
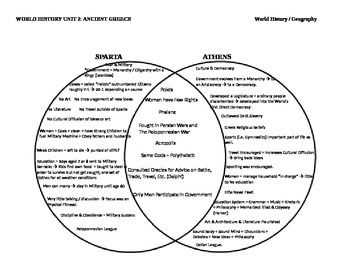
Athens and Sparta, two of the most famous city-states in Ancient Greece, were known for their contrasting political systems, military strategies, and cultural achievements. While both city-states were powerful in their own right, they had distinct differences that set them apart.
Athens, often called the birthplace of democracy, was known for its democratic government. The city-state valued the participation of its citizens in decision-making and had a system where all eligible citizens could vote on legislative matters. This led to a strong emphasis on individual freedoms and liberty in Athens.
Sparta, on the other hand, had a unique political system known as a military oligarchy. The city-state was ruled by two kings and a council of elected officials who were primarily focused on maintaining a strong military. Sparta was known for its military discipline and its emphasis on the collective over the individual.
In terms of military strategies, Athens focused on its naval power and had a strong navy known as the Athenian fleet. The city-state used its navy to protect its trade routes and maintain its hegemony in the region. Sparta, on the other hand, placed a strong emphasis on its land-based army and was known for its highly trained and disciplined soldiers, the Spartans.
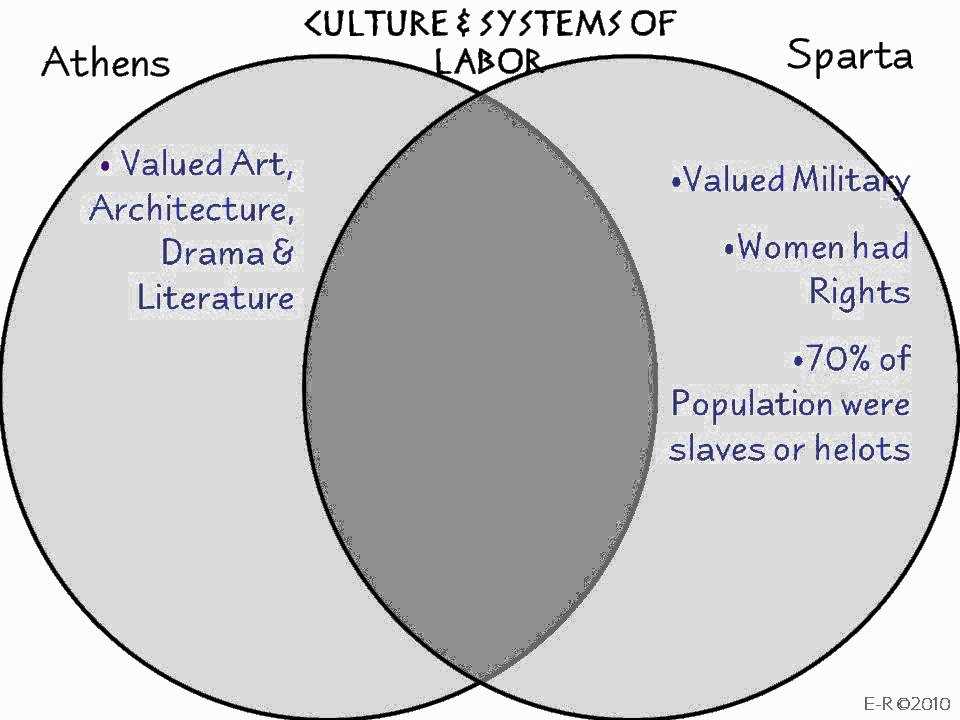
Culturally, Athens was known for its intellectual achievements and contributions to art, philosophy, and theater. The city-state was home to famous thinkers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, and its architecture and sculptures were renowned. Sparta, on the other hand, placed a higher emphasis on physical fitness and military training, and valued simplicity and discipline over artistic pursuits.
