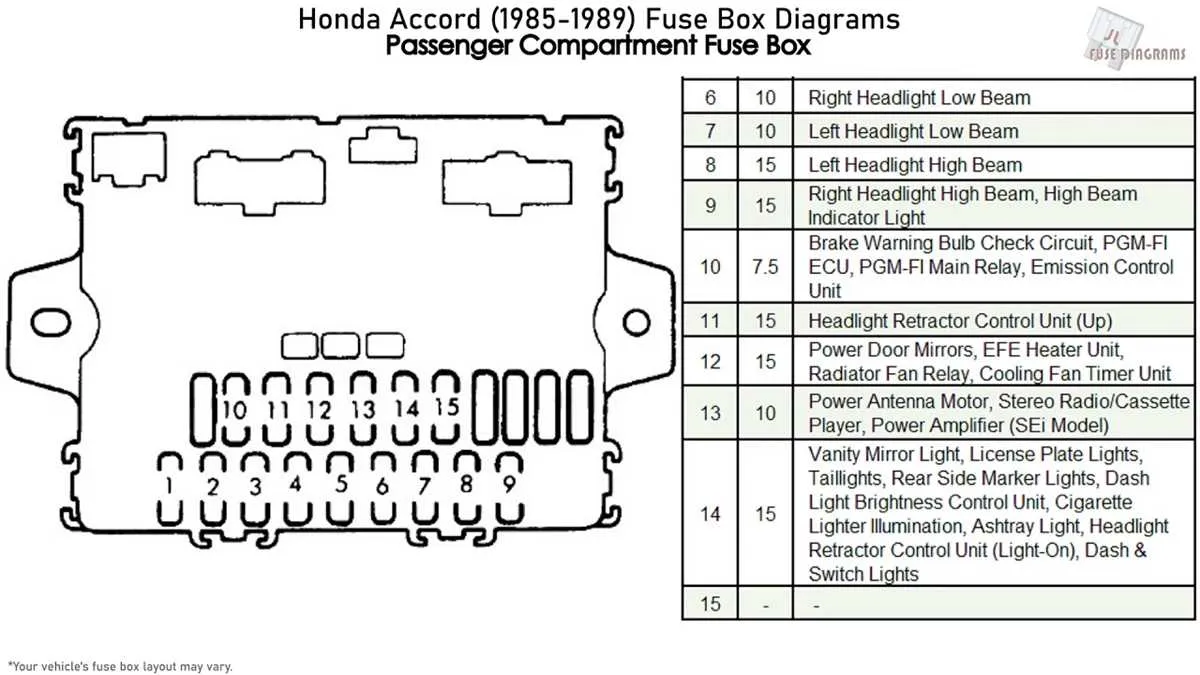
If you are experiencing issues with the electrical system in your vehicle, it’s crucial to locate the main component panel where all circuits are connected. This panel, typically positioned under the dashboard or near the engine compartment, houses all the critical fuses and relays that manage your car’s electrical functions.
Start by identifying the location of the main electrical panel. Once located, you can pinpoint which relays or fuses are associated with specific systems, such as lights, air conditioning, or the ignition. Referencing the layout guide will help ensure that each fuse is correctly assigned and that no errors are made when replacing or inspecting them.
Important: When replacing fuses, always use the correct amperage rating. Overcurrent protection is vital to prevent further damage to sensitive electrical components. Check that the new fuse matches the specifications provided in the vehicle’s manual or in the system layout.
Pro Tip: It’s always a good idea to keep a spare set of fuses in your car. If a particular system suddenly stops working, you can quickly inspect the panel, determine the faulty fuse, and replace it on the spot.
Electrical System Layout for the 1998 Vehicle
For optimal functionality, refer to the wiring arrangement in the main electrical compartment. Each circuit has its designated slot, ensuring that the system remains organized and accessible for troubleshooting. When inspecting the components, make sure to check the primary power terminals located near the battery area.
The interior section contains a set of smaller components that are protected by separate relays. For correct identification, always match the relay number with the corresponding component in the dashboard area. Pay special attention to fuses related to critical systems such as lighting, air conditioning, and the engine control unit. These are typically located in the rear panel section.
If an electrical malfunction occurs, it is recommended to start by visually inspecting each individual unit for signs of wear or corrosion. The main distribution section near the driver’s side provides easy access for maintenance tasks, while the auxiliary units are usually in sealed compartments to prevent moisture ingress.
Should any of the protective devices need replacing, ensure to use the correct rating specified for each slot to avoid electrical overload. Additionally, be sure to consult the vehicle’s manual for any model-specific variances in the wiring system.
Understanding the Electrical Layout for the 1998 Honda Accord
Start by identifying the location of the main power distribution panel, typically found beneath the dashboard or near the engine bay. The central unit contains numerous relays and terminals that manage various systems within the vehicle.
Refer to the specific labels for each terminal within the unit. They provide guidance on the function of each slot. Some of the common circuits to look for include the ignition, headlights, wipers, and air conditioning. Each system will have its designated position to avoid confusion during maintenance or troubleshooting.
If a particular electrical component fails to operate, the first step is to check its respective terminal for signs of a blown connector or loose connections. Each terminal should be clean, free from corrosion, and firmly connected. If unsure, refer to the vehicle manual for proper identification of components linked to each relay or terminal.
