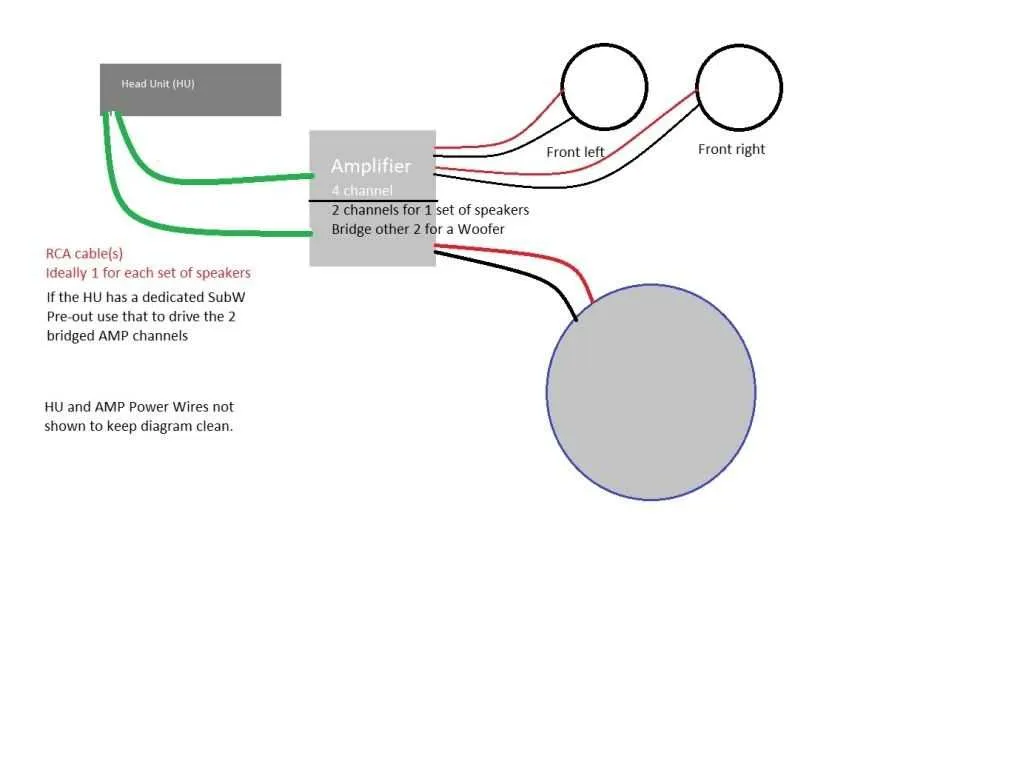
To achieve optimal sound output, connect your single low-frequency driver to the 4-output sound amplifier following a straightforward method. Begin by ensuring your power source is properly set up to avoid potential damage. Use high-quality cables to guarantee the best signal transmission.
For stable performance, connect each positive terminal of the amplifier to the corresponding input of the driver. It’s crucial to match the impedance ratings of both components. Most amplifiers provide individual control for each output, allowing you to fine-tune the output to match the specifications of your woofer.
Make sure the ground connection is securely fastened, as this ensures the integrity of the entire system. Additionally, when selecting the appropriate gauge for the power and speaker cables, consider the distance between the amplifier and the speaker. Too long a distance or thin wires can degrade the signal quality.
Important tip: If you encounter issues with volume or sound clarity, verify that all connections are tightly secured, and consider adjusting the gain settings on your amplifier to achieve balanced audio output.
