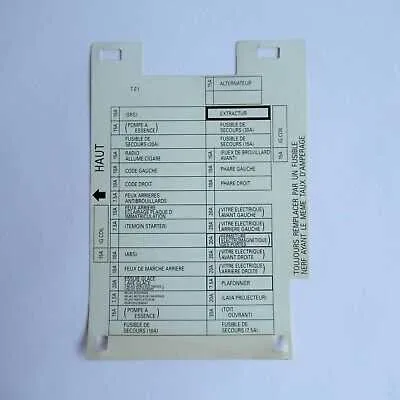
If you’re facing electrical issues with your car, a detailed map of its power distribution system can save you time and money. Identifying the correct circuits is crucial for efficient troubleshooting. The essential components for managing various electrical functions are located in the main control panel of the vehicle, often under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
Ensure you locate the proper layout to avoid confusion when diagnosing or replacing any malfunctioning parts. The layout provides a clear guide for each individual component’s location, making it easier to isolate the problem and perform the necessary fixes. Pay attention to the exact position of relays, fuses, and connectors to streamline your work.
Always disconnect the battery before inspecting any electrical components to prevent accidents or damage. A map will typically categorize each electrical component by function–such as lights, climate control, or entertainment systems–which is essential when replacing any malfunctioning part.
For an accurate reference, check your vehicle’s official maintenance guide, which will provide the exact configuration and the ratings for each connection. This ensures you’re using the correct amperage and components, reducing the likelihood of further electrical problems.
Fuse Layout and Locations for 2009 Vehicle

For optimal functionality, ensure that each electrical component in your vehicle is powered correctly. The main power distribution is located in the engine compartment and beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. The under-hood panel controls high-power components like the headlights and the ignition system, while the cabin unit manages systems such as interior lights, radio, and air conditioning.
In the engine compartment, you’ll find a primary unit which houses large amperage fuses for critical systems. For example, the cooling fan, alternator, and fuel pump rely on dedicated circuits. If these components are malfunctioning, check the corresponding fuses first.
The in-cabin unit is more focused on user-interface and comfort systems. Here, you’ll encounter fuses responsible for non-essential systems like seat heaters, dashboard lights, and accessory sockets. Pay special attention to the labeling on each fuse to avoid misdiagnosis of problems.
Make sure to reference the fuse chart located on the cover of each panel. It’s crucial to replace any blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating. Over-amperage can cause further damage, while an under-powered fuse might not protect the circuit effectively.
Common causes of fuse failure include short circuits or overloading of electrical components. Regular inspection of both fuse panels can help prevent costly repairs and ensure your vehicle remains in top condition.
Understanding the Main Electrical Layout in the 2009 Vehicle
To effectively troubleshoot electrical issues, familiarize yourself with the primary power distribution unit found near the driver’s side of the engine compartment. This panel contains critical components for various vehicle functions. Always begin by identifying the main connections for systems like the ignition, air conditioning, and lighting.
For accurate identification, note that each slot is labeled with numbers and letters, often corresponding to specific functions. Refer to the manual for exact identification of each component. Ensure to follow safety protocols when inspecting or replacing any units within the setup, as improper handling can cause system malfunctions.
Pay attention to the fuses linked to essential systems, as some are more sensitive to fluctuations. A common issue could involve the blower motor or headlights, both of which are directly linked to specific sections in the main power unit. The labels can guide you to quickly isolate problems related to these components.
Always test the connections after replacing any part of the setup. Regular checks will help identify wear and tear over time, preventing unexpected failures during operation.
How to Locate and Identify Fuses in the Interior Fuse Box
To find the electrical components in the cabin area of the vehicle, follow these steps:
- Start by opening the driver’s side door.
- Locate the panel on the lower part of the dashboard, just beneath the steering wheel. It is usually on the left side.
- Remove the panel cover by pulling it out gently. The cover may have clips or screws that need to be undone before removal.
Once the cover is removed, you’ll see a row of small rectangular components. Each component controls different systems, such as lights, entertainment, or power windows. Here’s how to identify them:
- Check the label or diagram inside the panel cover for a quick reference guide to each component’s function.
- Each element will be numbered and sometimes color-coded. Compare the numbers with the owner’s manual for precise identification.
- Use a plastic fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers to remove a component if necessary for inspection or replacement.
For safety, always ensure the ignition is off before handling any components. If the system doesn’t work after replacing a component, check the connections and re-verify the part number to ensure compatibility.
Common Electrical Issues and Replacement Tips
If you encounter a malfunction in your car’s electrical system, the first step is to inspect the relevant components for blown circuits. These can cause issues like inoperable lights, malfunctioning dashboard indicators, or non-functioning accessories.
Start by locating the fuse panel and checking each component. Ensure the ignition is turned off before you begin. Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the individual fuses, or visually inspect them for any breaks in the filament.
For replacements, make sure to use the correct amperage rating to prevent damage to the wiring or other parts of the system. Always opt for high-quality replacements to ensure longevity. If you replace a fuse and the issue persists, it’s likely that the electrical component or wiring is faulty and requires further inspection.
When dealing with the power distribution, pay attention to the relay components as well. Faulty relays can sometimes appear like a blown fuse but require a different approach for repair. If you experience recurring issues with specific circuits, it may be worth inspecting the ground connections as well.
Lastly, ensure that the fuse panel itself is in good condition. Rust or corrosion on the terminals can cause poor connectivity, leading to electrical failures. Clean the terminals with a non-corrosive cleaner and ensure a secure fit of the new fuses to avoid future problems.