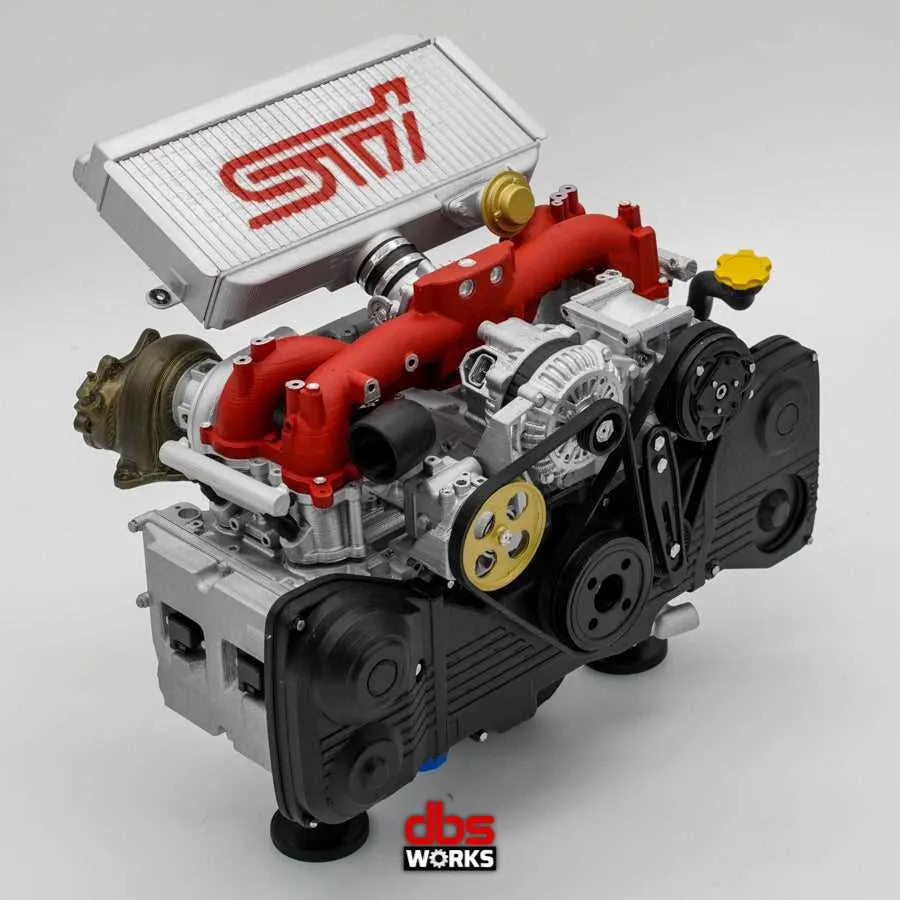

For a detailed view of the components in a horizontally opposed four-cylinder setup, start by locating the main assemblies: the crankshaft, pistons, and the cylinder heads. The flat configuration ensures a low center of gravity, which benefits the overall vehicle handling. Identify the two separate banks of cylinders, which are arranged opposite each other, reducing vibration.
Focus on the crankshaft positioning in the center, acting as the core rotational axis. From here, the connecting rods extend to each piston, transferring the power generated from combustion. The oil pump and cooling system play a critical role in maintaining engine health and performance–check their placement carefully.
Ensure the timing belt or chain aligns precisely with the camshaft to regulate intake and exhaust valves. This synchronization is essential for optimal combustion. Additionally, inspect the fuel injectors and spark plugs as part of the fuel delivery and ignition system for smooth operation.
When diagnosing or assembling the unit, examine the seals and gaskets that prevent leakage from the system. These components are critical to maintaining pressure and avoiding operational failures. If the system is being rebuilt or replaced, pay special attention to the torque specifications for each fastener, ensuring correct assembly.
Understanding the Flat-Four Powerplant Layout
For those working on the horizontally opposed four-cylinder configuration, it is crucial to grasp the unique structure of its components. The crankshaft, typically positioned low and at the core of the system, drives both pistons in an alternating motion. Each of the cylinders, arranged symmetrically on either side, moves with a parallel stroke, ensuring balanced power delivery.
The key components to focus on are the connecting rods, pistons, and cylinder heads. These elements interact in a precise sequence to maintain optimal compression and ignition timing. The intake and exhaust manifolds sit atop the assembly, with the former drawing air into the combustion chambers and the latter expelling exhaust gases following combustion.
