
If you’re in need of precise guidance for replacing or repairing individual elements of your chainsaw, identifying the main components and their layout is crucial. Start by referring to the schematic that clearly outlines the structure of key pieces like the engine, chain brake system, and bar assembly. This will give you an efficient approach to diagnostics and repairs.
Focus on high-impact parts, such as the ignition coil, carburetor, and air filter, which directly influence the performance and longevity of your tool. Pay close attention to the interaction between these components during assembly to ensure everything is correctly positioned and functioning.
For any disassembly, it’s important to follow the correct sequence of steps to avoid damaging sensitive components. Ensure the fasteners are tightened to the recommended torque specifications to avoid performance issues or safety risks. A detailed visual guide can be invaluable in this case, offering clarity in the often complex process of reassembling the chainsaw.
Understanding the Component Layout
To properly identify and replace components, refer to a detailed visual breakdown that clearly marks each individual element. Ensure the tool is powered off before disassembling. Pay close attention to the carburetor assembly and ensure it aligns with the air filter and intake manifold. The fuel tank setup requires careful inspection for cracks or leaks. Replace any damaged seals immediately to avoid performance loss. For the drive mechanism, focus on the sprocket and chain tension system. Regularly check the clutch assembly for wear and tear, as it affects overall efficiency.
When servicing the handlebar and throttle system, confirm that all fasteners are securely tightened. Inspect the trigger mechanism for smooth action. The ignition coil is vital for startup efficiency; check connections and replace faulty wiring. Verify that the spark plug is intact and free from carbon build-up to maintain engine performance. Use only recommended lubricants for the chain and bar to ensure smooth operation. Always replace the recoil starter rope if it shows signs of fraying or breaking.
After replacing any faulty components, reassemble carefully, ensuring no loose parts remain. Use proper torque specifications for all bolts and fasteners to avoid over-tightening, which could lead to damage. Test the tool on low power first to ensure all parts function correctly before full use.
Identifying Key Components for Replacement
Start by examining the drive mechanism, particularly the chain sprocket and tensioner. If the chain is loose or doesn’t run smoothly, check for wear or damage to these parts. For smooth operation, the sprocket should fit snugly and rotate freely.
The engine’s ignition system is another critical area. Inspect the spark plug and coil for signs of wear or corrosion. A weak spark often means a replacement of the spark plug or the coil is necessary. If the engine hesitates or fails to start, these parts are likely candidates for attention.
Next, evaluate the carburetor for clogging or leaks. A malfunctioning carburetor can result in poor fuel mixture and inefficient operation. If the unit has difficulty idling or starts rough, clean or replace the carburetor components like the diaphragm and gasket.