In conclusion, Athens and Sparta were two powerful city-states in Ancient Greece that had contrasting political systems, military strategies, and cultural achievements. Athens valued democracy, individual freedoms, and intellectual pursuits, while Sparta focused on military discipline, collective values, and physical fitness. These differences between the two city-states contributed to their unique identities and left a lasting impact on the history of Ancient Greece.
Athens vs Sparta Venn Diagram: A Comparison of Two Ancient Greek City-states
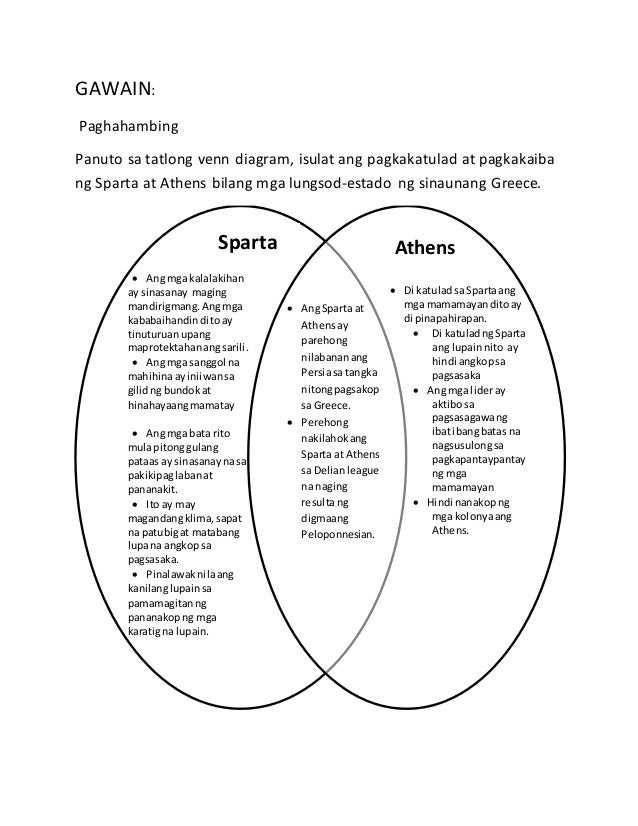
Athens and Sparta were two of the most powerful city-states in ancient Greece. Despite both being part of the same civilization, they had distinct differences in their political systems, social structures, and military strategies. By comparing these two city-states using a Venn diagram, we can identify the similarities and differences that set them apart.
Political Systems:
- Athens had a democratic government where the citizens had a direct say in decision-making through voting. They believed in the power of persuasion and often engaged in debates to reach a consensus.
- Sparta, on the other hand, had an oligarchic government where a small group of elite citizens, known as the Spartan council, made all the important decisions. They focused on maintaining a strong military and protecting their city-state.
Social Structures:
- Athens valued education, arts, and philosophy. They were known for their advancements in literature, science, and architecture. Athens believed in nurturing the mind and encouraging intellectual pursuits.
- Sparta, on the contrary, emphasized military training and discipline. They believed in producing strong and fearless warriors. Spartan society was highly militaristic and focused on physical fitness.
Military Strategies:
- Athens had a strong navy and relied heavily on their naval power for trade and defense. They focused on building alliances with other city-states and maintaining a well-equipped army to protect their interests.
- Sparta, known for its formidable land force, had a highly disciplined and professional army. They trained from a young age and focused on close combat and the art of war.
In conclusion, while Athens and Sparta were both influential city-states in ancient Greece, they differed significantly in their political systems, social structures, and military strategies. Athens emphasized democracy, education, and naval power, while Sparta favored an oligarchy, military training, and land force. Their contrasting values and approaches to governance shaped their respective societies and left a lasting impact on the history of ancient Greece.
