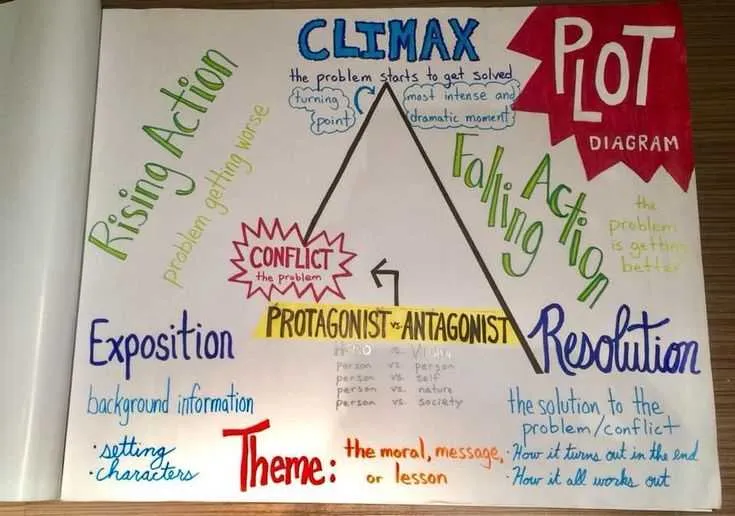
To improve your grasp of a narrative’s structure, focus on identifying the key stages that a story goes through. Start by pinpointing the exposition, where the setting, characters, and initial conflicts are introduced. This is the foundation that supports the entire plot development.
Next, pay attention to the rising action. This is where complications and challenges arise for the protagonist, leading to a turning point. These moments are crucial for building tension and shaping the direction of the tale.
Once the conflict reaches its peak, you will encounter the climax, a pivotal moment that defines the outcome of the narrative. It’s essential to analyze how characters respond and how this shift leads to the resolution of the primary issue.
Lastly, observe the resolution, where the loose ends are tied up, and the story comes to a satisfying conclusion. Understanding how each element transitions smoothly into the next can enhance your comprehension and appreciation of storytelling.
Understanding the Structure of a Story’s Narrative

Focusing on the key elements of a narrative structure can help break down a story into its fundamental parts, aiding in deeper comprehension and analysis.
- Exposition: This is where the setting, main characters, and conflict are introduced. It sets the stage for the unfolding of the story.
- Rising Action: The series of events that lead up to the climax. These moments build tension and develop the conflict further, keeping the audience engaged.
- Climax: The turning point in the narrative, where the main conflict reaches its peak. This is the most intense part of the story.
- Falling Action: The events that occur after the climax, leading to the resolution. The tension begins to subside as the story moves toward its conclusion.
- Resolution: The conflict is resolved, and the story reaches its conclusion. Loose ends are tied up, and the narrative comes to a satisfying close.
When analyzing a story, identifying these stages will help you understand how the events and characters evolve and how the author crafts a compelling narrative. This structure is applicable to both short stories and longer works of fiction.
Teachers often encourage students to identify these sections in texts as it promotes critical thinking and enhances literary skills. Start by highlighting the core events and how they connect, then look for patterns or themes that emerge across different stories.
How to Identify Key Elements of a Story Structure
Start by pinpointing the introduction, where characters and setting are introduced. The first part typically presents the main characters and their environment, setting the stage for the rest of the narrative.
Next, focus on the conflict. This is the central problem that drives the events of the story, usually occurring after the initial setup. Identify what the main characters struggle against, whether it’s an external force or an internal dilemma.
The climax comes after the conflict escalates. It’s the turning point, the moment of highest tension in the tale, when everything changes. This is the point where the characters must make decisions that will determine the story’s outcome.
Following the climax, watch for the falling action. This section deals with the consequences of the decisions made during the climax. It’s where loose ends are tied up, but the resolution has not yet fully arrived.
The conclusion wraps everything up, resolving the conflict and offering closure. Look for how the characters’ struggles are finally addressed and how the story ends.
Understanding these key parts allows you to break down any narrative and gain deeper insight into how stories are structured and unfold.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Narrative Structure for a Short Story

Start by identifying the key events in the story. Focus on the turning points and moments that drive the plot forward. These are the foundation of your structure.
Next, pinpoint the introduction. It sets the scene, introduces the main characters, and establishes the conflict. Make sure to clarify the setting and the initial problem or goal the protagonist faces.
Then, locate the rising action. This part develops the tension, complicates the conflict, and leads up to the climax. Break it down into smaller events or challenges that the protagonist must overcome, each one building toward the highest point of excitement.
The climax is where the conflict reaches its peak. This is the turning point, where things change dramatically. Describe the moment that forces the protagonist to make a critical decision or face their greatest challenge.
Following the climax, identify the falling action. These events occur after the peak, as the story moves toward resolution. Show how the protagonist deals with the aftermath of the climax and how the conflict begins to resolve.
Conclude with the resolution. The conflict is resolved, and the story ends with a sense of closure. Ensure the ending reflects the changes in the characters and ties up loose ends, leaving the reader with a clear understanding of the outcome.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Analyzing Story Structure

One frequent mistake is focusing too much on minor details that don’t influence the overall development of the narrative. Instead, prioritize the main events that drive the characters’ decisions and plot direction.
Another error is misinterpreting the climax. This critical moment is where the conflict reaches its peak, not simply the most intense scene. Look for the point where the protagonist faces their greatest challenge.
Avoid confusing the rising action with the falling action. Rising action builds tension and leads to the climax, while falling action resolves the conflict and leads to the conclusion. Pay attention to the sequence of events, not just the events themselves.
Don’t overlook the resolution. Many students focus on the conflict and ignore how it is resolved. Understanding how loose ends are tied up provides a clear picture of the story’s message.
Lastly, don’t forget character motivations. Analyzing what drives characters at each stage will help identify key turning points and relationships that are central to the narrative’s development.