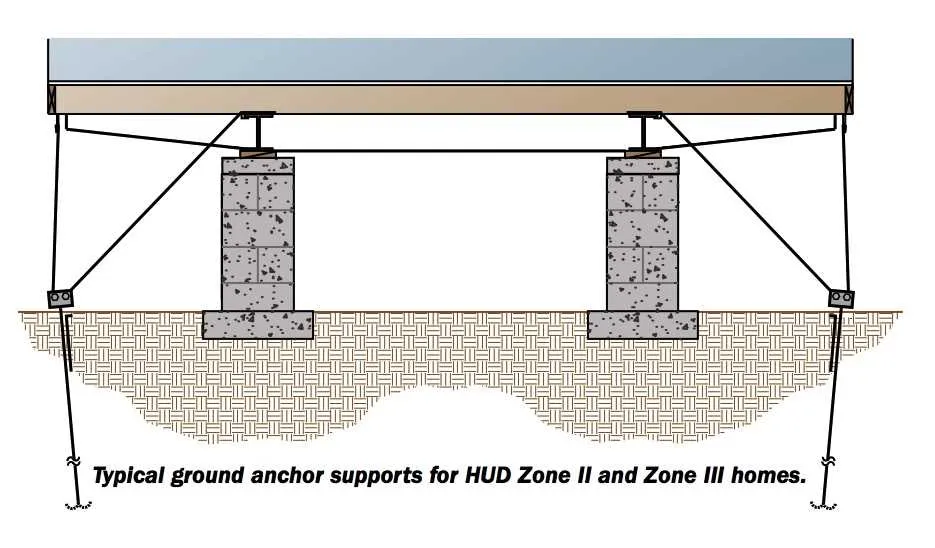
Proper anchoring of a prefabricated unit is critical to ensure stability during adverse weather conditions. Use the recommended support system to secure the structure to the foundation. This prevents movement, shifts, or potential damage caused by high winds or shifting ground. Follow local regulations and engineering guidelines for safety compliance.
Step 1: Choose the right type of anchors based on soil conditions. Concrete footings are suitable for soft ground, while steel anchors work well on firmer soils. Always ensure the anchors are deep enough to resist uplift forces.
Step 2: Install the anchors at regular intervals along the perimeter of the unit. The distance between each anchor should not exceed 6 feet to ensure even distribution of forces.
Step 3: Secure straps or cables to the anchors and the structural frame. These elements should be tightened securely to avoid slack, which could lead to instability during storms.
Step 4: Double-check all connections before finalizing installation. A thorough inspection ensures that all elements are properly secured, avoiding future maintenance issues.
Tip: Always consult with a local contractor or structural engineer for advice on the specific requirements in your area.
Secure Anchoring System for Prefabricated Structures
For optimal stability, place anchor points every 6 feet along the perimeter of the structure, ensuring that they are evenly distributed. Use high-strength steel cables or straps rated for at least 2,000 pounds of force per anchor to prevent shifting during extreme weather. Each anchor should be securely fastened to the ground using steel rods or concrete blocks, depending on soil conditions. Ensure the anchors are installed at an angle of 45 degrees to maximize resistance to horizontal movement.
It’s crucial to reinforce corner points with additional anchors, as these areas experience the most stress. A minimum of four additional anchor points should be placed near the corners to strengthen the overall structural integrity. For flat or less stable ground, consider using deep foundation anchors to prevent movement during heavy winds or floods.
Inspect the anchor system regularly for signs of corrosion or loosening, especially after severe storms. Re-tighten connections as needed to maintain a secure hold. Finally, verify that the materials used meet local building codes and are suitable for the climate conditions in your area.
