For optimal engine performance, it is crucial to follow the correct path for the serpentine belt on your vehicle. Misalignment can lead to premature wear, overheating, or failure of essential components like the alternator and power steering pump. If you’re working on a 3.6L V6 engine, make sure the belt runs through all the pulleys and tensioners in the proper order.
The first step is to identify the routing sequence, ensuring the belt runs from the crankshaft pulley, through the alternator, water pump, and power steering pump, to the tensioner and idler pulleys. The correct sequence prevents uneven wear and ensures smooth engine operation. Additionally, always check the condition of the belt for any signs of cracks, fraying, or stretching, as these can cause slipping or failure under load.
Key tip: Before installing the new belt, ensure the tensioner is properly adjusted. A loose belt will cause squealing noises and inefficient operation, while an overly tight belt can damage pulleys and bearings. Always refer to your vehicle’s manual for the precise routing and specifications to avoid errors during installation.
When replacing the serpentine belt, use a belt removal tool to relieve tension from the tensioner. After installation, rotate the crankshaft by hand to verify that the belt sits correctly in all grooves and that there are no issues with the tension or alignment.
Serpentine System Layout for 3.6L Engine
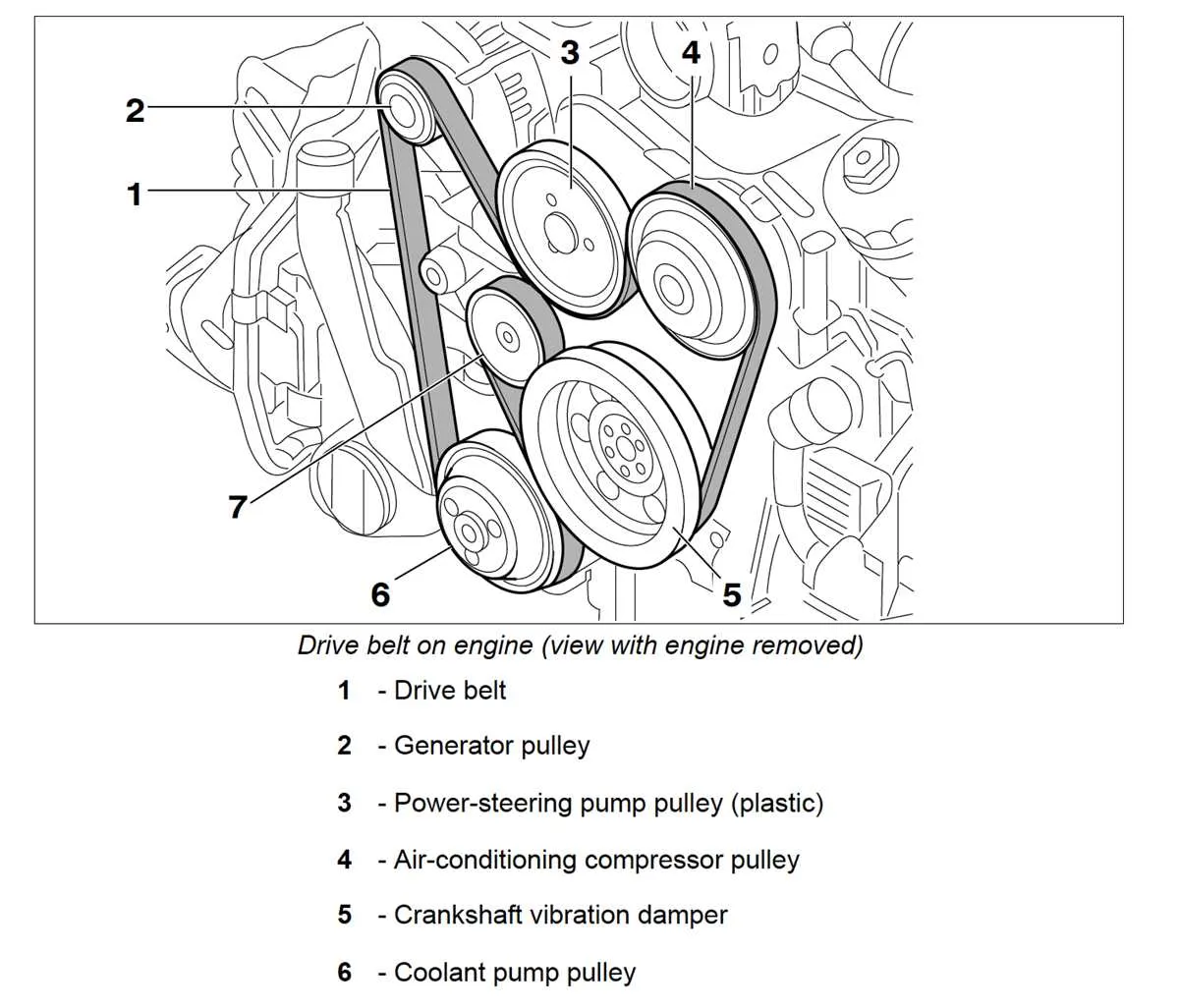
Ensure the proper routing of the serpentine system for the 3.6L engine by following this specific order: Start with the alternator, proceed to the power steering pump, then the air conditioning compressor, followed by the tensioner, and lastly, the water pump. Ensure the belt wraps around each pulley securely, with proper tension to prevent slipping.