Overview of Athens and Sparta
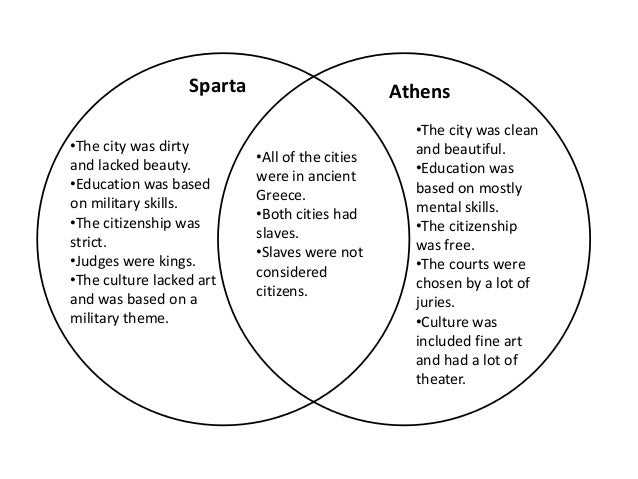
Athens and Sparta were two of the most powerful city-states in ancient Greece. Despite being located in the same country, they had very different political, social, and military systems, which often led to rivalry and conflict between them.
Athens, known as the birthplace of democracy, placed great importance on individual liberty and the participation of its citizens in the political process. It had a democratic government, where decisions were made by the majority of the citizens through open discussions and voting. Athens valued education and the arts, and it was home to famous philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. The city-state had a diverse economy, with trade and commerce playing a significant role, and it was renowned for its cultural achievements.
Sparta, on the other hand, had a militaristic society. It focused on discipline, loyalty, and military prowess. Sparta had a dual monarchy, with two kings ruling over different aspects of the state. Its government was based on a rigid system of laws and customs, which aimed to maintain social order and control. Education in Sparta was focused on military training, and the city-state had a powerful army that was feared by its enemies. Spartans were known for their simplicity of lifestyle and their strong sense of community.
- Athens
- Birthplace of democracy
- Focused on individual liberty
- Valued education and the arts
- Diverse economy with trade and commerce
- Sparta
- Militaristic society
- Focused on discipline and loyalty
- Powerful army
- Simple lifestyle and strong community
Despite their differences, Athens and Sparta both played significant roles in ancient Greece and left a lasting impact on history. They were both powerful city-states, but their distinct values and systems of governance set them apart from each other.
Political Systems
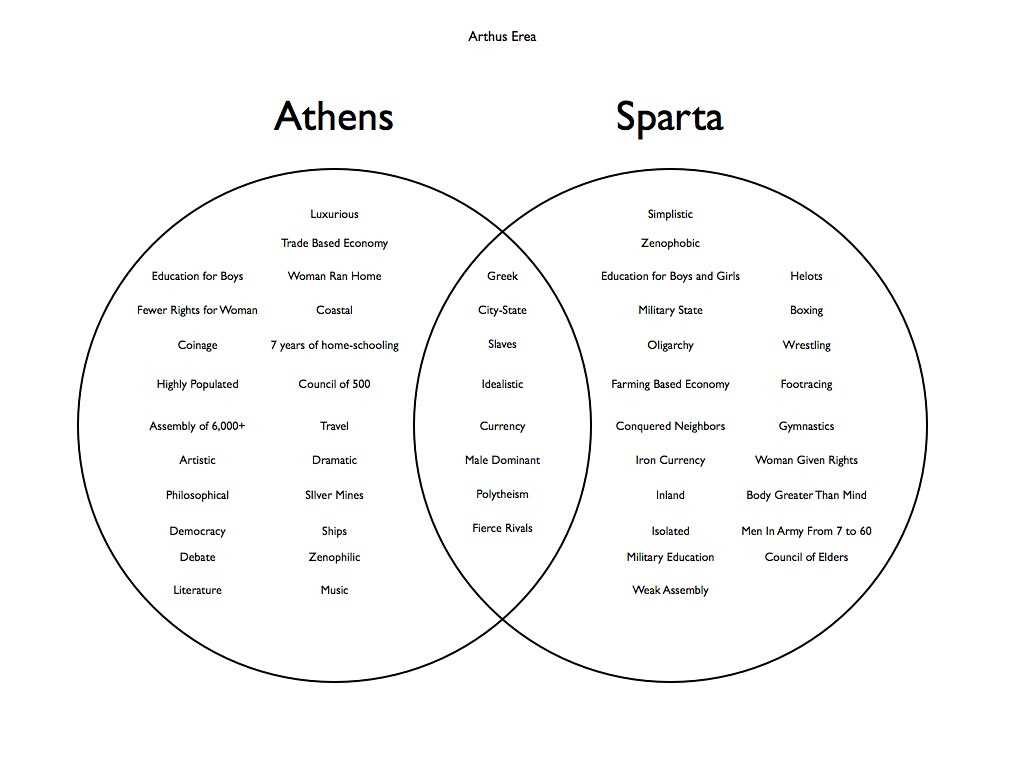
Political systems play a crucial role in shaping the governance and structure of a society. In ancient Greece, both Athens and Sparta had distinct political systems that were instrumental in defining the nature of their respective city-states.
