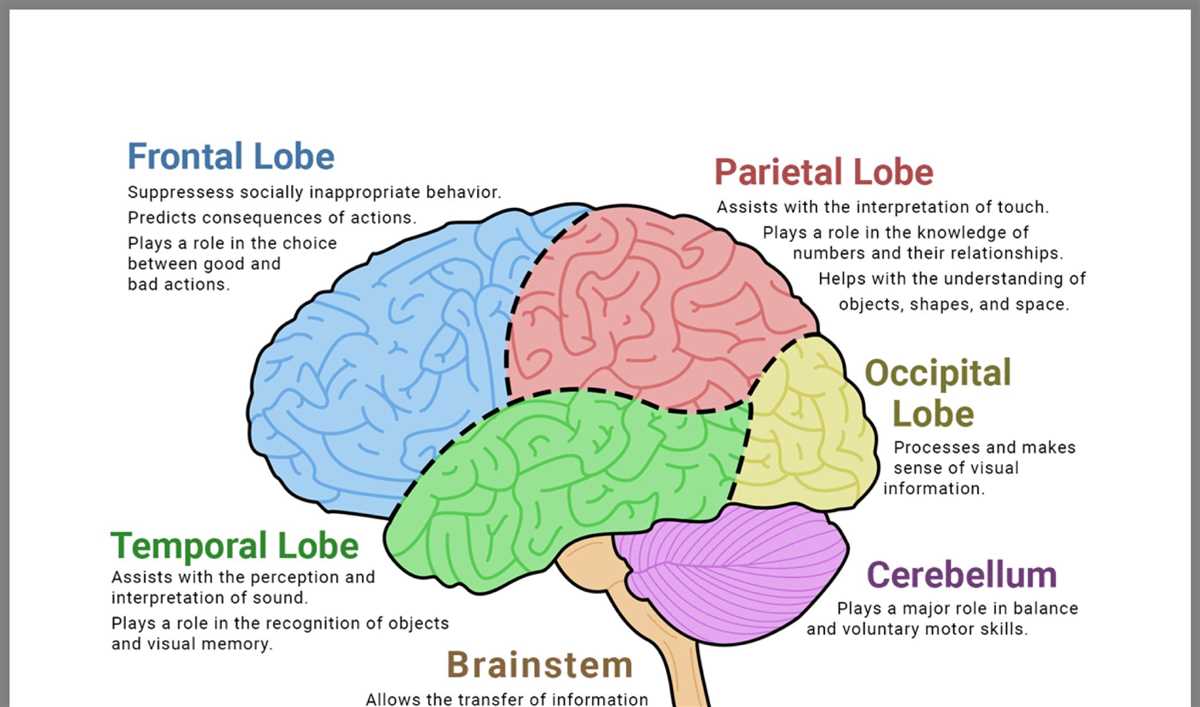
The human brain is a remarkably complex organ, responsible for controlling all of our thoughts, emotions, and bodily functions. To understand the structure and functions of the brain better, scientists and medical professionals often use brain diagrams to label its different parts. These diagrams provide a visual representation of the brain and help to identify regions associated with specific functions.
When labeling a brain diagram, it is important to familiarize oneself with the main structures and their functions. Some of the key areas that are typically labeled include the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and the different lobes of the cerebral cortex. Each region serves a unique purpose and contributes to our overall cognitive abilities and physical coordination.
Labeling a brain diagram can be a beneficial learning tool for students studying neuroscience, anatomy, or psychology. By understanding the different parts of the brain and their functions, students can gain a deeper appreciation for how the brain influences our thoughts, behaviors, and overall well-being. Whether studying for an exam or simply wanting to expand one’s knowledge, brain diagrams provide a visual aid that allows for a more comprehensive understanding of this fascinating organ.
The Importance of Understanding Brain Anatomy
The study of brain anatomy is essential for gaining a deeper understanding of the most complex organ in the human body. The brain controls virtually every aspect of human functioning, including thoughts, emotions, movements, and behaviors. By comprehending the structure and functions of different regions within the brain, researchers, physicians, and psychologists can better diagnose and treat various neurological disorders and mental illnesses.
