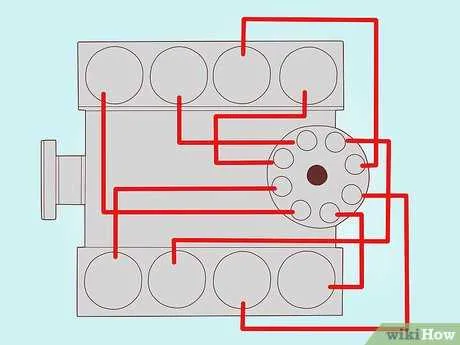
When setting up the wiring for your engine’s ignition components, ensure the proper alignment of each terminal to guarantee a reliable start-up. The setup consists of a series of well-defined connections between the central system and the terminals that transmit energy to the combustion chamber. For a fault-free operation, use high-quality, insulated wires that can handle the high voltage passing through them.
The terminals must be connected in a specific order, following manufacturer specifications for maximum efficiency. Incorrect installation may lead to poor engine performance or even prevent it from starting. It is essential to securely attach each wire to its designated contact, and check for any signs of wear or corrosion that might interfere with the signal transmission.
Double-check all connections before securing them. This will avoid potential issues such as misfires or irregular firing sequences. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can ensure consistent performance and extend the lifespan of the ignition system.
Key Tip: Always match the correct type of wire to each terminal, as specified in your engine’s manual. Not all terminals are compatible with every wire, and using the wrong combination can lead to inefficiency or damage to the system.
Wiring for Engine Ignition Components
To ensure optimal engine performance, carefully wire each electrode setup to the ignition coil as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. Align the terminal for each component according to the correct order to avoid misfiring and reduce electrical resistance. Proper attachment ensures a stable spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture efficiently.
Order of Connections: Start by connecting the first terminal of the ignition coil to the primary electrode, followed by the subsequent connections in the prescribed sequence. Each terminal should be securely fastened to avoid loose contacts that could cause misfires or weak combustion.
Key Tips: Always use a high-quality wire that can withstand engine heat and vibrations. Avoid using wires with frayed insulation, as this can lead to shorts and potential damage to the ignition system.
For engines with multiple cylinders, ensure the leads are color-coded or labeled to avoid confusion during installation. Make sure each wire is routed properly to prevent interference with moving parts.
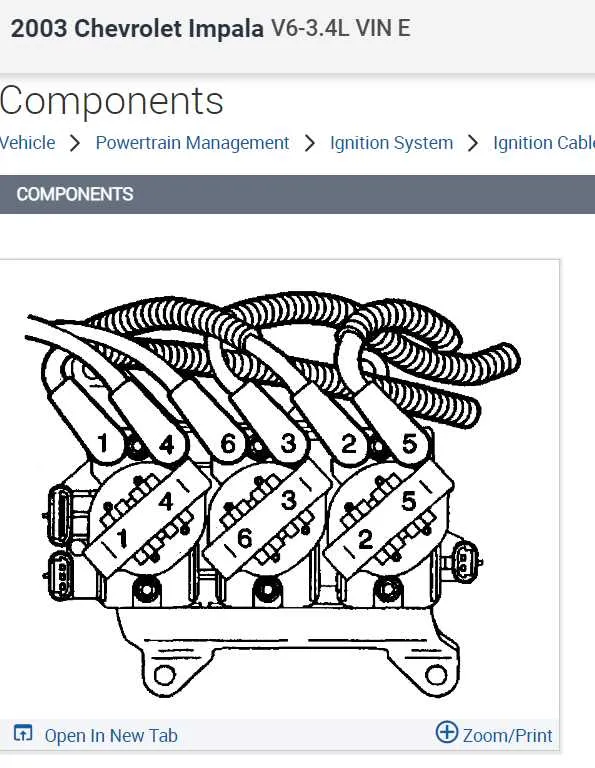
Understanding the Wiring Layout for Ignition Terminal Connections
Ensure proper alignment of the terminals by following these key steps:
- Identify the correct terminal types for each cylinder. Each terminal has a specific configuration and should only be connected to its corresponding wire.
- Verify the terminal sequence, ensuring the order matches the ignition coil’s output. Incorrect sequencing can cause misfires or engine performance issues.
- Check for corrosion or wear on each terminal. Clean or replace any damaged parts to ensure a reliable electrical contact.
When connecting the wires to the terminals:
- Firmly attach each wire to the terminal to avoid loose connections, which could lead to electrical faults.
- Avoid over-tightening, which could damage the terminal threads.
- Ensure the wire insulation does not touch any metal surfaces to prevent short circuits.
For multi-terminal systems:
- Double-check the wiring layout according to the engine’s specific model to ensure the correct terminal-to-wire matching.
- Use high-quality connectors to maintain a strong electrical connection under high temperature conditions.
Common Issues in Ignition System Components and How to Fix Them
1. Poor Contact Between Wires and Terminals: A frequent issue is insufficient contact due to corrosion or dirt. Clean terminals with a wire brush or contact cleaner to ensure good conductivity. If corrosion persists, consider replacing the affected wires or terminals.
2. Loose or Damaged Leads: Leads that are either too tight or too loose can cause misfiring. Ensure that leads are properly seated and free of visible damage. Replace any leads that are frayed or cracked to avoid weak electrical flow.
3. Insufficient Voltage: A weak signal can lead to weak combustion. Inspect the ignition coil and the wire routing for any faults. Test voltage with a multimeter to ensure that it meets manufacturer specifications. Replace faulty coils if necessary.
4. Faulty Insulation: When the insulation around wires is compromised, short circuits may occur. Carefully inspect the insulation for cuts, abrasions, or signs of wear. Replace damaged wires and consider using high-quality heat-resistant insulation for better durability.
5. Poor Grounding: Ensure that the grounding of the system is intact. A loose ground can cause electrical interference, leading to performance issues. Tighten any ground connections and check for rust or dirt around grounding points.
6. Misaligned Components: Misalignment of the terminal or contact surface can prevent efficient energy transfer. Make sure components are aligned according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Re-align or replace misaligned parts to restore optimal functionality.
Tools Needed for Proper Terminal Maintenance
Multimeter: Use a digital multimeter to check electrical continuity. This tool helps identify faulty terminals, wiring issues, or irregular voltage distribution that could hinder performance.
Wire Strippers: Essential for stripping the insulation from cables without damaging the wire underneath. Ensure you use the right gauge for the task to maintain proper conductivity.
Torque Wrench: A torque wrench ensures that the fasteners are tightened to the correct specifications. Over-tightening or under-tightening can lead to malfunction or improper contact.
Contact Cleaner: Regular cleaning of the terminals with an appropriate contact cleaner removes dirt, grease, or corrosion, ensuring a clean surface for a stable electrical connection.
Heat Shrink Tubing: Use heat shrink tubing for insulation after repair or replacement of terminals. This prevents exposure to external elements and enhances longevity.
Needle Nose Pliers: Handy for reaching tight spaces and adjusting small components without causing damage to surrounding parts.
Terminal Crimping Tool: If replacement of terminal ends is required, a crimping tool is essential to securely attach new connectors to the cables without damaging them.