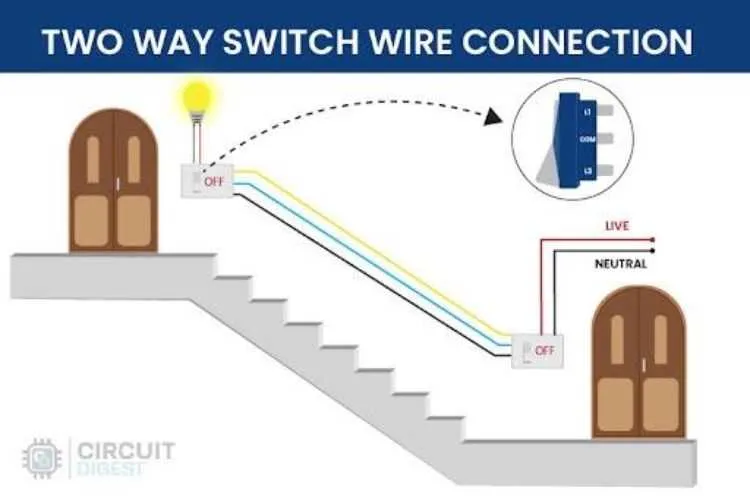
To effectively control your electrical system, ensure that the connection components are arranged to allow seamless activation and deactivation. Begin by establishing clear paths for current flow, where each connection point must be securely fastened for proper functionality.
For accurate setup, focus on the placement of each conductor that handles the flow of energy to the device. Position the input and output terminals so that a reliable break in the current path can occur when required. Confirm that the voltage ratings for each conductor are well-suited to the system’s requirements.
Next, ensure that all terminals are securely isolated from unintended contact. Insulation around the conductors prevents short circuits, and the correct polarity is essential for the system’s stability. Double-check each component for durability and resistance to wear.
Additionally, it is recommended to utilize a clearly marked configuration to identify each terminal or connection point. This step eliminates any confusion and guarantees that maintenance or modifications can be conducted safely and efficiently.
How to Connect a Power Control Mechanism
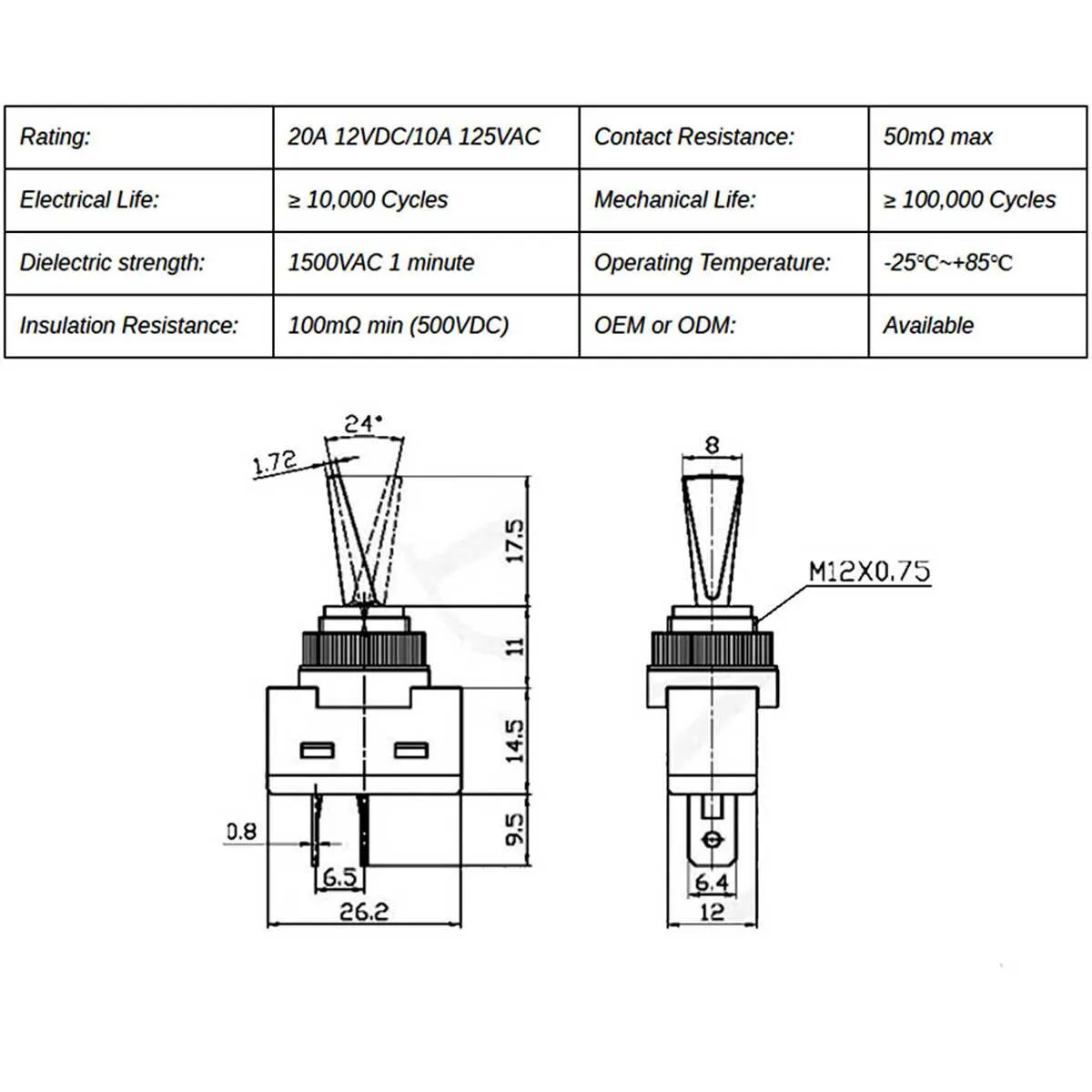
To set up an efficient power control system, connect the device’s two main terminals to the primary power supply. Ensure that the terminals are securely fastened to avoid loose connections, which could lead to electrical issues. Use appropriate connectors to ensure a stable electrical pathway.
