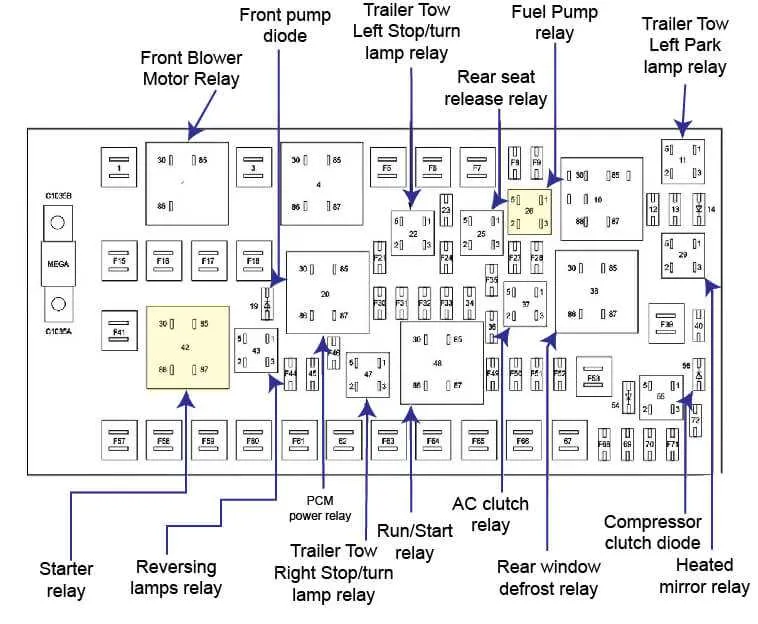
If you’re experiencing electrical issues in your 2007 model, referencing the vehicle’s component layout is essential. Understanding the positioning of relays and connectors can significantly expedite troubleshooting. The primary power distribution area is located inside the cabin, near the driver’s side, with a secondary location under the hood, adjacent to the engine bay.
Start by locating the internal fuse panel, typically on the left side of the dashboard, behind a removable cover. This is where you’ll find the majority of circuits for cabin electronics, including lights, sensors, and control units. The external distribution area, housed near the engine, manages systems related to ignition, airbags, and powertrain components.
Consulting the vehicle’s wiring map is crucial before replacing any component. It helps to ensure you’re addressing the right circuit and to prevent unnecessary damage. Always double-check the amperage ratings of the fuses and relays to match the manufacturer’s specifications.
For a quick resolution, it is recommended to use a multimeter to test the current flow and continuity of individual components. In cases where the layout is unclear, a detailed guide or electrical system map for your specific model year will be invaluable for accurate diagnostics.
07 Vehicle Electrical System Layout
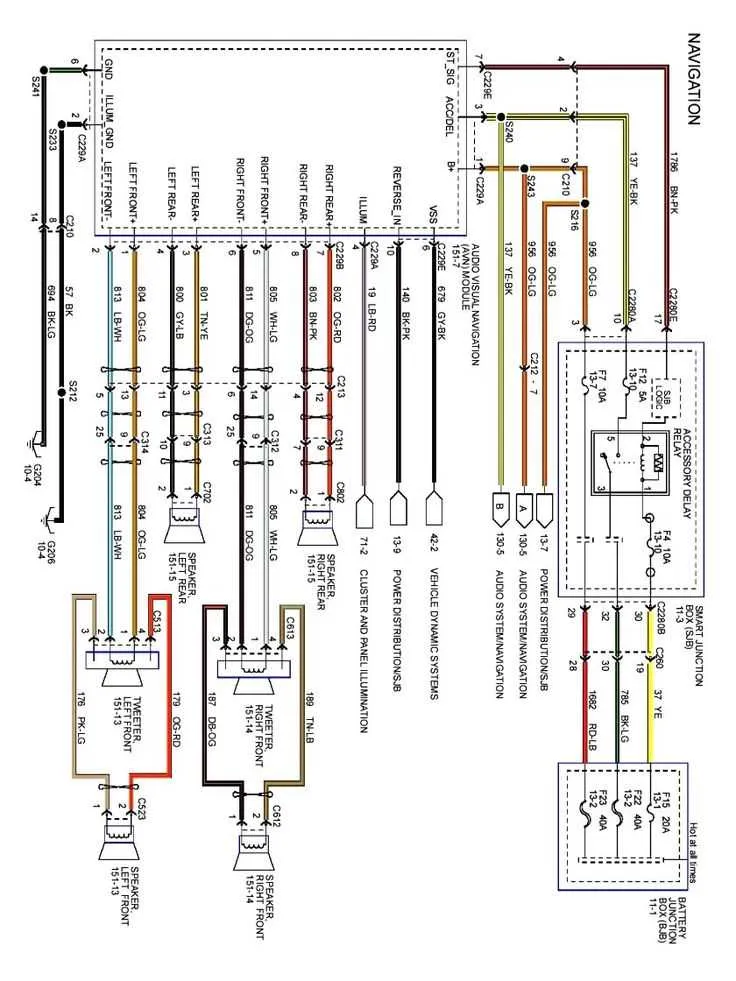
The 2007 model requires careful inspection of the electrical system layout to ensure proper connection and functionality. Locate the main control panel under the dashboard, which houses critical relays and circuits for internal and external components. On the left side of the panel, you’ll find the components that manage lights, air conditioning, and power windows. Make sure the right side is checked for connections controlling wipers, radio, and HVAC systems.
For troubleshooting, begin with the central section for ignition and engine-related connections. If a circuit failure is noted, refer to the label on the rear of the access cover, where you’ll find a quick reference for each numbered slot. For better accessibility, it’s advised to remove the cover carefully and inspect the connectors, as loose or damaged pins can lead to malfunction.
