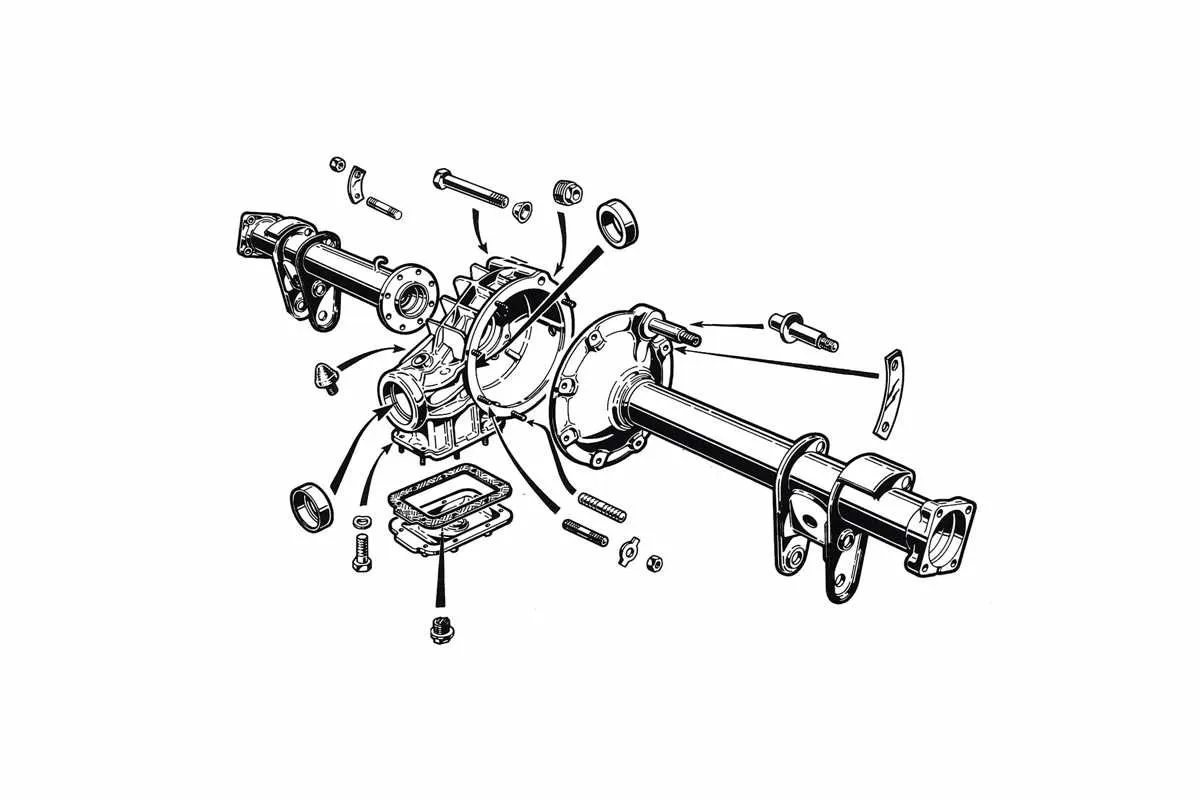
For anyone working with or repairing vehicles, a clear understanding of the suspension layout is essential. This section focuses on the key structural elements that contribute to the stability and handling of a vehicle. Begin by identifying the main structural elements that transfer force between the wheels and the car body.
The supporting shaft, which connects to the powertrain, serves as the central component in providing rotational force. It’s crucial to ensure that it is properly aligned and free from wear, as any distortion can lead to poor performance or even failure.
Next, the connecting mechanisms like bearings and mounts are vital in securing the main structure and allowing for smooth rotation. Regular checks for corrosion or signs of damage will prevent unwanted friction, which could impair functionality.
Additionally, the transfer unit plays a pivotal role in distributing power evenly across the system. If the power is not properly split, it can lead to uneven tire wear or difficulties in maintaining speed and control.
Understanding how each part fits together and functions is crucial for both maintenance and troubleshooting. Regular inspection and precise adjustments ensure the longevity and efficiency of the entire system.