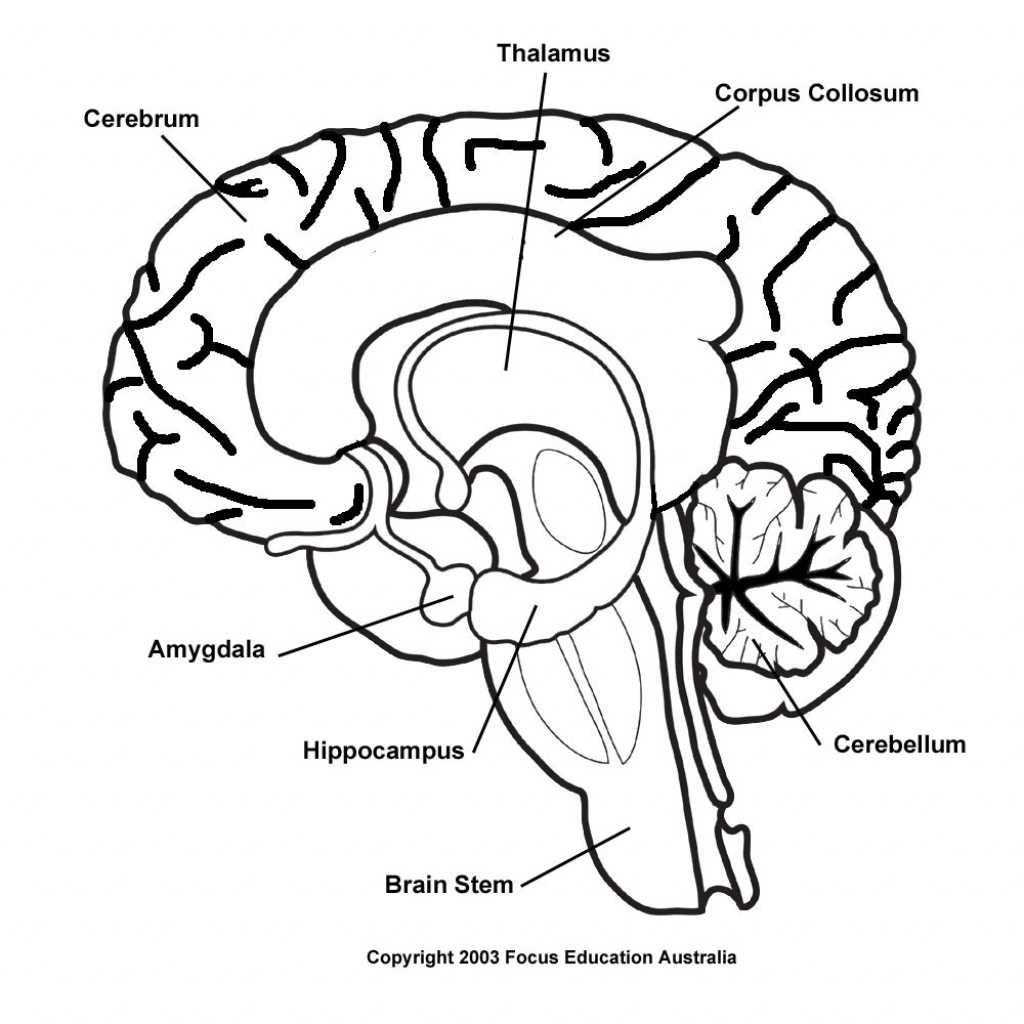
Brain diagram to label. One effective way to learn about brain anatomy is through a brain diagram that can be labeled with different regions and structures. This visual representation allows learners to identify and remember the key parts of the brain. By labeling the diagram, individuals can associate each region with its respective functions, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of brain anatomy.