Connecting One Bass Unit to a Four-Output System
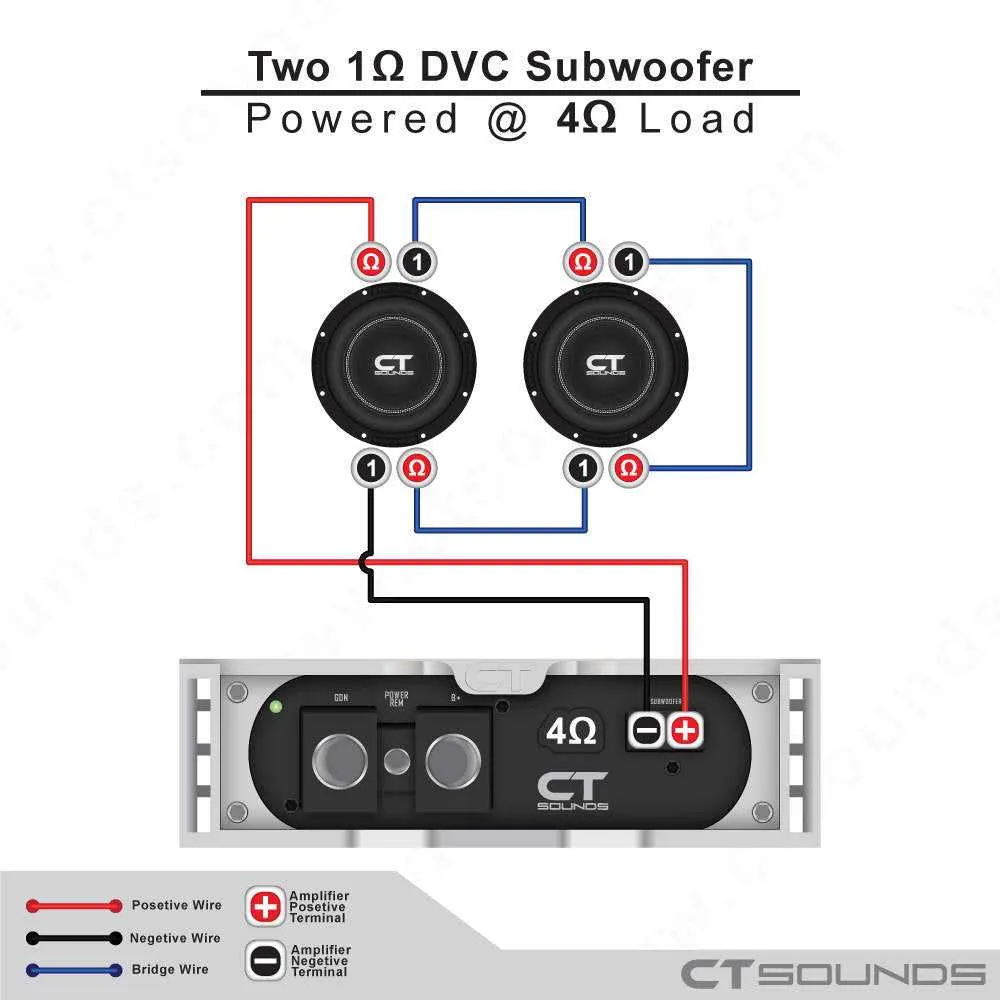
To properly connect a single low-frequency speaker to a four-output system, use the bridge configuration. This method combines two outputs from the system into one stronger connection. Choose two adjacent terminals from the first pair of outputs, then link them to the terminals of the speaker for enhanced power delivery.
Ensure the impedance of the speaker matches the output ratings to avoid overloading the system. For instance, if you’re working with a 4-ohm bass unit, select the corresponding bridge mode that supports 2-ohms per pair of outputs. This will maximize power efficiency while maintaining a stable output.
When wiring the connections, make sure to use quality, thick gauge wires to minimize resistance and avoid potential heat buildup. A secure and tight connection is crucial for safe operation, and any loose wiring could lead to power loss or system failure.
How to Connect a 4-Channel Amplifier to a Single Subwoofer
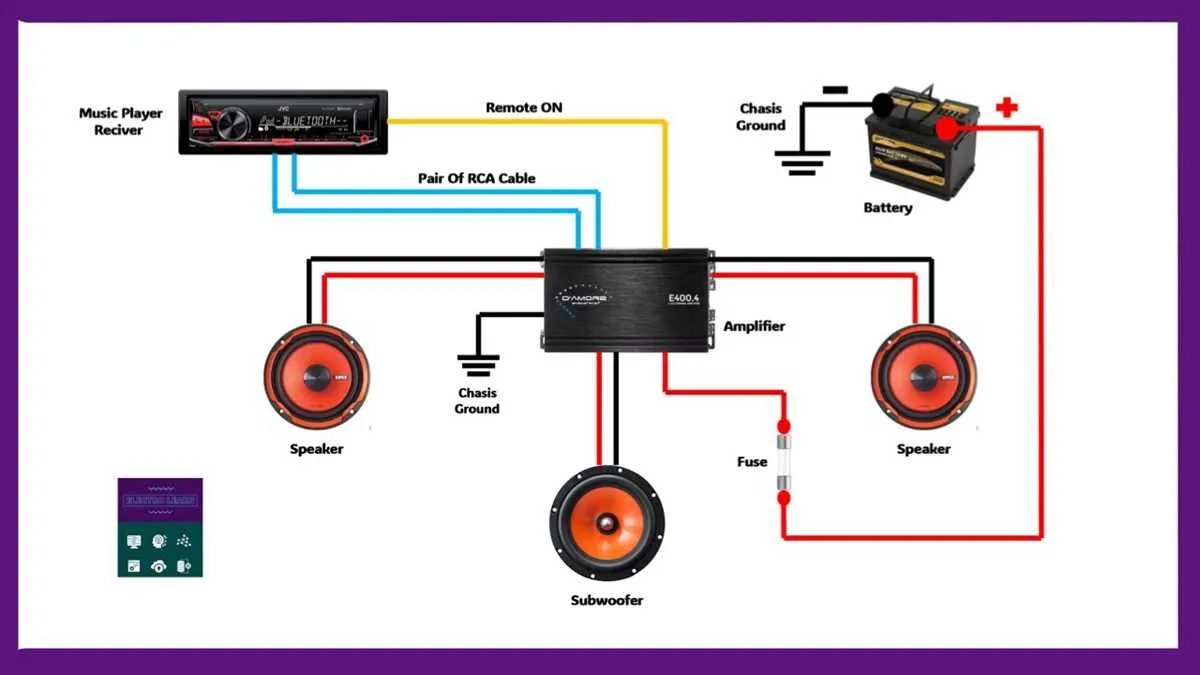
To achieve optimal performance when hooking up a four-way power unit to a single bass unit, follow these detailed steps:
- Step 1: Ensure the amplifier is set to bridge mode, which allows it to provide more power to the bass unit by combining two channels into one. This is essential for proper performance.
- Step 2: Locate the positive and negative terminals on both the amplifier and the bass unit. Properly identifying these connections is crucial for proper polarity and sound quality.
- Step 3: Use high-quality speaker cables to connect the positive terminal of the amplifier to the positive terminal of the bass unit. Repeat this for the negative terminals.
- Step 4: If your amplifier features multiple outputs, ensure you connect only the paired channels, as they are designed to be bridged. Never connect a single terminal from separate outputs, as this can cause damage to both the amplifier and the bass unit.
- Step 5: Check the impedance rating of the bass unit. It’s important that the amplifier is compatible with the impedance to avoid overloading. Common values are 2, 4, or 8 ohms.
- Step 6: Secure all connections to ensure they are tight and free of corrosion. Loose connections can lead to poor sound quality or even damage the system over time.
- Step 7: Test the setup by turning on the amplifier at a low volume. Gradually increase the volume while checking for any distortion or power issues.
Choosing the Right Configuration for Optimal Power Distribution