Understanding the Structure of the Vehicle’s Drive System
For efficient operation and longevity of your vehicle, it is essential to understand the main components responsible for transmitting power to the wheels. Here’s a breakdown of key elements that make up the system transmitting motion from the power source to the wheels:
- Power Transfer Housing: Houses gears and differentials, ensuring smooth distribution of torque from the transmission to the wheels.
- Drive Shaft: Transfers rotational power from the engine or transmission to the final drive gears, enabling motion.
- Final Drive Mechanism: A set of gears that adjusts the rotational speed, ensuring the wheels rotate at appropriate speeds relative to the engine.
- Wheel Hubs: Connect the wheel assembly to the frame, allowing for rotational motion and stability of the vehicle.
Regular maintenance of these parts is crucial for optimal performance. Ensure that fluid levels are checked and that components are free of wear or damage to avoid costly repairs.
Key Components of a Rear Assembly
Ensure the housing is properly sealed to prevent contamination and damage to internal parts. It provides structural integrity and supports other components. The shaft transmits rotational force from the engine, so regular inspection for wear and lubrication is essential.
Check the bearings regularly. They reduce friction and are crucial for smooth operation. If they show signs of wear, replace them promptly to avoid further damage to surrounding components.
The differential distributes power evenly to the wheels. When servicing it, check for any signs of fluid leaks or unusual noises. Insufficient lubrication can lead to overheating and eventual failure.
Inspect the gears for any signs of wear or cracking. Proper alignment and adequate lubrication prevent early failure. Always use the manufacturer-recommended gear oil for best performance.
The brake components should also be checked regularly. The brake rotors, pads, and calipers must be in good working order to ensure the vehicle stops safely. Any signs of uneven wear or corrosion should be addressed immediately.
Finally, the support links and suspension arms play a critical role in maintaining stability. Ensure these components are tight and free from any damage that could compromise vehicle control.
How to Read a Rear Suspension Layout
Start by identifying the key components: the housing, differential, gears, and shafts. The housing is usually represented as a large rectangular or oval shape. Inside, the differential, often marked with a ‘D,’ is crucial for power distribution. The gears are shown as small circles or teeth, and shafts may be indicated by straight lines connecting these parts.
Focus on connections: Lines indicate how components are linked, either mechanically or via fluid connections. Each line represents either a physical shaft or hydraulic line depending on the system. The arrowheads on these lines indicate direction or flow.
Understand the movement: Look for labels or annotations detailing rotational direction. This is essential to understand how the force is transmitted from the engine to the wheels. Pay attention to symbols indicating load-bearing components like bearings and bushings–they’re often marked with a circle or oval around the part name.
Look for orientation: Ensure you’re interpreting the layout in the correct position. A common mistake is flipping the diagram upside down, leading to confusion in understanding how torque is transferred. Some layouts will have specific references to which side is ‘front’ or ‘back’ in the system.
Lastly, check for any maintenance symbols or notes that highlight parts requiring lubrication, cleaning, or frequent inspection. These details often appear in smaller text or specific icons near the components. Understanding these helps in proactive system maintenance.
Common Issues in Rear Suspension Systems
Check for unusual noises when turning, as this can indicate worn bearings or damaged seals. Addressing these early can prevent further damage to internal components. If you notice vibration or instability while driving, inspect the connecting joints for wear or misalignment. These issues often lead to uneven tire wear, which should be corrected immediately to ensure smooth performance.
Leakage of lubricants from the differential housing is another common concern. If you spot any fluid spots, replace the seals or gaskets promptly to avoid contamination and operational failures. Pay attention to abnormal tire wear patterns, such as scalloping or excessive tread wear on one side, which typically points to misalignment or suspension issues that need realignment.
Listen for grinding noises or lack of responsiveness when shifting gears. This might indicate issues with the differential gears or worn drive shafts, which could eventually lead to failure. Inspect the suspension bushings and ensure they are not cracked or deteriorating, as this can significantly impact vehicle handling and comfort.
Frequent maintenance and timely replacement of worn components can significantly extend the lifespan of your vehicle’s rear suspension system. Regular inspections are essential to avoid costly repairs and ensure optimal functionality.