For any car owner or mechanic, understanding the location and configuration of the electrical components is crucial. If you’re experiencing issues with your vehicle’s electrical system, first check the main panel that controls power distribution. This central unit ensures that each circuit is properly connected and safeguarded from overloads.
Locate the main panel under the dashboard or within the engine compartment. Refer to your car’s manual to identify the specific location, as this may vary depending on the model. It’s essential to regularly inspect the fuses and relays inside this unit, as a malfunction in these components can cause critical system failures.
Ensure safety before working on any electrical components. Always disconnect the battery to avoid accidental short circuits or electric shocks. Afterward, visually inspect each section, looking for any burnt or damaged elements. If you’re unsure about any part, it’s advisable to consult a professional technician to avoid causing further issues.
For those looking to repair or replace individual fuses, make sure to use the correct ratings. Mismatched fuses can lead to further electrical damage or system malfunctions. Always use the recommended fuse types and check for any signs of wear or corrosion before proceeding with replacements.
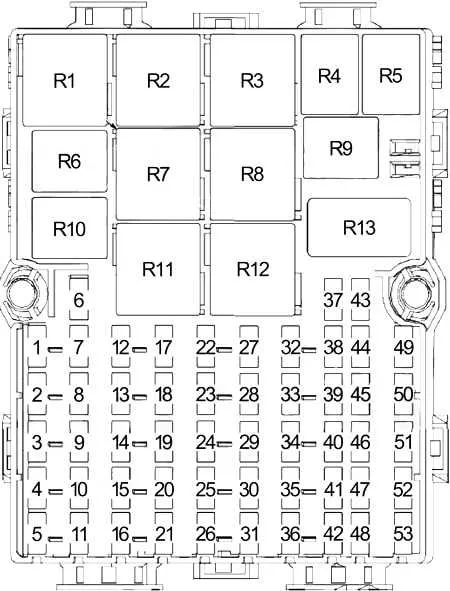
Electrical Circuit Layout for the Vehicle
For optimal maintenance of your car’s electrical system, locate the central power distribution unit in the engine bay and cabin. It contains the relays and connections essential for the operation of various components such as lights, wipers, and climate control systems. Each slot in the unit corresponds to a specific function, ensuring that power flows correctly to individual parts.
Check the lid for a label or printed chart indicating which component each slot controls. If it’s worn or unreadable, use the vehicle’s manual to cross-reference the functions of the listed relays and circuits. The engine compartment unit typically handles higher-voltage components like the alternator and headlights, while the cabin unit focuses on lower-power systems such as radio and air conditioning.
When replacing any circuit elements, always verify the current rating and the correct placement of the new part. Incorrect installation can lead to circuit overloads or short circuits, which may damage sensitive electronic systems. For troubleshooting, inspect the connectors for corrosion or wear, especially in high-humidity environments.
In case of a malfunction, start by checking the relevant relays or fuses in both locations. If necessary, use a multimeter to test the continuity of the circuits or ensure the proper voltage is being delivered to the components. Always replace any faulty part with a component that meets the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent further electrical issues.
Understanding the Location of the Electrical Component Panels
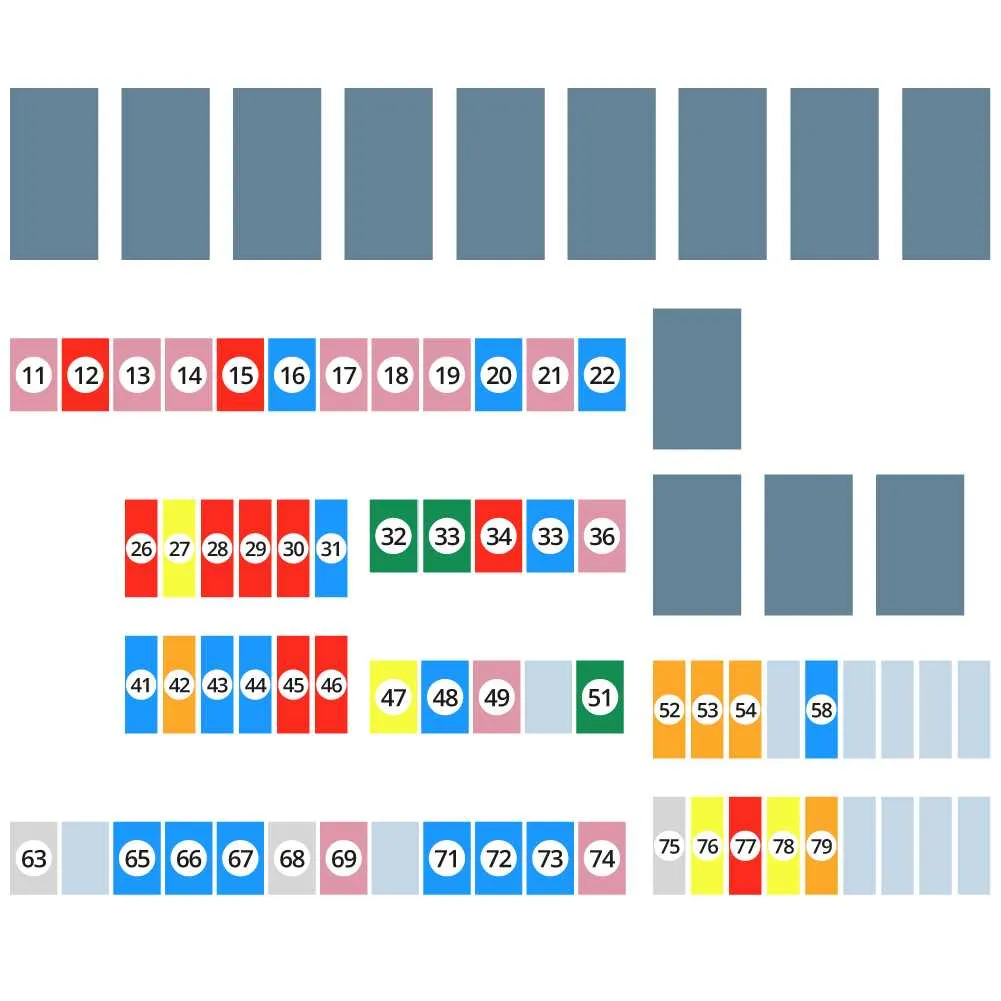
For quick access to the vehicle’s electrical circuits, locate the first panel behind the glove compartment. You’ll need to remove the compartment itself to reveal the unit. The second panel is placed underneath the dashboard, on the driver’s side, near the left footwell. Both are critical for diagnosing electrical issues, ensuring proper circuit functionality.
Another essential location is under the hood, near the engine bay. This external unit is responsible for handling higher voltage components, like the alternator and main power relay. It’s protected by a plastic cover that must be removed for inspection or maintenance.