The crankcase houses the lower half of the pistons, where the connecting rods transfer mechanical energy to the crankshaft, which is positioned horizontally. The oil pump, typically located near the bottom of the unit, ensures continuous lubrication throughout the operation of the engine.
Pay close attention to the configuration of the valvetrain system, which operates in a precise sequence to open and close intake and exhaust valves. This is typically controlled by camshafts, positioned at the top of each bank, rotating in sync with the crankshaft to control valve timing.
Proper alignment and timing of the various components are critical. For example, the timing belt or chain ensures that the crankshaft and camshaft rotate in perfect harmony, preventing valve and piston interference. Any misalignment can cause catastrophic engine failure, so always follow manufacturer specifications for timing and valve clearance adjustments.
Understanding the Components of the Subaru Boxer 2.0 Engine
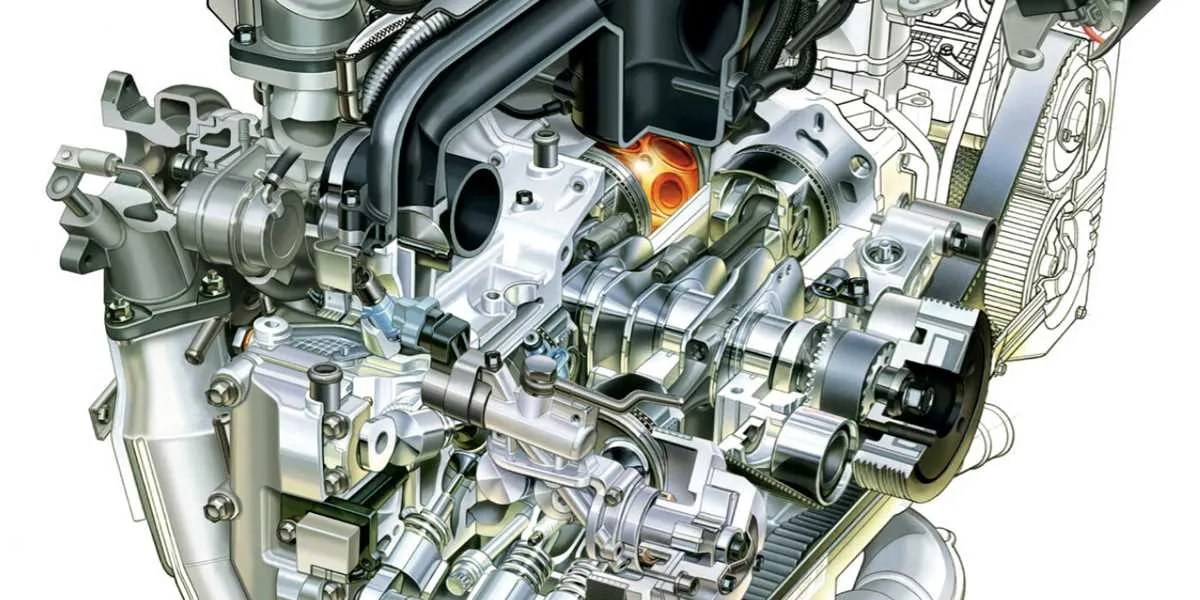
To maintain peak performance, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the internal parts of the horizontally opposed unit. Start by focusing on the crankshaft, which plays a pivotal role in converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion. Ensure proper lubrication and alignment to avoid premature wear.
The cylinders are arranged in a flat configuration, promoting balance and reducing vibration. Keep an eye on the cylinder heads, as they house the valves, camshaft, and valve springs, all of which control air and fuel flow into the combustion chamber. Regular inspection of these parts can prevent airflow issues and enhance combustion efficiency.
The pistons, coupled with connecting rods, are essential for compressing the air-fuel mixture and transferring the force to the crankshaft. A balanced piston design reduces stress and improves the overall longevity of the unit. Check for any signs of wear or damage during routine service intervals.
Fuel injection and ignition systems must be calibrated for optimal timing. A malfunction in either can disrupt the combustion process, leading to inefficient power output or engine misfires. Regular maintenance of the spark plugs and injectors is recommended to ensure smooth operation.
For heat dissipation, the cooling system plays an integral part. The water pump, radiator, and thermostat should all be inspected for blockages or leaks. Overheating can cause severe damage to the block and other vital components.
