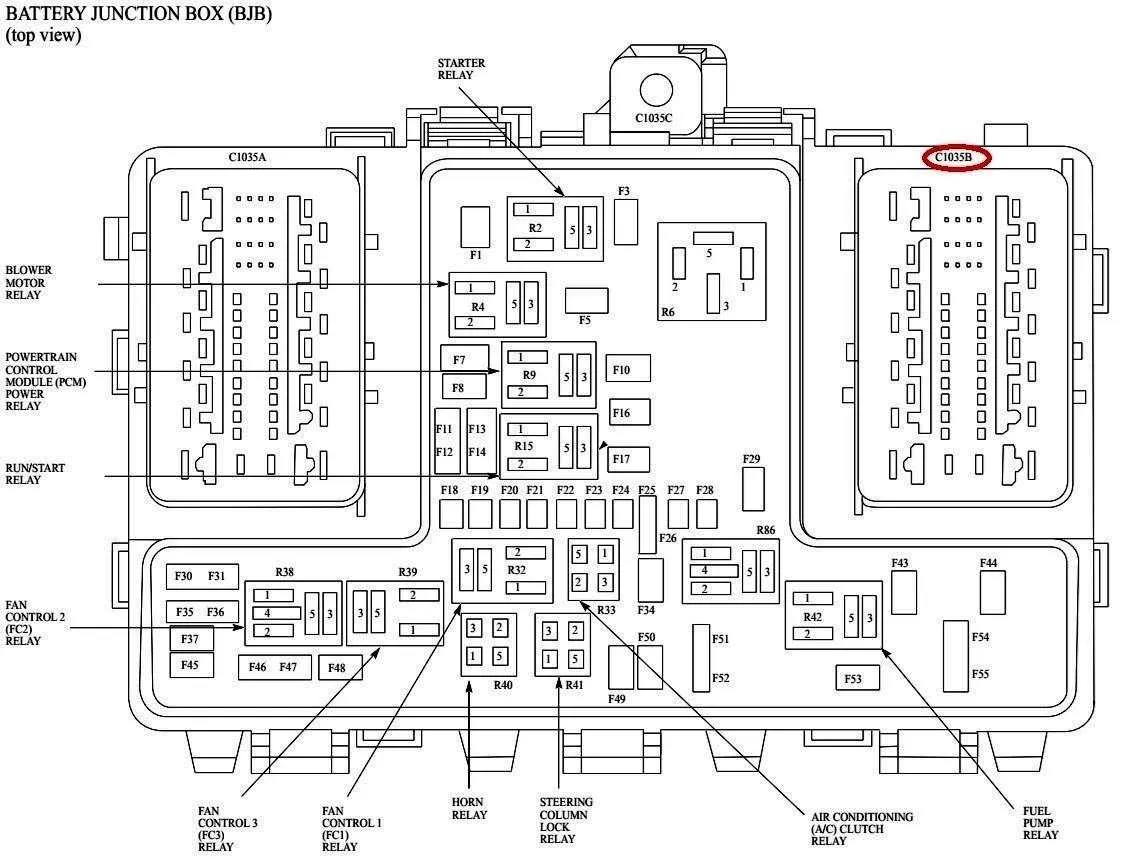
If you’re experiencing electrical issues or need to replace a blown fuse, it’s crucial to identify the correct placement of the circuits in your vehicle. Understanding the layout of electrical components can save time and prevent errors when working with the system. The system’s main components are located in different areas, with the primary unit typically found near the driver’s side or under the hood.
Key Areas to Focus On: Pay close attention to both the cabin and the engine compartment for specific modules that power essential features like lighting, HVAC, and entertainment systems. Many vehicles use a centralized unit that integrates all the critical connections, and having access to the manual can be beneficial for pinpointing each individual fuse or relay.
For safety, always disconnect the power source before starting any work. It’s also recommended to use a fuse puller for easy removal and replacement of components. Checking the electrical flow and ensuring there are no broken or malfunctioning parts will help maintain the proper functioning of the car’s electrical system.