For optimal performance, use a 2-ohm load for a setup involving a single low-frequency driver. This configuration ensures that the amplifier can deliver maximum wattage, especially if it is designed to work best with lower resistance. If your equipment supports 4-ohm resistance per speaker, you may want to connect the driver in parallel to allow for higher power transfer. Be cautious about exceeding the amplifier’s power ratings to avoid damage.
When balancing the power, ensure the total impedance matches the specifications of the system. If your driver and amplifier specifications are closely matched in terms of impedance, you’ll achieve a smoother power delivery without causing strain on any of the components. Avoid overloading by staying within the limits of the hardware’s rated impedance, as underpowering can also result in inefficient energy use and poorer sound quality.
Finally, consider whether your setup requires bridging for extra output. Bridging connections increase power to the speaker, but it’s essential to double-check your amplifier’s capabilities to prevent overheating or overdriving. This method is especially useful when you need to push more wattage to a single driver without losing stability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Connecting Your Audio System
1. Incorrect speaker impedance matching can lead to overheating or damaging the components. Always ensure that the impedance of the connected speakers matches the output capacity of your system. Mismatched impedance can cause poor performance or even failure.
2. Neglecting to check ground connections is a frequent error. A poor ground connection can introduce noise and distortion into the sound. Ensure that all grounding points are clean and securely attached to a solid, bare metal surface.
3. Using inadequate power cables can limit the current flow, leading to weak sound or system malfunction. Always use cables rated for the correct power requirements, ensuring they are thick enough to handle the load without overheating.
4. Not properly securing the power wire can lead to accidental disconnections or short circuits. Use cable ties and fasteners to keep the wiring organized and avoid contact with sharp objects or heat sources.
5. Connecting more than one component to a single output is a common mistake. This can overload the output and cause damage. Always check the specifications for the maximum number of units that can be safely linked together.
6. Incorrect phase wiring is another issue that can cause muddled or weak sound. Ensure that the positive and negative terminals are consistently matched across all components to maintain proper polarity.
7. Using subpar connectors can degrade sound quality. Opt for high-quality connectors and ensure they are securely crimped to avoid intermittent connections that can introduce noise or signal loss.