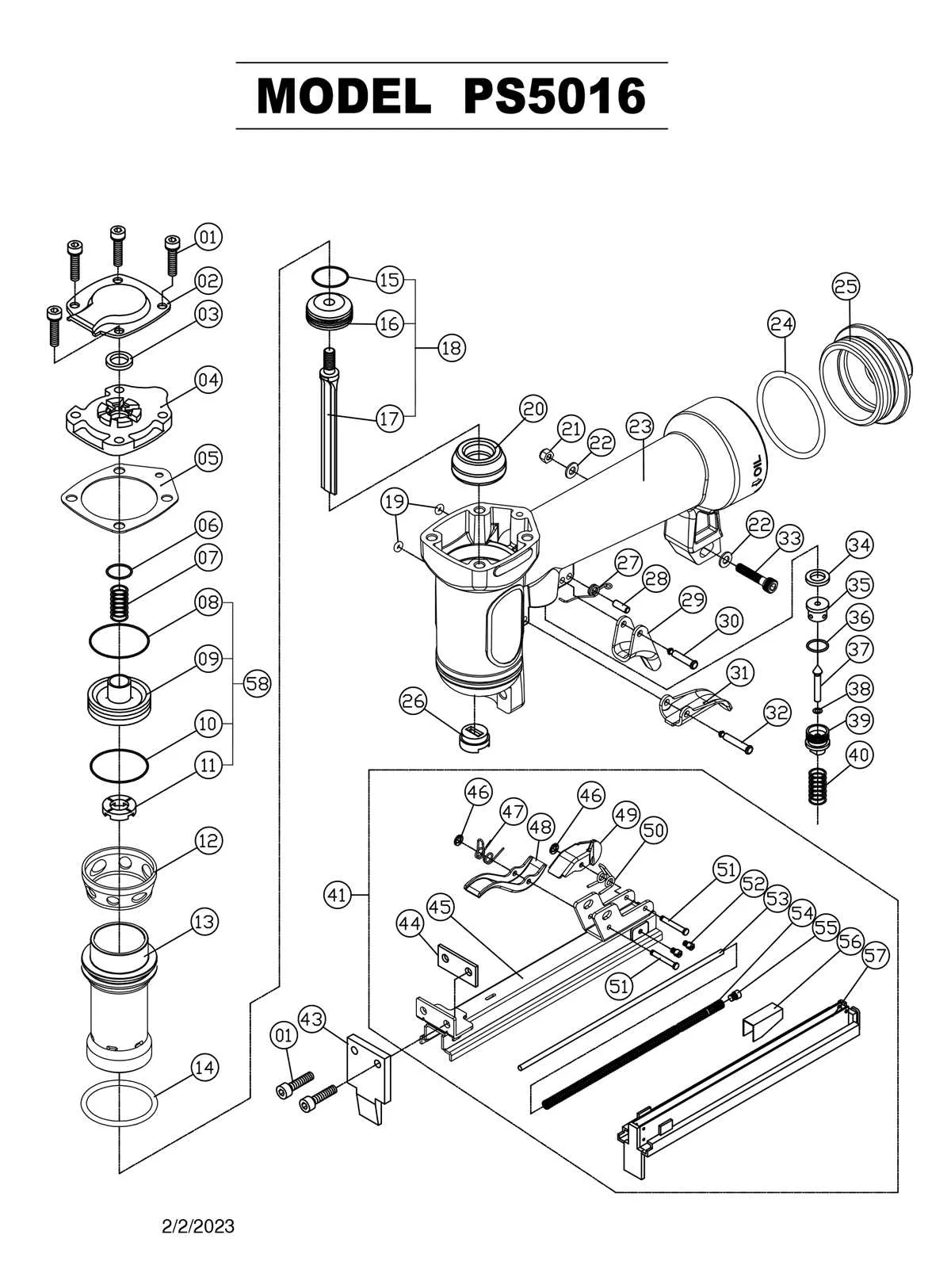
To enhance your repair and maintenance efforts, familiarize yourself with the detailed breakdown of the internal structure and key elements of your tool. This guide will provide you with a clear overview of each crucial part, its function, and the best approach to troubleshooting or replacing damaged sections. Knowing the exact configuration of these segments will allow you to work more efficiently and accurately when making adjustments or repairs.
Begin by identifying the primary functional groups. The trigger mechanism, feeding system, and pressure chamber are the starting points of any repair. Understanding how these components work together will prevent mishandling during disassembly. Take extra caution when working with the power source and pneumatic connections–ensure you have a reliable air compressor and check all seals before reconnecting.
