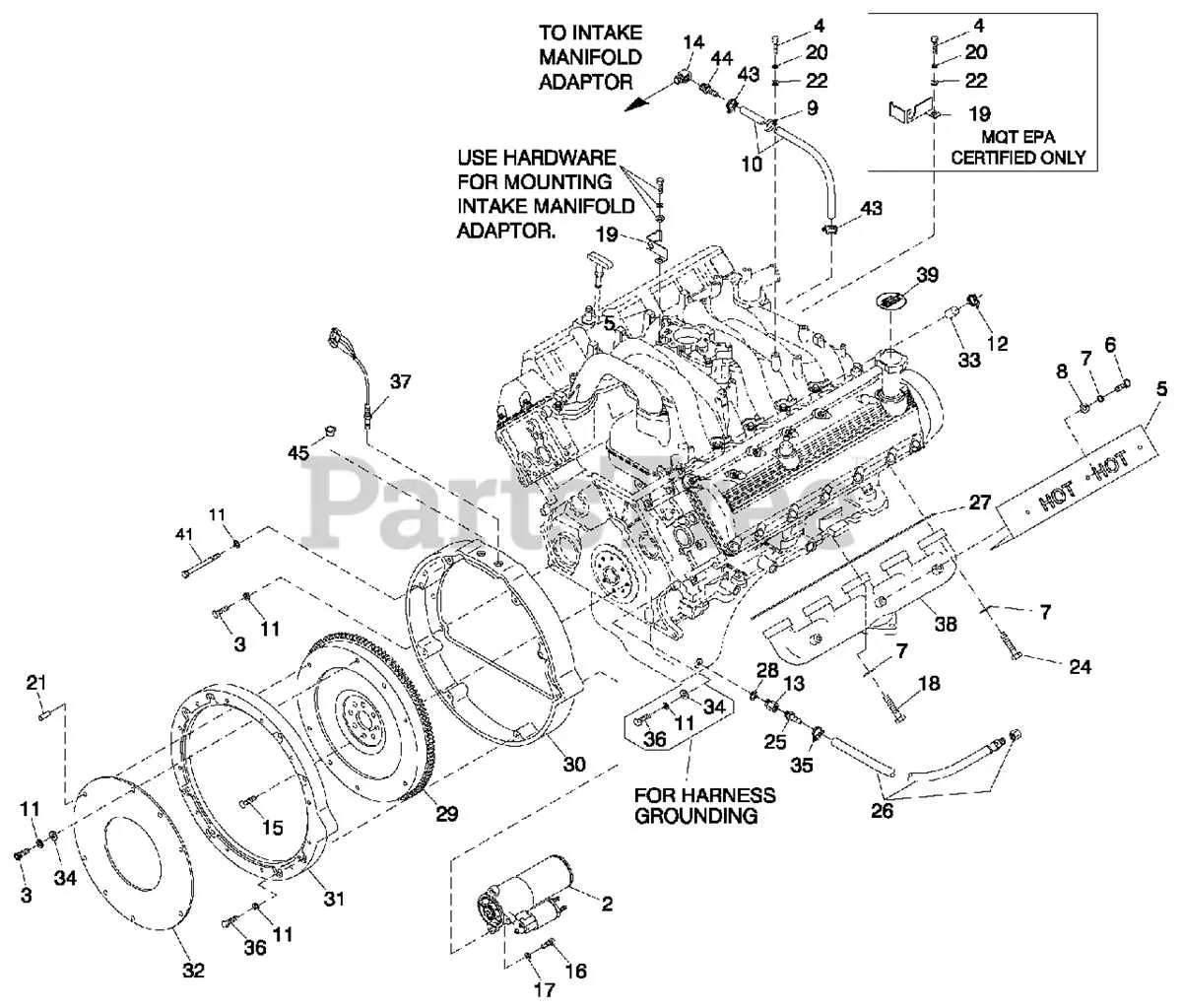
If you’re planning to overhaul or maintain your high-performance vehicle, it’s essential to understand the structure and connection of critical elements within the power unit. By familiarizing yourself with the layout of internal mechanisms, you can effectively manage repairs or upgrades. Knowing how various pieces interact ensures more accurate diagnostics and enhances longevity.
Key Areas to Focus On: The structure incorporates elements such as pistons, cylinders, camshaft, and timing mechanisms, each playing a distinct role in overall function. Prioritizing the maintenance of these parts will significantly contribute to improved efficiency and reduced wear.
