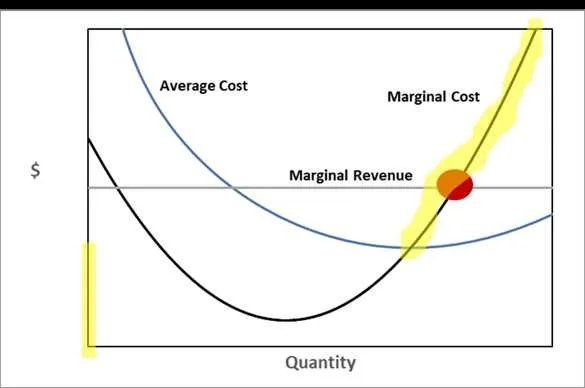
Focus on efficiency by analyzing production expense patterns, including fixed and variable elements. Pay close attention to how changes in output levels directly affect overall spending. Look for inflection points where additional production leads to either a diminishing or increasing cost per unit.
Next, explore how income changes with varying output levels. Identifying a clear relationship between quantity produced and earned revenue is essential. Monitor the point where further output increases do not significantly enhance total earnings, signaling a need for strategic adjustments.
Maximize profitability by balancing production volume with corresponding costs and income generation. Recognizing these critical thresholds can lead to more informed decision-making and a more efficient business operation.
Understanding the Relationship Between Expense Patterns and Incremental Earnings
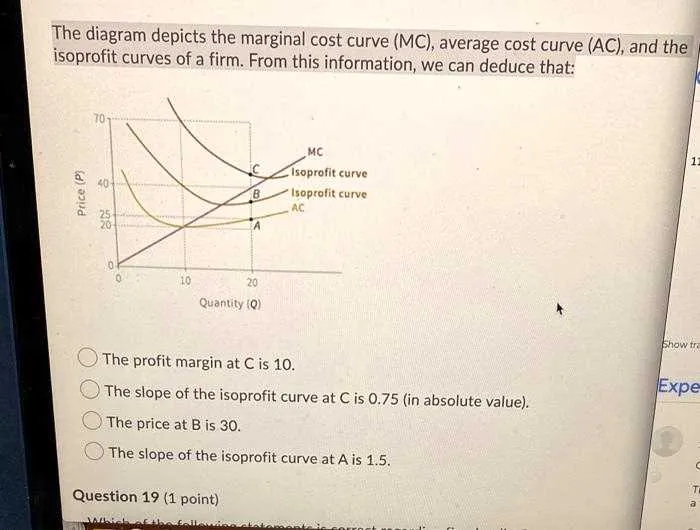
To optimize decision-making in pricing strategies, focus on how variations in total spending interact with additional income from each unit produced. Below are key insights for grasping this connection:
- When additional production leads to decreasing marginal costs, profits rise, making pricing adjustments crucial to maximize returns.
- Watch for points where diminishing returns set in. Once extra production yields lower returns, reevaluate output levels to avoid inefficiency.
- Identifying the breakeven point is vital for cost-effective operation. The point where total earnings match total expenses is critical for sustainable growth.
Key Takeaway: For profitability, align production rates with points where added output results in positive financial impact, balancing expenses against returns at every stage.
How Marginal Revenue Influences Profit Maximization Decisions
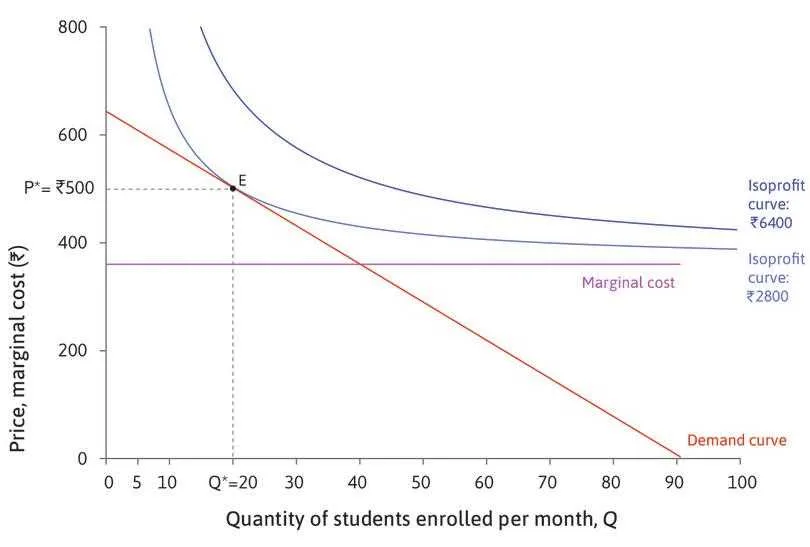
Profit optimization occurs when additional income generated from selling one more unit matches or exceeds extra expenses incurred. When income growth per unit sold declines, firms must adjust production levels to avoid diminishing returns. Maximizing profits requires a clear understanding of when added income no longer compensates for higher operational costs.
At the point where additional income equals variable expenses, production should be halted to prevent losses. Exceeding this balance leads to inefficiencies, lowering profitability. Firms should aim to increase output up until income from each additional unit sold matches or exceeds incremental expenditures. This equilibrium point marks optimal profit levels.
Shifting output beyond this level results in reduced returns per unit, affecting bottom-line performance. By closely monitoring variations in income per unit, businesses can fine-tune their production strategy, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently while maximizing profitability.
Practical Applications of Cost Curves in Business Pricing Strategies
Understanding price determination involves identifying key factors influencing profitability. By analyzing fluctuations in expenses tied to production volume, businesses can determine optimal pricing strategies.
Minimizing losses is crucial when assessing economies of scale. As output increases, unit production costs typically decrease. Recognizing when a business reaches its minimum efficient scale helps set competitive prices while maintaining healthy margins.
Optimization of pricing strategies is driven by recognizing where average total expenses align with marginal income. Identifying output levels that balance between production cost increases and pricing maximization enables firms to prevent oversupply, which may lower unit prices.
Strategic decisions often hinge on understanding fixed and variable expense distinctions. For example, businesses with significant fixed expenses can lower unit costs at higher production levels, thus giving room to adjust market prices for optimal return.
Break-even analysis serves as a key decision-making tool, helping firms calculate minimum sales necessary to cover operational expenditures. By using this knowledge, firms can set initial price points that ensure profitability while staying competitive in the market.
Price discrimination becomes viable when considering different segments of consumers. By adjusting prices based on consumer willingness to pay, firms can increase their returns without overpricing, ensuring broader market reach while still covering variable and fixed production costs.