The lubrication system, including the oil pump and filter, ensures smooth movement of all internal parts. Regular oil changes and the use of the correct oil type are crucial for reducing friction and maintaining engine health over time.
How to Read and Interpret the Subaru Boxer 2.0 Engine Diagram
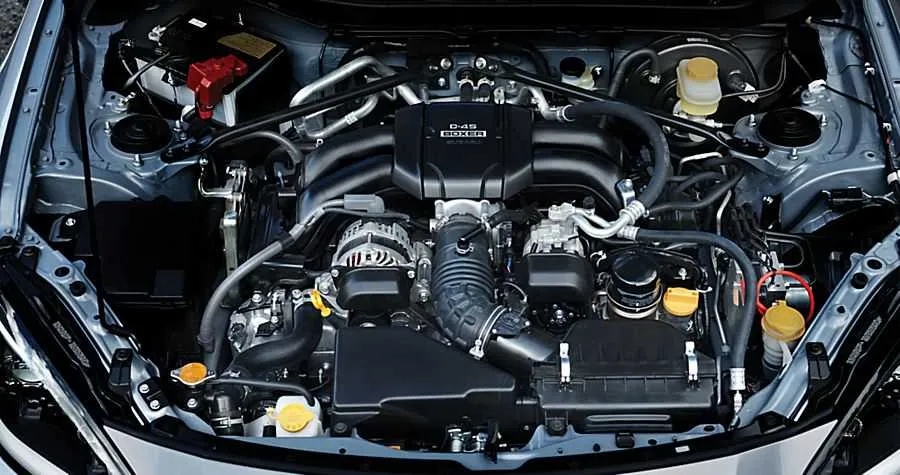
Start by identifying key components. Focus on the powertrain, focusing on the cylinders, pistons, and crankshaft layout. Each part will be numbered for easy identification. Refer to the manual or legend to understand the symbols used in the schematic.
Follow these steps to effectively decode the schematic:
- Locate the Piston and Cylinder Positions: These are typically depicted in the first section of the illustration, showing the placement of the combustion chambers and how they correspond to the crankshaft.
- Understand the Fuel and Air Flow: Pay attention to the flow lines. These will guide you through the intake manifold to the combustion areas and exhaust components. Recognizing these helps you identify the intake and exhaust cycle.
- Identify the Timing Components: The timing gears and camshaft positions are crucial for understanding valve movements. Typically located near the top of the diagram, these components interact with the crankshaft to control valve timing.
- Recognize the Cooling and Lubrication Systems: Look for lines indicating coolant and oil paths. These systems are often depicted with dashed or dotted lines. Cooling components help regulate temperature, while lubrication ensures proper functioning of internal parts.
- Look for Wiring and Electrical Schematics: Electrical diagrams will be integrated into the schematic, showing sensors, spark plugs, and ignition systems. These are vital for understanding electronic control systems.
Check each component’s orientation. The angle and relationship of components, particularly the pistons to the crankshaft, help in understanding the movement and power generation.
Finally, cross-reference the visual with the service manual. This ensures you’re reading the schematic in the correct context for maintenance or diagnostics.
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips for the Subaru Boxer 2.0 Engine
Keep the ignition system in top condition by regularly inspecting spark plugs and coils. Failing to replace worn-out spark plugs can result in misfires and inefficient combustion, leading to power loss and poor fuel economy.
Check the oil regularly to prevent sludge build-up, which can hinder engine performance. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals and use the correct grade for optimal lubrication and cooling.
Coolant leaks are common in the lower hose area. Inspect all hoses and seals for signs of cracks or wear. Replacing a compromised hose immediately can prevent overheating and engine damage.
Inspect the timing belt or chain for wear. If it’s nearing the recommended replacement interval, replace it proactively to avoid costly damage to the internal components if it snaps or slips.
Regularly check the air filter and replace it as needed. A clogged filter reduces airflow, affecting combustion efficiency and engine responsiveness.
Fuel injectors can become clogged over time. Use a fuel injector cleaner periodically to maintain smooth fuel delivery, which helps preserve power output and fuel efficiency.
Monitor exhaust emissions for unusual increases in pollutants. This could indicate issues with the catalytic converter or the combustion process, requiring immediate attention to avoid damage to other components.
Listen for unusual sounds, especially knocking or ticking noises, which could indicate a problem with lubrication, timing, or internal components. Early detection can prevent severe damage.