The tensioner pulley should maintain enough pressure to keep the belt firmly in place without excessive slack. This setup is crucial for the engine’s smooth operation, preventing overheating and ensuring the alternator and other accessories function correctly.
When replacing components like the water pump or alternator, double-check the routing. An incorrect setup can lead to inefficiencies, such as power loss or damage to pulleys. If necessary, refer to the manual for any special considerations related to the engine’s specific configuration.
For optimal performance, check for signs of wear on the belt, such as cracking or fraying, and replace it when needed. A properly installed serpentine system minimizes strain on engine parts, ensuring longevity and preventing potential failures.
Understanding the Routing for the Accessory Drive System

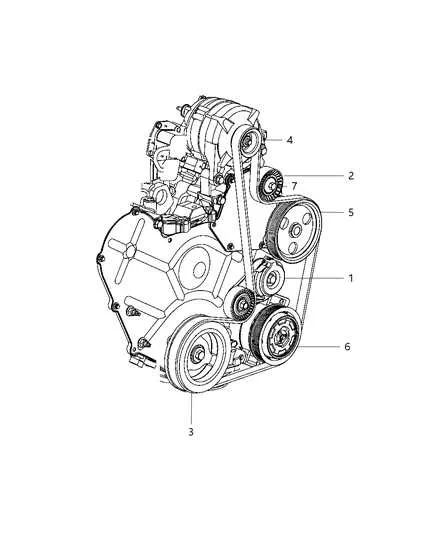
Ensure correct alignment of the components in the engine bay by following the detailed routing of the serpentine system. Misplacement can lead to wear, noise, and potential component failure.
- Start by locating the crankshaft pulley as the main anchor point. The system is routed in a clockwise direction from here.
- Position the tensioner pulley in a way that allows for optimal slack when replacing the drive components.
- Ensure the alternator is properly engaged with the main pulley, keeping in mind the correct tension to avoid undercharging.
- Inspect the water pump placement, ensuring it aligns smoothly with the routing path to avoid leakage.
- Double-check the routing path for the power steering and air conditioning pulleys to ensure smooth operation without misalignment.
Before finalizing, rotate the engine by hand to verify the alignment and ensure the system operates without interference.
Common Issues with the Serpentine Drive System
The serpentine system can fail due to wear and tear, often causing operational issues. One frequent problem is the cracking or fraying of the rubber due to prolonged exposure to heat and friction. This leads to slippage, which may cause the engine to overheat or result in power loss for accessories like the alternator or air conditioning.
Improper tension is another issue, commonly caused by a failing tensioner pulley. If the pulley becomes worn out or its spring loses tension, the drive belt will be too loose or too tight, impacting its performance. This can result in squealing noises or inconsistent operation of engine components.
Oil or coolant contamination is another common cause of premature wear. Leaks from surrounding components, like the power steering or water pump, can cause fluid to drip onto the system. The exposure to these fluids accelerates degradation, leading to cracking or deterioration of the drive components.
One more issue arises from misalignment of pulleys, often caused by worn or damaged components like the idler pulley or tensioner. Misalignment leads to uneven wear on the serpentine system, causing it to come off track or function inefficiently.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the Serpentine Belt on Your Vehicle
Start by disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery to ensure safety while working under the hood.
Locate the tensioner pulley, usually positioned near the front of the engine, and use a ratchet wrench to rotate it counterclockwise. This will relieve the pressure on the serpentine pulley system, allowing you to remove the old one.
Carefully remove the serpentine pulley from the engine compartment. Make sure to note the exact routing before removing it for proper reinstallation.
Inspect the new serpentine pulley to ensure it matches the specifications for your vehicle. Carefully route it over the pulleys according to the diagram, ensuring each groove is aligned with the pulleys.
Once the new pulley is in place, rotate the tensioner pulley again to tighten it around the new component. Ensure the new pulley is secure and fully seated in its grooves.
Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery and test the installation by running the engine briefly to check for any unusual noise or misalignment.