Athens: Athens was known for its democracy, which was one of the earliest recorded democratic systems in history. The political power in Athens was vested in the hands of all citizens who were eligible to participate in the government. This included adult male citizens over the age of 18 who had completed their military training. The citizens of Athens had the right to vote, propose and debate laws, and hold various political offices.
Sparta: Sparta, on the other hand, had a unique political system known as oligarchy. The political power in Sparta was concentrated in the hands of a small group of Spartan citizens called the Spartiates. Only those who were born to Spartan parents and completed the rigorous military training were considered Spartiates. These Spartiates held all the political power and controlled the governance of the city-state.
- Role of Women:
Another notable difference between the two city-states was the role of women in politics. In Athens, women did not have any political rights and were not allowed to participate in the democratic process. They had limited roles and were primarily responsible for managing the household affairs. On the contrary, Spartan women had more freedom and played a significant role in society. They had the right to own property, were encouraged to participate in physical activities, and could influence political decisions through their husbands.
- Strengths and Weaknesses:
Athens’ democratic system allowed a wider participation of citizens in the political process, fostering a sense of inclusion and empowerment. It promoted debate, deliberation, and the possibility of passing fair laws that could benefit the majority. However, Athens’ democracy also had its weaknesses, such as the exclusion of certain groups like women and slaves.
Sparta’s oligarchic system, with power concentrated in the hands of a few, allowed for swift decision-making and efficient governance. This system was particularly suitable for a highly militaristic society like Sparta, where the focus was on maintaining military prowess. However, the exclusion of a majority of the population from political power limited the representation and potential for a more inclusive governance system.
In conclusion, the political systems of Athens and Sparta differed significantly, with Athens operating as a democracy and Sparta as an oligarchy. These systems influenced the rights and participation levels of citizens, particularly women. Both systems had their strengths and weaknesses, shaping the course of their respective city-states and contributing to their unique identities in ancient Greece.