Next, examine the fastening and alignment features. Misalignment is a common issue that leads to jamming or inconsistent operation. Pay special attention to the positioning of internal gears and springs. If the firing system isn’t responding correctly, a thorough inspection of the recoil springs and air valve may reveal the underlying issue.
Finally, keep in mind the exact specifications when replacing any worn-out element. Opt for high-quality replacements that match the original configuration. Using parts of incompatible design can lead to poor performance and even damage to the overall system.
Essential Guide for Tool Component Breakdown
For efficient maintenance, ensure you have a clear visual reference of all individual elements of the tool. Identifying the specific components that need attention or replacement can save time and enhance the tool’s performance.
Start by examining the trigger assembly, which is a critical area for ensuring the smooth operation of the device. It’s crucial to maintain the spring-loaded mechanism within this section for proper functioning. The piston housing should be inspected regularly, especially the seal and O-ring, as these components are prone to wear over time.
The drive mechanism must be kept clean and free from debris. The piston is especially vulnerable to damage due to excessive force or improper use, so regular lubrication is necessary for long-term efficiency. Additionally, the nosepiece can become loose, leading to misfires or reduced accuracy, so check the screws and ensure they are tight.
It’s also important to pay attention to the safety mechanism, which prevents unintentional firing. Over time, the safety lock can become less responsive, so testing it before use is highly recommended. Finally, ensure that the air supply filter is clear of any obstructions to maintain optimal power and efficiency.
Having a precise breakdown of each part allows for quicker identification of potential issues and ensures the tool functions at its best for longer periods.
Identifying Key Components of the Senco Model L Pneumatic Tool
To effectively repair or maintain your pneumatic tool, first focus on the air intake valve, which controls the airflow into the mechanism. Ensure it’s free of debris and properly sealed to prevent leaks. The trigger assembly is crucial for proper operation–check for wear and ensure the spring tension is correct for responsive action. The piston chamber, often overlooked, must be clean and lubricated to maintain consistent firing power.
Next, examine the exhaust system, ensuring no blockages that could affect the tool’s efficiency. The front housing holds the internal mechanism and is essential for the tool’s alignment; inspect it for any cracks or loose fittings. The magazine guide and loading spring ensure smooth nail or fastener feeding–inspect for alignment and replace any worn-out parts that might cause jamming.
Finally, inspect the O-rings and seals. Any signs of damage or excessive wear on these can lead to air leakage, reducing performance. Regular maintenance of these components will extend the life and effectiveness of your tool.
How to Replace Worn-Out Components in the Pneumatic Tool
To maintain peak performance, it’s crucial to replace any worn components in your pneumatic tool promptly. Here’s how to do it step-by-step:
- Disassemble the Tool: Start by safely disconnecting the tool from its power source. Remove the nosepiece and any fasteners securing the body.
- Inspect and Identify the Worn-Out Parts: Look for components showing signs of wear such as seals, gaskets, or O-rings. Pay close attention to any air leaks or reduced efficiency.
- Remove Damaged Components: Carefully extract the damaged components using appropriate tools. Be gentle with seals to avoid damaging the surrounding parts.
- Install New Components: Align and insert the new parts into the tool. Ensure a snug fit to prevent any air leaks or malfunctioning.
- Reassemble the Tool: Once the new components are in place, reassemble the tool in reverse order of disassembly. Tighten screws and reattach the nosepiece securely.
- Test for Proper Function: After reassembly, conduct a functional test to ensure the tool operates smoothly. Check for any unusual noises or leaks.
Regularly replacing these key elements will extend the lifespan and efficiency of your equipment, ensuring reliable performance for years to come.
Understanding the Function of Each Component in the Tool Assembly
Each individual element within the assembly plays a critical role in the overall operation of the tool. The trigger mechanism, for example, initiates the entire sequence of actions by activating the firing pin. The air inlet valve regulates the airflow to control the pressure within the system, ensuring smooth operation and preventing unnecessary strain on internal components. The piston is responsible for transferring energy to the nail-driving mechanism, enabling precise impact force. The nosepiece ensures proper alignment of fasteners, minimizing the risk of misfires or jams.
The spring mechanism within the housing ensures a consistent return motion of the piston, aiding in rapid sequential use. The safety latch prevents accidental discharge, adding a layer of protection for the user. The exhaust vent directs expelled air away from the user’s face, reducing discomfort during extended use. Additionally, the magazine assembly holds a load of fasteners, feeding them into position for each cycle and significantly enhancing efficiency.
The housing structure, typically made from durable materials, protects sensitive components from external damage, while keeping the tool balanced for ergonomic handling. Regular maintenance and understanding of these components will ensure optimal performance and extend the longevity of the equipment.