Understanding Assembly Configurations: With a solid grasp of how components fit together, you can better recognize potential issues like misalignment, inefficient fuel combustion, or excessive wear on moving parts. Identifying weak points and taking preventative measures will not only optimize the system’s performance but also save on long-term repair costs.
Understanding the Key Components of a V8 Powerplant
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your V8 motor, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with its internal mechanisms. The following list includes the most vital elements, along with their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Block | Houses the cylinders and supports various engine components. |
| Crankshaft | Converts the linear motion of pistons into rotational motion. |
| Pistons | Move within cylinders to create power by compressing the air-fuel mixture. |
| Camshaft | Controls the timing of the valves’ opening and closing. |
| Valves | Regulate the intake of the air-fuel mixture and the exhaust gases’ exit. |
| Timing Chain | Synchronizes the rotation of the camshaft with the crankshaft. |
| Connecting Rods | Link the pistons to the crankshaft and transfer motion. |
| Oil Pump | Circulates lubricant throughout the motor for smooth operation. |
| Cylinder Heads | House the valves and fuel injectors, sealing the cylinders from the top. |
Understanding these core components will help you maintain, troubleshoot, and modify your powertrain with greater accuracy. Regular inspections and upkeep will keep your motor running smoothly for years.
Understanding the Key Components of the 5.7 Hemi Engine
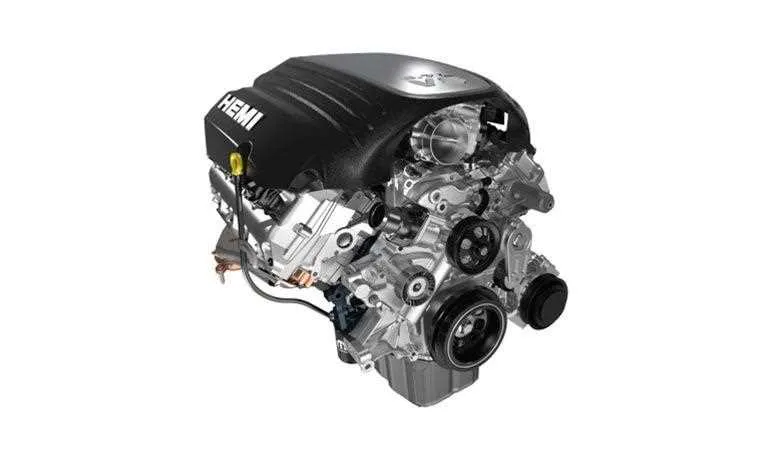

The most important elements in a high-performance V8 configuration are the cylinder heads, pistons, crankshaft, and camshaft. These elements work in tandem to generate maximum power output, ensuring efficiency and durability. The cylinders house the pistons, which are integral to compression and combustion, creating the power needed to drive the vehicle. The crankshaft, linked to the pistons via connecting rods, transforms linear motion into rotational energy, while the camshaft regulates the timing of valve operations, ensuring optimal air and fuel intake.
The ignition system is another critical aspect of performance. The coil packs ensure a precise spark at the right moment, while the fuel injectors deliver a precise amount of fuel to each cylinder, optimized for power and efficiency. Additionally, the intake manifold directs air into the combustion chambers, contributing to engine responsiveness and throttle control. Proper maintenance of these components is essential for preventing performance degradation and ensuring long-term reliability.
A properly tuned exhaust system also plays a key role in maximizing performance. The headers, exhaust pipes, and catalytic converters work together to expel gases efficiently, reducing backpressure and enhancing engine breathing, which improves overall power delivery and fuel efficiency. Without proper exhaust flow, even the best internals can struggle to perform at their peak potential.