Education and Philosophy
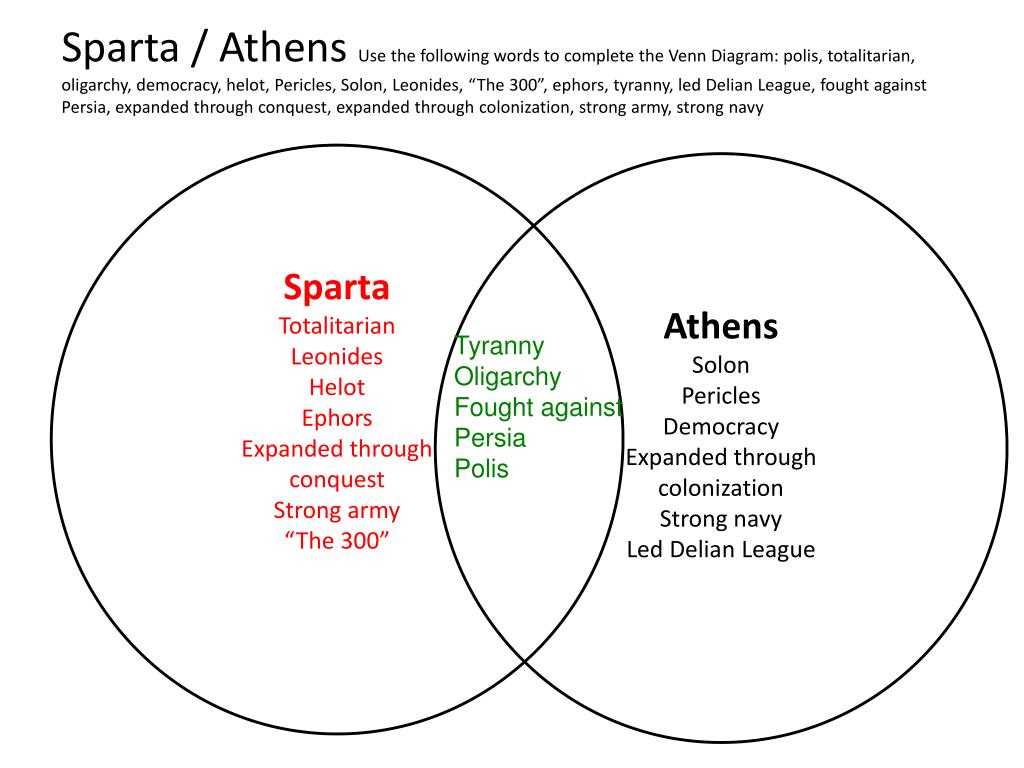
The education system in ancient Athens and Sparta differed significantly, reflecting the contrasting values and priorities of the two city-states. In Athens, education was highly valued and considered essential for the development of individuals as well as the well-being of the city-state as a whole. On the other hand, in Sparta, education primarily focused on preparing individuals for a life of military service.
In Athens, education was primarily provided by private tutors and paid teachers known as sophists. Boys received a well-rounded education that encompassed various subjects such as reading, writing, mathematics, music, and physical education. This education aimed to cultivate critical thinking, eloquence, and the ability to participate in democratic discussions and debates. Philosophy also played a significant role in Athenian education, with philosophers such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle contributing to the intellectual development of the city-state.
- Athens: emphasized well-rounded education
- Athens: private tutors and paid teachers
- Athens: subjects included reading, writing, mathematics, music, and physical education
- Athens: focus on critical thinking and democratic participation
- Athens: prominent philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle
In contrast, education in Sparta was mainly aimed at producing highly disciplined and efficient soldiers. Boys in Sparta were enrolled in military training at a young age and underwent rigorous physical and combat training. Academic subjects were not prioritized, and Spartan education revolved around cultivating strength, endurance, and obedience. The goal was to produce individuals who were physically fit, ready to defend the city-state, and loyal to the Spartan way of life.
- Sparta: focused on military training
- Sparta: rigorous physical and combat training for boys
- Sparta: academic subjects not prioritized
- Sparta: emphasis on strength, endurance, and obedience
- Sparta: goal to produce loyal and disciplined soldiers
Overall, education in Athens and Sparta reflected the values and goals of each city-state. While Athens emphasized a well-rounded education with a focus on critical thinking and democratic participation, Sparta prioritized military training to create disciplined soldiers. These differing approaches to education significantly influenced the development and characteristics of each society.
Military Strength and Focus
In terms of military strength, both Athens and Sparta were formidable city-states in ancient Greece. However, there were significant differences in their military strategies and emphasis.
Athens, known for its powerful navy, placed a strong focus on maritime warfare. The Athenian fleet, consisting of trireme warships, played a crucial role in their military dominance. This focus on naval power allowed Athens to establish a strong maritime empire that included several islands and coastal territories. The Athenians were skilled sailors and their naval forces were well-trained and experienced.