Make sure to check these locations before starting any repair work. Identifying the correct panel can prevent unnecessary disassembly and ensure a quicker solution to any electrical problem.
How to Identify and Replace Blown Fuses in Your Vehicle
When electrical components stop functioning properly, the first thing to check is whether a protective link has been blown. Here’s how to identify and replace them:
- Locate the electrical panel: The protective links are housed in a central location within the cabin and engine area. Refer to the vehicle manual for precise locations.
- Identify a blown component: A blown unit typically shows visible signs like a broken wire or discoloration. A multimeter can also be used to test continuity.
- Turn off the ignition: Before removing any units, ensure the ignition is off to prevent any electrical shock or further damage.
- Remove the faulty unit: Use pliers or a fuse puller to extract the defective link. Be gentle to avoid damaging the surrounding elements.
- Check amperage: Always replace with a unit of the same rating. Installing a higher or lower-rated one can lead to electrical issues or damage.
- Insert the new unit: Firmly place the replacement link in the corresponding slot, ensuring it’s securely fitted.
- Test the electrical system: After replacement, turn the ignition on and check if the components are functioning as expected.
If the problem persists after replacing the link, inspect the wiring for possible damage or consider professional assistance.
Common Electrical Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
If you experience a sudden loss of power or malfunctioning components, check the main circuit distribution panel under the dashboard or in the engine bay. Often, malfunctioning electrical systems stem from faulty relays or burnt connections. If a light or system fails to operate, it’s essential to first identify which relay or connection controls the function and inspect it carefully.
One of the most frequent causes of electrical failures is a blown connector, especially when a specific accessory or function ceases to work. To determine whether the problem is related to the connections, use a multimeter to test continuity across the affected component’s connection points. Pay attention to corrosion or burnt marks around the terminals, which indicate electrical failure. Replace or clean the damaged components as needed.
For accessories such as the radio or interior lights not working, verify the integrity of the electrical connection by checking fuses or any nearby connectors that power the affected component. If the issue persists after inspecting the connections, trace the wire back to its original power source to rule out any further electrical faults.
In cases where multiple systems stop functioning simultaneously, the issue might be linked to a central relay responsible for distributing power to several circuits. This should be examined closely, as replacing a faulty relay can often restore multiple systems to normal operation.
In case of persistent electrical irregularities, seek a professional to ensure no damage to the vehicle’s main electrical circuit has occurred, which could require more intricate repairs. It’s also recommended to periodically inspect the fuse panel for early signs of wear or loose connections that could lead to future malfunctions.