How to Identify Each Component in the V8 Motor Layout
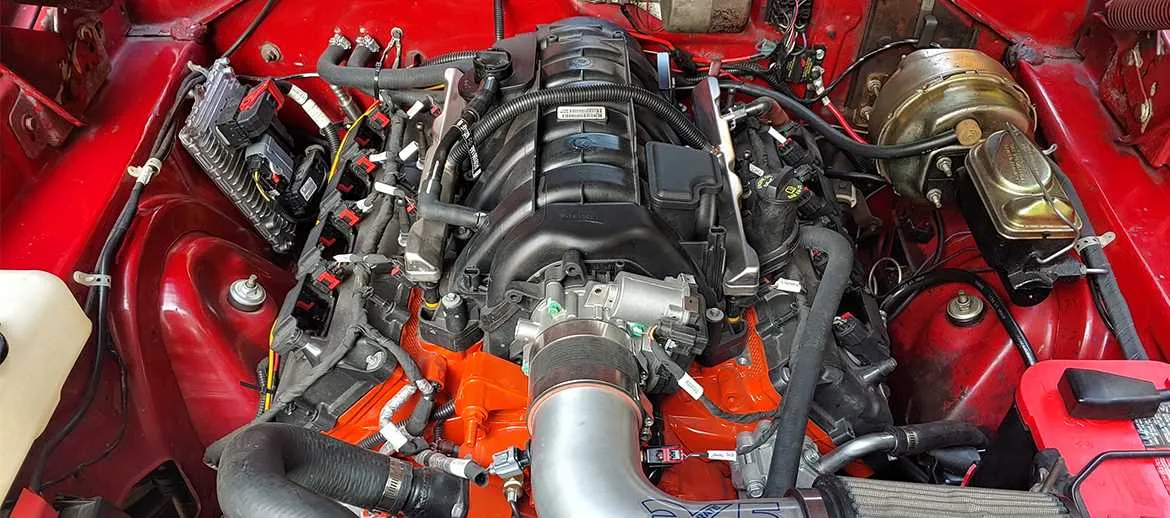

To accurately identify every component in the V8 motor system, follow these steps:
- Start with the cylinder head: This is a crucial area, housing the intake and exhaust valves. Look for the intake manifold, typically at the top of the engine block, and distinguish the exhaust valves along the side near the exhaust manifold.
- Locate the crankshaft: Found at the bottom of the assembly, it plays a central role in transferring energy from the pistons to the drive system. It connects to the flywheel on one side.
- Identify the camshaft: It is positioned above the crankshaft and is responsible for controlling the timing of the intake and exhaust valves. The camshaft is commonly located near the top of the motor block.
- Examine the timing chain or belt: This component links the camshaft and crankshaft. It’s essential for synchronizing valve operation with piston movement.
- Spot the pistons: These are found within the cylinders. Their movement is powered by combustion, and they work in conjunction with the crankshaft to produce rotational force.
- Check the oil pump: It is typically positioned on the front or side of the block. Its role is to circulate lubricating oil throughout the motor, reducing friction and cooling components.
- Fuel injectors: These are located on the intake manifold and are responsible for delivering the precise amount of fuel to each cylinder based on the engine’s requirements.
- Identify the spark plugs: Spark plugs sit in the cylinder heads and initiate the combustion process. These are easy to spot with their metallic connections running to the ignition system.
Pay attention to these elements as they are essential in understanding the layout and function of the motor system. Each component plays a vital role in performance and efficiency.
Common Issues and Repairs for 5.7 Hemi Engine Parts

When addressing the common failures in this powertrain, the first thing to check is the ignition system. Misfires are often caused by faulty spark plugs or coils. Replacing the spark plugs every 30,000 miles can prevent ignition issues. If you notice engine hesitation or rough idle, inspect the spark plug wires for wear or corrosion.
Another frequent concern is oil consumption. This can be linked to faulty valve seals, which are prone to wear over time. Replacing the seals will significantly reduce the amount of oil lost during operation. It’s also advisable to perform regular oil changes with the recommended oil grade to maintain optimal lubrication and prevent internal friction.
Engine overheating is often caused by a malfunctioning cooling system. A leaking radiator or worn-out thermostat can reduce cooling efficiency. Always check the coolant level and ensure there are no leaks around the hoses or radiator. If overheating persists, consider replacing the thermostat and checking for blockages within the cooling system.
The timing chain is another crucial component. If you hear rattling noises coming from the front of the motor, this could indicate wear in the chain or tensioner. If left unchecked, this can lead to timing issues that can damage other components. Regular inspection and timely replacement of the chain or tensioner will avoid major damage.
Finally, intake manifold leaks are a common problem, especially around the gasket. This can cause a rough idle and poor fuel efficiency. Replace the gasket promptly if you notice any leaks or if there is a decrease in engine performance. Ensuring that all connections are properly sealed will also help maintain consistent air and fuel mixtures.