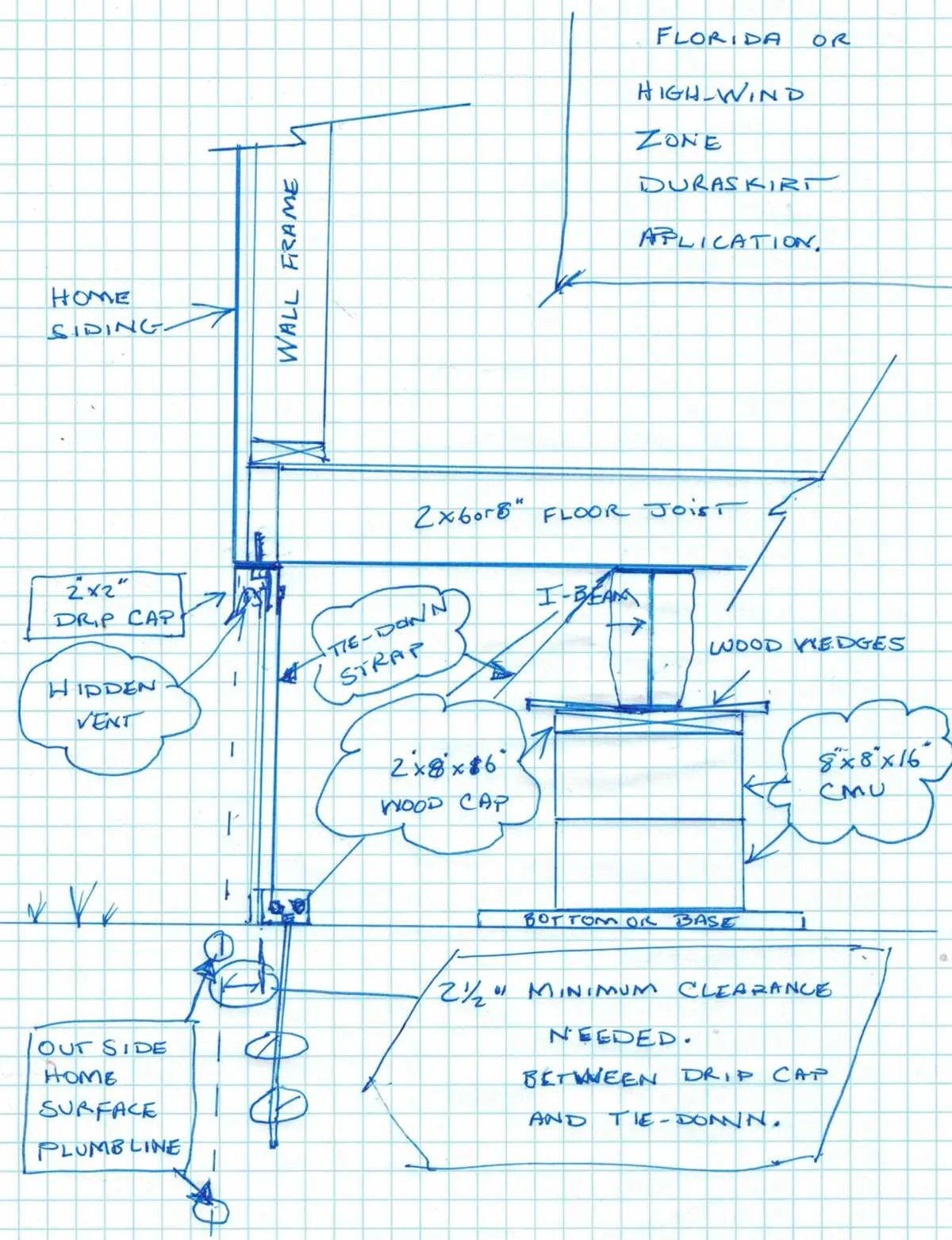
Choosing the Right Materials for Anchoring Systems
Use galvanized steel straps for strong, rust-resistant connections. They are durable and offer superior resistance to corrosion, ensuring long-term security. Opt for ground anchors made from high-quality steel or heavy-duty aluminum to handle varying soil conditions. For clay-rich or sandy soil, spiral anchors work best, providing greater holding power. In areas with frequent winds or heavy storms, additional reinforcement, such as concrete anchor blocks or auger systems, may be necessary for optimal stability.
For securing supports, choose pressure-treated wood or steel beams, depending on your environmental exposure. Pressure-treated lumber can withstand moisture and pests, making it ideal for humid regions. Steel beams, on the other hand, offer unparalleled strength and are perfect for areas prone to high winds. Check local building codes to ensure compliance with material specifications for structural integrity and safety.