Be mindful that certain slots may have higher amperage ratings to support heavy-duty components, such as the engine control module or anti-lock braking system. It’s crucial to never exceed these ratings by installing incorrect fuses. Doing so can lead to system failure or even cause damage to sensitive circuits.
After replacing a faulty unit, always double-check that the terminal is securely fixed and that the new relay or fuse matches the recommended specifications. This will ensure the vehicle remains fully operational without any risk of electrical faults.
Identifying Common Electrical Components and Their Functions
To effectively troubleshoot electrical issues, it’s crucial to recognize the most common components and understand their roles within the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Ignition System – Located in the primary section of the electrical network, this component is essential for powering the vehicle’s engine start-up process. A malfunction here may prevent the car from starting.
- Headlights – Often connected to a dedicated power unit, the headlights rely on a specific relay for proper illumination. If the headlights flicker or fail to light up, this relay should be checked for functionality.
- Air Conditioning – The air conditioning system is supported by a high-amperage power supply. Problems with this system might be related to faulty connections or a blown circuit responsible for cooling control.
- Power Windows – A common issue with power window operation may result from an overloaded relay. Ensure the window control circuits are intact for smooth functionality.
- Windshield Wipers – Wiper functionality is controlled by specific units that ensure movement during rainy conditions. Issues here often result from the malfunction of a protective relay or excessive current draw.
Always refer to your vehicle’s detailed manual for exact component identification, and regularly inspect the electrical system to avoid complications. A consistent maintenance schedule can prevent costly repairs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Fuses in the 1998 Honda Accord
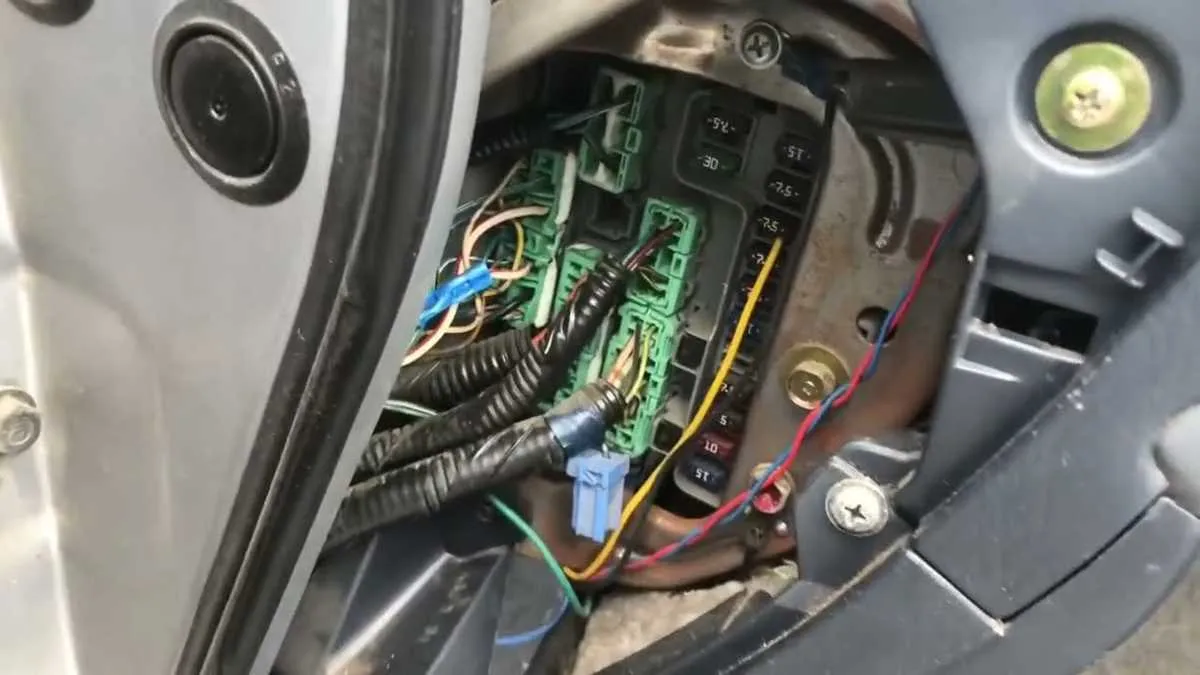

Start by turning off the ignition and removing the key. This ensures safety while working with electrical components. Locate the electrical panel under the dashboard on the driver’s side or near the engine compartment, depending on where the malfunctioning component is located.
Once the panel is visible, identify the specific fuse responsible for the malfunctioning system by referring to the guide printed inside the cover of the panel. The components are usually labeled, so make sure to locate the one matching the system needing repair.
Using a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers, carefully remove the damaged component. Be gentle to avoid damaging surrounding parts. Check the wire inside the fuse: if it’s broken or burnt, it will need to be replaced.
Select a new fuse with the same amperage as the original. It’s critical that the replacement matches the correct rating to avoid electrical issues. Insert the new component firmly into the slot, ensuring it is seated properly.
After replacing, turn on the vehicle and test the system to ensure the issue is resolved. If the new component blows quickly, there might be an underlying electrical issue requiring professional attention.
Repeat the process for any other damaged components, ensuring all are replaced with the correct amperage. Finally, close the cover of the panel and ensure it locks into place securely to prevent exposure to dust or moisture.