Make sure to replace damaged components with ones of the correct amperage to avoid future malfunctions. Refer to your owner’s manual or service guide to confirm the ratings and locations for each element in the vehicle’s electrical grid.
Electrical System Layout and Component Location
For efficient troubleshooting, always refer to the specific location of components in the vehicle’s electrical setup. Locate the main control panel under the dashboard, typically on the driver’s side, which houses the critical relays and connections. Additionally, check the power distribution module located in the engine compartment for connections to the battery and critical systems such as the alternator and air conditioning system.
Each circuit is marked with a specific code, often associated with its function, such as lights, wipers, or power windows. Ensure to cross-reference each fuse number with its designated function to avoid replacing components unnecessarily. The fuse elements are generally color-coded for easy identification of their amperage and load capacity. Pay close attention to the color and size when replacing a blown component to maintain the integrity of the system.
Important: When working with electrical components, always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental short circuits. Use only the recommended fuse ratings for replacements to avoid damaging the vehicle’s electrical system. If you’re unsure of the required fuse, consult the owner’s manual or an experienced technician.
To ensure safety and prevent damage, avoid overloading the circuits. Always replace a damaged fuse with one that matches the exact specifications. If the new fuse blows repeatedly, this indicates a deeper issue in the electrical circuit, which requires professional diagnosis.
Locating the Electrical Components in Your Vehicle
Check the driver’s side of the cabin, near the dashboard, for the main electrical panel. This is typically located on the left side, below the steering wheel. In some models, a cover may need to be removed for access.
Another location to look is under the hood, where you’ll find a larger compartment containing relays and other electrical components. It’s usually situated near the battery or along the fender area.
If your vehicle has a rear compartment, check near the trunk or cargo area for additional electrical circuits, especially in larger models or those with extended features.
For vehicles with multiple configurations, consult the manual for exact positioning based on trim level or optional features, as these can influence the layout of electrical units.
Understanding the Function of Each Component
Each electrical element within the vehicle’s system plays a specific role in ensuring smooth operation. Begin by checking the owner’s manual for precise descriptions of each component and its purpose. Different relays control systems like lighting, power windows, and air conditioning. The allocation of current to various components ensures that they operate efficiently without overload.
For example, the relay for the airbag system provides crucial protection during an impact. It is important to inspect the integrity of such relays regularly. Similarly, certain relays control the functionality of the engine, including the ignition and fuel systems, making them critical for safe vehicle operation.
Over time, some of these parts may degrade or become faulty due to wear and tear or exposure to extreme conditions. If a component malfunctions, replace it promptly to maintain proper vehicle functioning. Additionally, use only recommended replacement parts to avoid potential electrical issues and preserve overall system integrity.
Each relay’s specification, such as amperage and voltage ratings, is essential for ensuring proper function. Matching these parameters ensures that the electrical flow is optimized for each part, reducing the risk of overheating or malfunction.
Common Electrical Component Issues and Solutions
When electrical components malfunction, it’s often due to issues with the protective circuits. Here are the common problems and their fixes:
- Blown Connections: If certain functions stop working, a blown component might be the cause. Inspect connections to see if any are burnt out or broken. Replace faulty ones immediately to restore functionality.
- Loose or Corroded Terminals: Over time, corrosion or loose connections can disrupt the circuit. Clean terminals with a corrosion remover or tighten connections with a proper wrench to ensure stable power flow.
- Overloaded Circuits: An overload occurs when excessive power draws are placed on one circuit. Check the power requirements of the components connected to the same circuit, and redistribute power load evenly across different circuits to prevent damage.
- Short Circuits: A short can cause sudden power cuts and even fire hazards. Inspect wires for exposed sections or frayed insulation. Replace damaged cables immediately and consider adding protective sleeves to prevent future wear.
- Incorrect or Old Components: Replacing damaged parts with incompatible or outdated models can lead to malfunctions. Always ensure that replacement components are the exact type and specifications as the original parts.
To avoid recurring issues, it’s critical to perform routine checks on electrical systems. Identifying potential problems early can save both time and money on costly repairs.