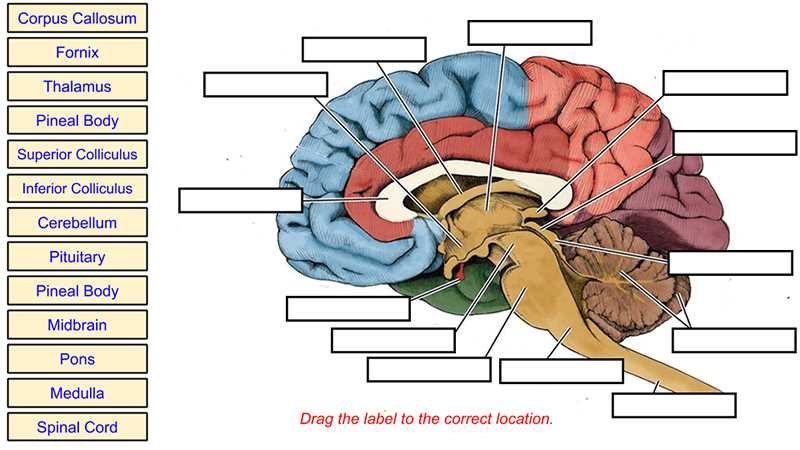
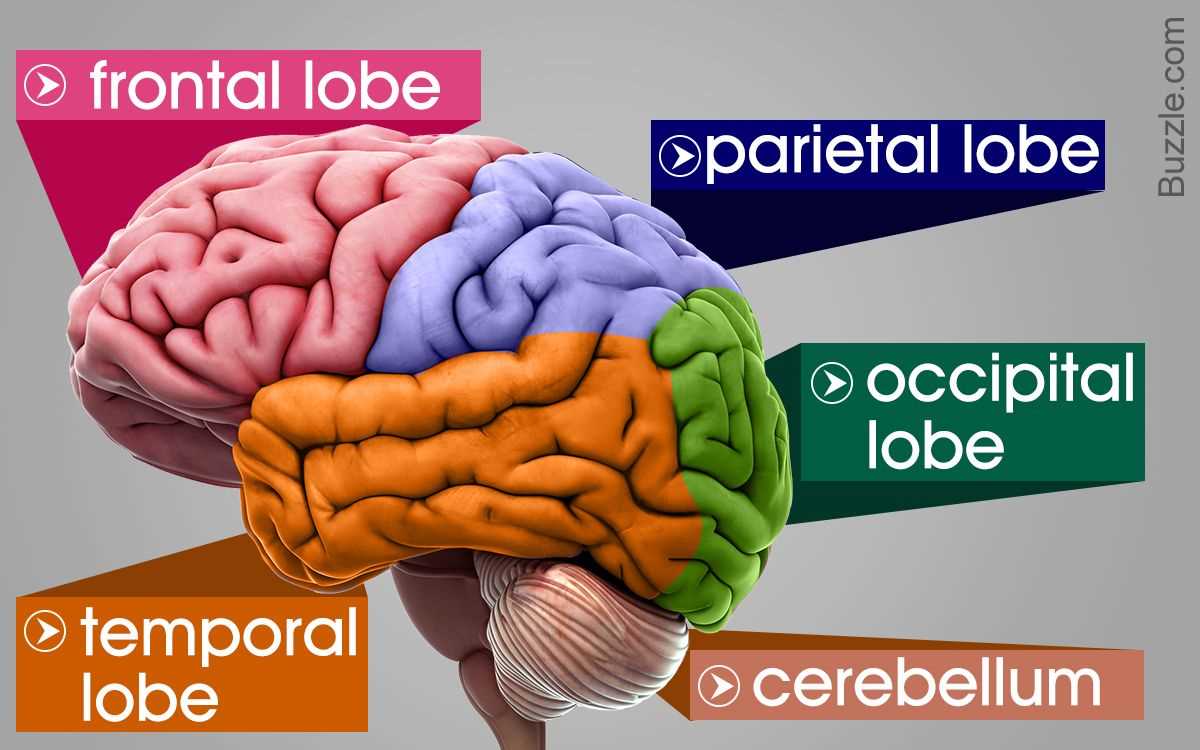
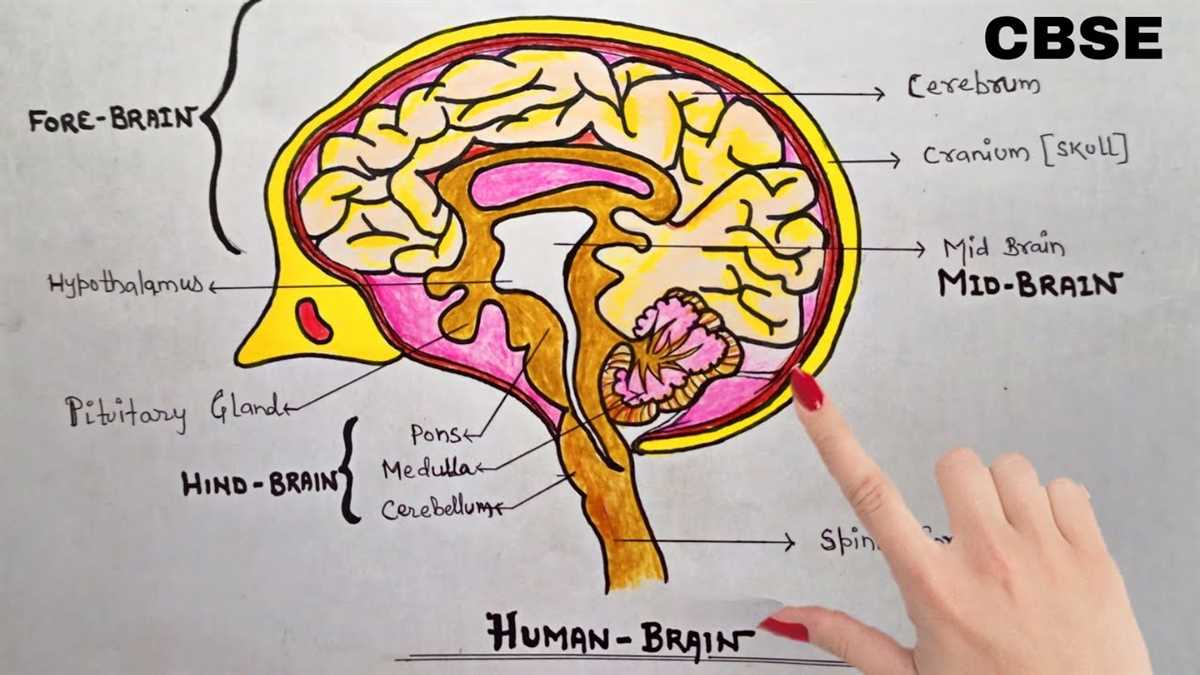
Cerebrum: The cerebrum is responsible for higher cognitive functions, such as thinking, memory, and decision-making. It is divided into two hemispheres, each controlling the opposite side of the body. The outer layer of the cerebrum, called the cerebral cortex, plays a crucial role in language processing, sensory perception, and motor control.
Cerebellum: Located at the back of the brain, the cerebellum is involved in coordination, balance, and motor control. It receives information from the sensory systems and other parts of the brain to ensure smooth and coordinated movements. Damage to the cerebellum can result in difficulties with balance and coordination.
Brainstem: The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and is responsible for vital bodily functions, including respiration, heart rate, and digestion. It consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. The brainstem also plays a role in the regulation of sleep and consciousness.
Understanding brain anatomy is crucial not only for medical professionals and researchers but also for individuals who want to take better care of their overall brain health. By knowing the different parts of the brain and their functions, people can make informed decisions about lifestyle choices, prioritize mental well-being, and seek appropriate medical attention for any neurological issues that may arise.
Key parts of the brain and their functions
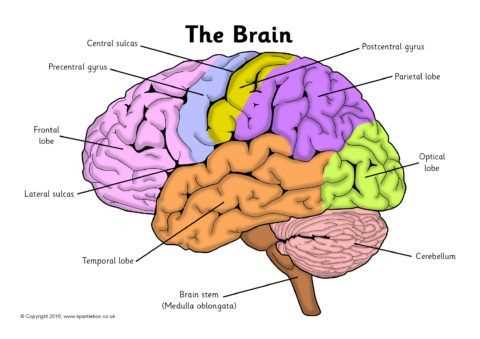
The brain is a complex organ that controls various functions in the body. Different parts of the brain have different functions, and understanding these key parts can help us better understand how the brain works.