On the other hand, Sparta was renowned for its exceptional land-based military strength. The Spartans boasted a highly disciplined and professional army, known as the Spartan hoplites. These hoplites were renowned for their formidable skill in close combat, especially in the use of the phalanx formation. The Spartan army was heavily focused on land warfare and its soldiers were trained from a young age to be some of the most fearsome warriors in Greece.
While Athens and Sparta had different military strengths and focuses, both cities were highly respected and feared by their enemies. Athens’ naval supremacy allowed it to control trade routes and project its power across the Mediterranean, while Sparta’s renowned army ensured its dominance on land. These military strengths played a crucial role in shaping the political, social, and cultural dynamics of ancient Greece.
Gender Roles and Treatment of Women
In both Athens and Sparta, gender roles and the treatment of women were significantly different. In Athens, women were considered inferior to men and had limited rights and freedoms. They were primarily expected to marry and bear children, with their main roles being centered around the household and family. Women were not allowed to participate in politics, and their education was limited to basic household and domestic skills. They had little say in important decisions and were often treated as property by their husbands.
On the other hand, in Sparta, women had a higher status and more rights compared to their counterparts in Athens. Spartan women had more freedom and independence, and they were encouraged to participate in physical activities and sports. They received physical training and education that focused on developing their strength and fitness. This emphasis on physical well-being meant that Spartan women were often healthier and more active than women in other city-states.
Despite these differences, it is important to note that both Athens and Sparta were patriarchal societies, where men held the majority of power and authority. In both city-states, women were not considered equal to men and were expected to fulfill traditional roles as wives and mothers. However, the treatment of women in Sparta was relatively more progressive compared to Athens, as they had more rights and opportunities for physical development and education.
Comparison of Gender Roles in Athens and Sparta:

- In Athens, women had limited rights and were expected to focus on household duties and childbearing.
- Spartan women had more freedom and independence, and they were encouraged to participate in physical activities and sports.
- In Athens, women were excluded from politics and had little say in important decisions.
- Spartan women had more opportunities for education and physical training.
- Both Athens and Sparta were patriarchal societies, with men holding the majority of power and authority.
Overall, while women in both Athens and Sparta were subject to gender inequalities, Spartan women enjoyed relatively more freedom and opportunities compared to their Athenian counterparts. These differences in gender roles and treatment of women were indicative of the contrasting values and ideologies of the two city-states.
Legacy and Impact
The legacies and impacts of Athens and Sparta can still be felt today. Both city-states have left lasting impressions on various aspects of society, government, and culture.
Athens:
- Athens is often referred to as the birthplace of democracy. The city-state’s system of government, in which citizens had the power to participate and make decisions, has influenced countless democracies throughout history.
- Athens was a center for intellectual and philosophical development. Prominent thinkers and philosophers, such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, emerged from Athens and their ideas continue to shape modern philosophy.
- Athens placed great importance on education, leading to the establishment of schools and academies. This emphasis on knowledge and learning still plays a role in today’s educational systems.
Sparta:
- Sparta’s military prowess and discipline have become legendary, and its military strategies are still studied today. The Spartan military system, which focused on discipline, physical fitness, and toughness, has had a lasting impact on military training worldwide.
- Sparta’s emphasis on physical strength and endurance inspired the concept of the Spartan “warrior” and has influenced popular culture, including movies, books, and video games.
- Sparta’s society was highly organized and hierarchical, with a strong emphasis on duty, loyalty, and collective responsibility. These values continue to be admired and celebrated in various forms of media and literature.
In conclusion, both Athens and Sparta have left indelible marks on history. Athens is remembered for its contributions to democracy, philosophy, and education, while Sparta is revered for its military prowess and disciplined society. The legacies of these city-states continue to shape various aspects of our modern world.