Key Steps:
- Ensure the device is disconnected from any power source before starting the installation process.
- Use insulated tools to prevent accidental shorts or contact with live terminals.
- Connect the input terminal to the positive side of the power source.
- Connect the output terminal to the corresponding device to control the flow of electricity.
Safety Considerations:
- Always check that the voltage rating of the components matches the required specifications.
- Verify all connections using a multimeter before reapplying power.
- Install a safety fuse to protect the device from potential power surges.
Note: After installation, perform a final check to ensure everything is properly connected and there are no exposed conductors.
Understanding the Basic Circuit of a Power Control Mechanism

To establish a functional control mechanism for electrical devices, ensure a clear path is created for current flow when needed and obstructed when not. This system uses two key components: an electrical conductor and a component that opens or closes the circuit, either allowing or halting current. Proper wiring and connection are essential for safe and efficient operation.
When assembling the components, the circuit needs to include the following essential elements:
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Conductor | Transmits electrical current between two points |
| Control Device | Regulates the current flow based on user input or pre-set conditions |
| Power Source | Provides the necessary energy to the system |
| Load | The device that consumes the electricity, like a light bulb or motor |
Ensure the control device is correctly aligned with the current path to prevent electrical faults. The control mechanism should seamlessly engage or disengage the flow without causing unnecessary resistance or heat buildup. Proper insulation and material quality will help avoid short circuits and improve long-term reliability.
It’s also crucial to verify the circuit’s design for compatibility with the electrical specifications of the device in use. Double-check the voltage ratings to prevent overloading, and regularly inspect for wear or corrosion that could compromise the connection.
How to Identify the Correct Connections for Power Control Units
To ensure proper functionality, follow these steps when determining the right connections for power control devices:
- Identify the terminal types: Commonly, devices will have at least two terminals for electrical connection. Check for markings such as “L” (live), “N” (neutral), or “C” (common).
- Check polarity: Always ensure that the live wire is connected to the terminal marked “L” or equivalent. The neutral wire should be connected to the “N” terminal. Polarity mistakes can cause malfunctions.
- Confirm grounding: If applicable, ensure that the ground connection is properly linked to the terminal marked with the ground symbol (⏚) to avoid electrical hazards.
- Refer to manufacturer labels: Most units come with a clear label that indicates which terminals correspond to specific functions. Double-check these labels before proceeding with connections.
- Ensure correct load routing: In some cases, you may need to identify the device’s load line. It should always be routed to the appropriate terminal responsible for the operation.
- Use a multimeter: Testing continuity with a multimeter can help identify correct paths and connections, verifying the proper flow of electricity.
By following these steps, you can confidently determine the correct routing of wires in a power control device, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
Common Wiring Issues and Troubleshooting for On-Off Controls

When the control mechanism fails to operate properly, it’s essential to first check for poor connections. A loose or corroded connection can lead to intermittent performance. Inspect the terminals for secure attachment and clean any rust or dirt.
Another common issue is incorrect polarity. Ensure that the live and neutral conductors are correctly assigned to the appropriate contacts. A reversed connection can prevent proper activation and may cause sparking or damage.
Faulty contacts within the mechanism can result in no response. Test the internal components for continuity using a multimeter. If the internal contacts are damaged or worn out, replace the component entirely.
Overloaded circuits are also a frequent cause of malfunction. Verify that the system isn’t drawing more current than it is designed to handle. If necessary, reduce the load or upgrade the capacity of the installation.
Inconsistent function might also be caused by faulty insulation. Check for any exposed or frayed wires that could cause shorts or leaks. Insulating material should be intact and without any signs of wear.
If you experience erratic operation, ensure the installation is free from interference. Nearby equipment or electrical appliances might induce noise or unwanted signals, leading to operational glitches. Shielding and proper grounding can mitigate these issues.