Cerebrum
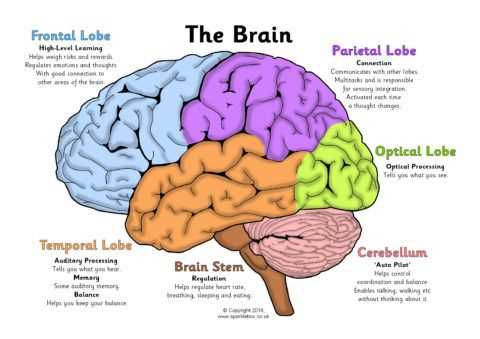
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for higher-level functions such as conscious thought, language, and sensory processing. It is divided into two hemispheres, each controlling the opposite side of the body. The outer layer of the cerebrum, called the cerebral cortex, plays a critical role in processing information from the senses and initiating voluntary movements.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain, below the cerebrum. Although it is much smaller in size, it plays a crucial role in coordinating voluntary movements, maintaining balance, and fine-tuning motor skills. It receives information from sensory systems, the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain to ensure smooth and accurate movements.
Brainstem
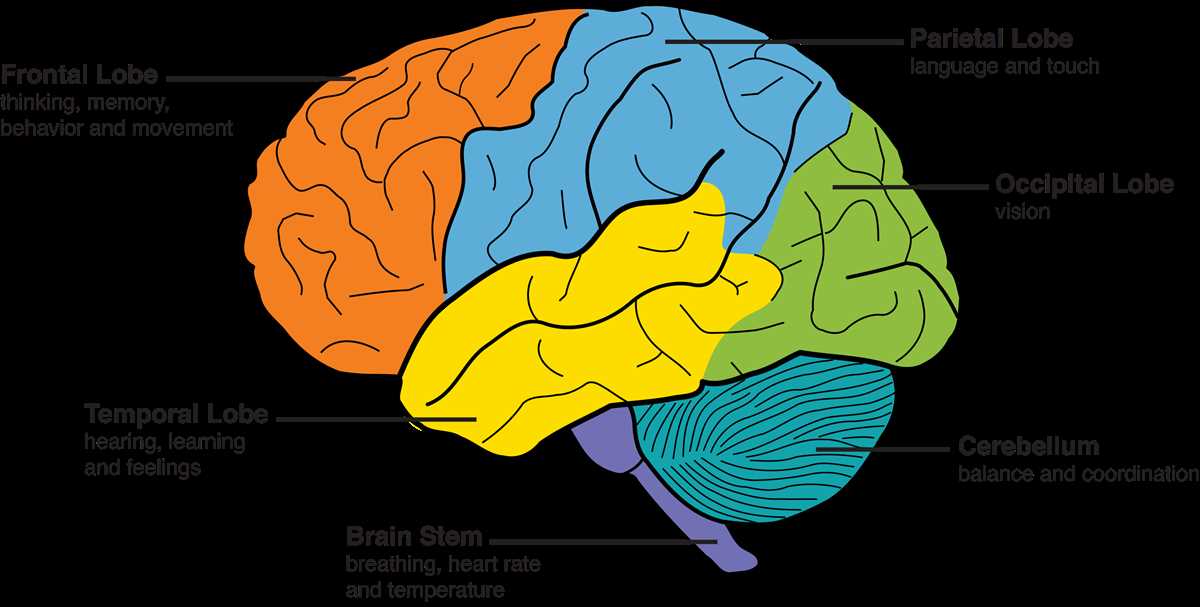
The brainstem is the lowest part of the brain and connects the spinal cord to the rest of the brain. It is responsible for controlling basic functions necessary for survival, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. It also serves as a relay station, transmitting signals between the brain and the spinal cord.