Ensure the battery and alternator connections are secured to avoid disruptions in power flow. The secondary fuse panel in the engine compartment provides protection for external electrical elements like headlights and indicators. It’s crucial to verify that all components are correctly rated for the corresponding wires, avoiding overloading, which could cause damage.
When replacing any damaged component, use a multimeter to check for continuity in the affected circuits. This step will confirm whether the issue is isolated to a single relay or more widespread in the system. Keep a set of spare relays and connectors on hand, as these parts are often the first to fail.
Understanding the Location of the Electrical Component Panels in the 2007 Model
To locate the electrical component panels in the 2007 model, follow these specific steps:
- The first panel is located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Look beneath the steering wheel, near the footwell. It’s easily accessible by removing the lower panel cover.
- The second unit is in the engine compartment. Open the hood, and you will find it near the battery, positioned on the driver’s side. It’s protected by a plastic cover, which needs to be lifted to gain access.
- A third location can be found in the rear of the cabin, behind the seat area. This unit serves specific rear functions and is housed under a small access panel.
These locations allow quick identification and access for any necessary repairs or part replacements. Each unit is labeled with the specific circuits it controls, making it easier to troubleshoot electrical issues.
How to Identify and Replace Fuses in the 2007 Ford Fusion Fuse Box
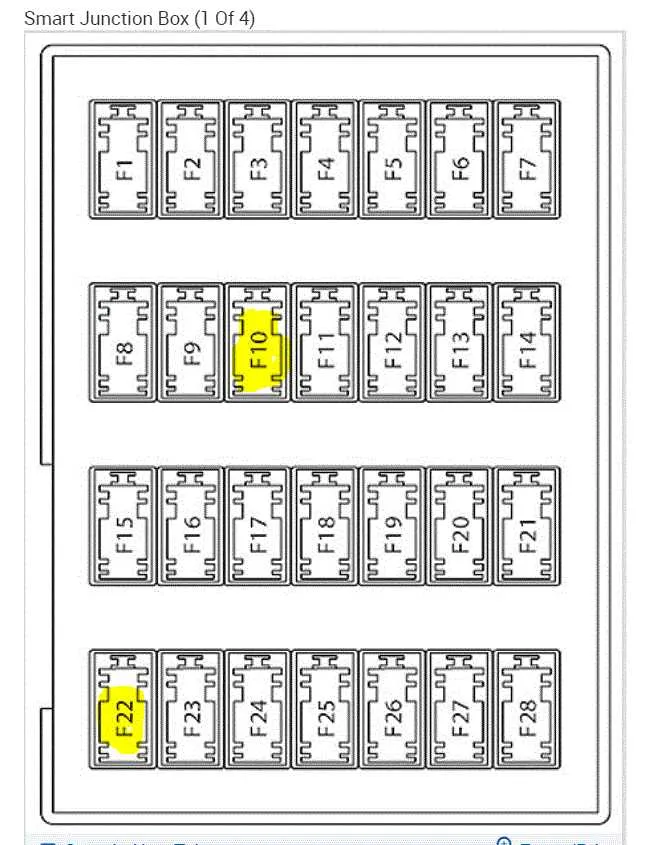
To identify the correct fuse to replace, refer to the labeling on the lid of the electrical panel. The diagram will indicate which fuse controls each system, such as lights, power windows, or the radio. It’s essential to match the amperage rating of the damaged component with the new part. For example, a 20-amp fuse should be replaced with another 20-amp fuse to prevent further issues.
Before starting, turn off the ignition and disconnect the vehicle’s battery to avoid accidental shorts. Using a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers, carefully remove the faulty part. Check the metal strip inside–if it’s broken, this confirms the fuse needs replacement.
Insert the new part into the same slot, ensuring it fits securely. After replacing, reconnect the battery and test the electrical components to verify the repair is successful. Always keep extra fuses of different amperages in the vehicle for emergency replacements.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues in the 2007 Model

Start by checking the 10A and 20A circuits for dashboard lights, as these are often the first to fail when there’s an issue. The 10A circuit located in the cabin can be found behind the glove compartment. Use a multimeter to test if the current is reaching the designated pins. If there’s no power, replace the faulty component with an equivalent-rated one.
If your headlights or taillights fail, focus on the 15A section located near the engine compartment. This part is directly linked to exterior lighting. A blown section here can easily cause both front and rear lights to malfunction simultaneously. Again, a multimeter will confirm the absence of voltage. If power is missing, inspect the connectors for corrosion or loose connections before replacing the part.
For issues involving the air conditioning or heater, check the 40A section that controls the HVAC system. Over time, components like the compressor can overload, resulting in a malfunction. Inspect the system’s relay and connections for any signs of wear or physical damage. If the issue is persistent after replacing the relay, further inspection of the internal circuits might be necessary.
Another common problem is the power windows not responding. This is often caused by a malfunction in the 30A section in the interior section of the car. Check for continuity across the connection terminals. If there’s a break in the path, replace the damaged component. Be sure to also test the window switch for proper function.
If the car’s accessories (radio, seat heaters) are unresponsive, focus on the 5A or 10A circuits that provide power to these components. Faulty wiring or a break in the circuit could cause intermittent power loss. After confirming no current is reaching the component, replace the damaged section and reconnect any loose wiring.
Lastly, a general loss of electrical power to the vehicle might indicate a larger issue within the main power distribution system. Inspect the main relay and ensure all cables leading from the battery are intact. Also, double-check for any potential shorts in the wiring harness.