Finally, use high-strength bolts or heavy-duty screws for attachment points. Stainless steel is recommended for its resistance to rust and strength. Ensure that each fastener matches the size and load requirements specified by the manufacturer to prevent failure under stress.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Secure Installation Plan
Start by identifying the base structure’s dimensions. Measure the length, width, and height accurately, ensuring precise placement for each anchoring point.
- Mark anchor points: Choose four or more points around the perimeter for securing the structure. Ensure each point is evenly distributed.
- Determine anchor types: Select appropriate anchors based on soil conditions and structural weight. Options include concrete, auger, or dead-man anchors.
- Calculate anchor depth: For stability, anchors should penetrate deep enough into the ground. Depth varies based on soil type and environmental factors.
- Placement angles: Set each anchor at a 45-degree angle relative to the ground to maximize holding power against wind and shifting forces.
- Secure connections: Use robust steel straps or cables for each anchor, ensuring the structure is firmly connected to the ground. Regularly inspect for wear or corrosion.
- Label each point: Clearly mark the positions on your plan, noting anchor type and depth for easy reference during installation and future checks.
Double-check measurements and placements to confirm everything is positioned to withstand environmental forces. Proper installation significantly reduces the risk of movement or structural damage.
Common Mistakes in Anchor Installation
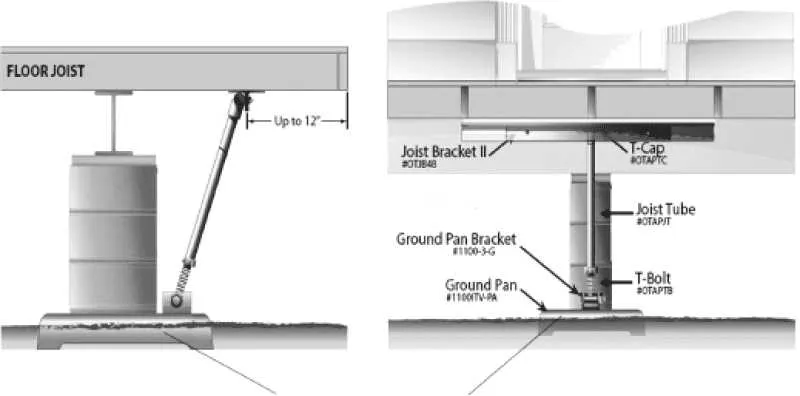
Improper placement of anchors is one of the most frequent errors. Ensure anchors are positioned at the correct intervals according to local regulations and manufacturer guidelines. Installing anchors too far apart can compromise stability, while placing them too close may create unnecessary strain on structural elements.
Another common mistake is using incorrect materials for securing the structure. Always verify that the straps, bolts, and anchors are rated for the required load. Using substandard or incompatible materials can result in premature wear, causing the system to fail under pressure.
Incorrect tensioning of the securing straps is often overlooked. Straps should be tightened enough to prevent excessive movement but not so much that they create undue stress on the frame. Over-tightening can lead to deformation or damage to the structure.
Failure to account for soil conditions is a critical mistake. Anchors must penetrate deep enough to secure the structure in place, but varying soil types may require different anchoring techniques. Always test the ground’s stability before proceeding with the installation.
Ensure that every anchor is installed perpendicular to the base of the structure. A slight tilt can reduce the effectiveness of the anchoring system, leading to uneven stress distribution and potential failure during strong winds or adverse weather conditions.
| Issue | Consequence | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect anchor placement | Inadequate structural support | Follow manufacturer guidelines for anchor spacing |
| Using wrong materials | Premature system failure | Ensure materials meet or exceed load requirements |
| Improper strap tensioning | Damage to the frame or ineffective securing | Adjust straps to proper tension, avoiding over-tightening |
| Ignoring soil conditions | Instability in high winds | Test soil and adjust anchoring method as needed |
| Anchor tilt | Reduced anchor effectiveness | Ensure anchors are installed perpendicular to the base |