Thalamus
The thalamus is located in the center of the brain and acts as a relay station for sensory information. It receives signals from various sensory systems, such as vision, hearing, touch, and taste, and relays them to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for further processing. The thalamus also plays a role in regulating sleep and consciousness.
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a small, seahorse-shaped structure located in the temporal lobe. It is primarily involved in the formation and retrieval of memories. The hippocampus helps us navigate our surroundings, remember past events, and create new memories. It is also essential for spatial awareness and learning.
Amygdala
The amygdala is an almond-shaped structure located in the temporal lobe. It plays a critical role in processing emotions and is particularly involved in fear and fear-related responses. The amygdala helps us recognize and respond to threats, and it also plays a role in memory formation and emotional regulation.
Understanding the key parts of the brain and their respective functions is essential for comprehending how the brain influences our thoughts, behaviors, and overall well-being. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring the proper functioning of the brain and the body as a whole.
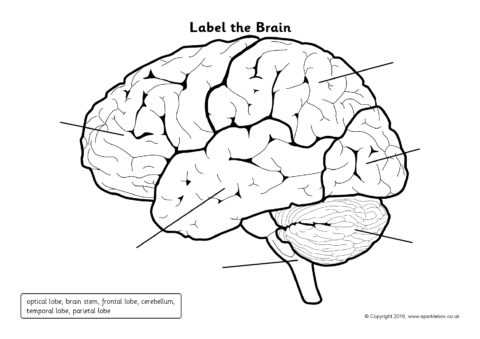
How to label a brain diagram
Labeling a brain diagram can be a helpful way to study and understand the different parts and functions of the brain. Whether you are studying neuroscience, anatomy, or simply want to learn more about the brain, following these steps can guide you in accurately labeling a brain diagram.
1. Identify the major anatomical parts of the brain
Before labeling the brain diagram, it is important to have a basic understanding of the major anatomical parts of the brain. These include the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and limbic system. The cerebrum is responsible for higher cognitive functions, such as thinking and decision-making, while the cerebellum plays a role in coordination and balance. The brainstem controls basic life functions, such as breathing and heart rate, and the limbic system is involved in emotions and memory.
2. Use a labeled reference image or diagram
Having a labeled reference image or diagram can be extremely helpful when labeling a brain diagram. This can be a textbook illustration, an online resource, or even a hand-drawn diagram. Use this reference as a guide to help you accurately identify and label the different parts of the brain.
3. Start with the major structures
Begin labeling the brain diagram by focusing on the major structures. This includes labeling the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and limbic system. Use clear and concise labels to identify these structures on your diagram.
4. Move on to the specific lobes of the brain
After labeling the major structures, you can move on to labeling the specific lobes of the brain. These include the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe has its own unique functions, and labeling them will further enhance your understanding of the brain.
Note: It’s important to research and understand the functions of each structure before labeling the brain diagram. This will ensure accurate labeling and a better grasp of the brain’s complex functions.
By following these steps and utilizing a labeled reference image or diagram, you can effectively label a brain diagram and gain a better understanding of the different parts and functions of the brain.
Tips for memorizing brain anatomy
Memorizing brain anatomy can be a challenging task, especially considering the complex structures and intricate connections within the brain. However, with the right techniques and strategies, it is possible to make the process easier and more efficient. Here are some tips to help you memorize brain anatomy effectively.
1. Break it down
Instead of trying to memorize the entire brain at once, break it down into smaller sections and focus on one part at a time. Start with the major structures, such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem, and then gradually move on to studying the subdivisions and specific regions within each part.
2. Use visual aids
Visual aids can greatly enhance your understanding and retention of brain anatomy. Utilize diagrams, labeled illustrations, and interactive apps or websites that allow you to explore 3D models of the brain. By associating the names of the structures with their visual representation, you can create a stronger mental image and facilitate memorization.
3. Create mnemonics
Mnemonics can be powerful tools for memorization. Create catchy phrases or acronyms that help you remember the names or functions of different brain structures. For example, “Silly Monkeys Try Jumping Over Rainbows” can help you remember the functions of the cranial nerves (Sensory, Motor, or Both).
4. Use repetition and active recall
Repetition is key when it comes to memorizing intricate details. Regularly review the names, locations, and functions of different brain structures to reinforce your memory. Additionally, actively recall the information by testing yourself or explaining the concepts to someone else. This helps solidify your understanding and improves long-term retention.
5. Create a study group
Studying with peers who are also learning brain anatomy can be beneficial. Discussing the information, quizzing each other, and explaining concepts to one another can deepen your understanding and help you remember the material better. Collaborative learning can make the process more engaging and enjoyable.
6. Practice labeling diagrams
Find brain anatomy diagrams online or in textbooks and practice labeling them. This hands-on approach allows you to actively engage with the material and reinforces your memory of the structures. Alternatively, create your own diagrams and label them from memory to identify areas that need further review.
By employing these strategies, you can make the task of memorizing brain anatomy less daunting and more achievable. Remember to be patient with yourself and incorporate regular studying into your routine to ensure long-term retention of the information.
Common mistakes when labeling a brain diagram
Labeling a brain diagram can be a challenging task, especially for those who are not familiar with the different structures and functions of the brain. Making mistakes is common, but it is essential to try to avoid them as much as possible to ensure accurate labeling.
1. Incorrect placement of labels: One of the most common mistakes is putting the labels in the wrong location. It is crucial to carefully study the diagram and understand the correct positioning of each structure before labeling. Reference materials and textbooks can be helpful in identifying the correct placement of labels.
2. Misspelling labels: Another common mistake is misspelling the labels. It is important to double-check the spelling of each label before writing it on the diagram. Misspelled labels can lead to confusion and misinterpretation of the diagram.
3. Lack of clarity: Clarity is essential when labeling a brain diagram. Using neat handwriting and placing labels appropriately can ensure that the diagram is easy to understand for others. Avoid crossing out labels or using arrows to indicate corrections, as this can create confusion.
4. Confusing similar structures: The brain has several structures that may appear similar but have distinct functions. It is crucial to understand the differences between these structures and label them accurately. Mistaking one structure for another can misrepresent the diagram and lead to misunderstandings.
5. Omitting labels: Forgetting to label certain structures is a common mistake. It is important to review the diagram thoroughly and ensure that all significant structures are labeled correctly. Omitted labels can make the diagram incomplete and less informative.
Overall, labeling a brain diagram requires attention to detail and a good understanding of the different structures. By avoiding these common mistakes and taking the time to accurately label each structure, the diagram can be a useful educational tool.
Resources for further learning about brain anatomy
Understanding the anatomy of the brain can be a complex and fascinating subject. If you’re interested in delving deeper into this topic, there are numerous resources available to help you expand your knowledge. Here are a few recommendations:
- Books: There are several books that provide detailed information about brain anatomy. “Brain Anatomy and Function: A Guide for Students” by Dr. Jean Angebault is a comprehensive resource that covers the structure and function of the brain, while “The Human Brain Book” by Rita Carter offers a visually stunning exploration of the brain’s anatomy through detailed illustrations and diagrams.
- Online Courses: Many reputable online platforms offer courses on brain anatomy. Websites like Coursera, Udemy, and edX provide a wide range of courses taught by experts in the field. Some recommended courses include “The Neuroscience of Learning” and “Introduction to Neuroanatomy: Brain Structures and Their Functions.”
- Interactive Websites: Websites such as the Brain Explorer provide interactive tools and animations that allow you to explore the different regions of the brain and learn more about their functions. These resources can be a great visual aid in understanding the complex 3D structures of the brain.
- Medical Journals and Research Papers: If you’re interested in more advanced and scholarly information, medical journals and research papers are valuable resources. PubMed is a widely used database that provides access to scientific articles related to brain anatomy and neuroscience.
No matter which resource you choose, remember to approach the subject with curiosity and patience. Understanding the brain’s anatomy is a lifelong learning journey, and these resources can serve as excellent starting points to deepen your knowledge and broaden your understanding of the incredible organ that is the brain.