Check the fuel lines and filter. Over time, fuel lines can crack or become brittle, leading to fuel leakage. Ensure the fuel filter is free of debris to maintain proper fuel flow. Replacing these parts regularly can prevent engine performance issues.
Lastly, inspect the clutch and brake components. If the clutch fails to disengage properly, it may need adjustment or replacement. Similarly, worn brake pads can lead to a reduction in stopping power, requiring timely replacement to ensure safety and efficiency.
How to Interpret the Assembly Schematic
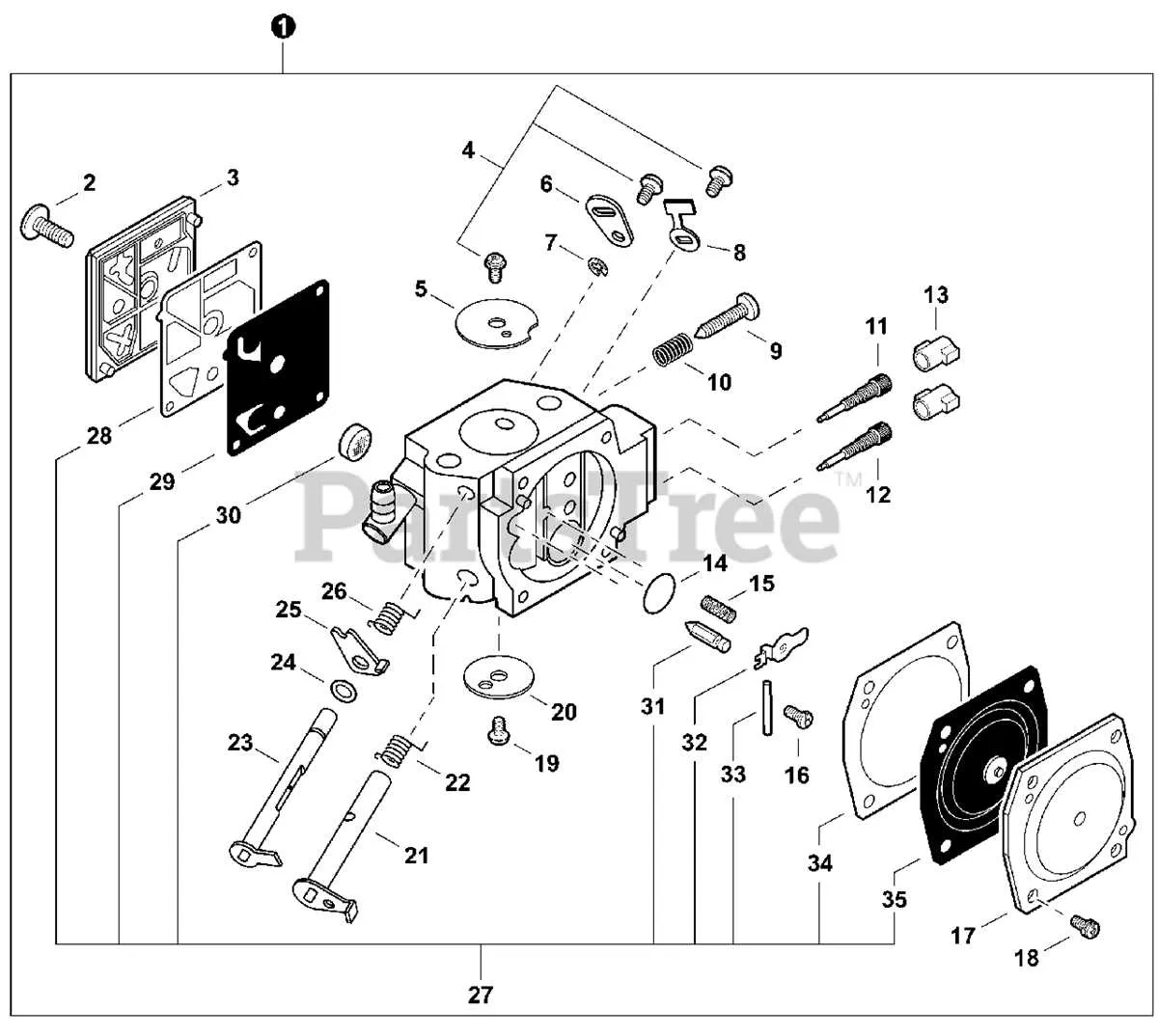
To properly assemble the equipment, follow these steps:
- Identify Key Components – Begin by locating the main parts, such as the engine housing, throttle, and carburetor. These are typically highlighted in different sections for easier identification.
- Understand the Numbering System – Pay attention to the numbers assigned to each item. These usually correspond to a list, which provides part names and detailed descriptions. Cross-reference these to confirm their function and fit.
- Group Similar Elements – Components that belong to the same subsystem (e.g., fuel delivery or ignition) are usually grouped together. This helps in organizing the assembly process, reducing the chance of errors.
- Check Orientation – Some parts must be installed in a specific orientation. For example, the carburetor may need to be aligned with the intake manifold. Look for arrows or guidelines that indicate the correct positioning.
- Match Fasteners – Ensure that each screw, bolt, or nut is matched with the corresponding part. Use the part list to verify which size or type of fastener is needed for each section of the assembly.
- Follow Sequential Assembly – If there is a clear sequence shown in the schematic, follow it step by step. This ensures that parts are assembled in the proper order, which is crucial for functionality.
- Consult Troubleshooting Notes – Often, the schematic includes troubleshooting tips for common assembly mistakes. Refer to these sections if you face any issues during the build.
By following these points carefully, you’ll be able to assemble the machine with confidence, ensuring all components fit together as intended.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with Assembly Breakdown
If you notice difficulty starting the machine, the first step is to check the spark plug. A worn or fouled spark plug can prevent proper ignition. Inspect the plug for signs of damage or carbon build-up. Replace it if necessary.
Another frequent issue is inconsistent engine performance, often caused by a clogged air filter. Regularly clean or replace the filter to ensure proper airflow and engine function.
If the tool runs unevenly or stalls, the fuel lines may be deteriorated or obstructed. Inspect the hoses for cracks or blockages, and replace them if necessary to maintain a smooth fuel flow.
For poor cutting performance, check the condition of the blades or chains. If the cutting edge is dull or damaged, sharpen or replace it. Additionally, ensure the correct tension for optimal cutting efficiency.
Should you experience difficulty with the throttle response, it may be a sign of an issue with the carburetor. Cleaning or adjusting the carburetor can resolve this. Ensure the fuel mixture ratio is correct and that no fuel is leaking from the system.
Regular maintenance checks for wear and tear on various components, such as the ignition system, fuel tank, and air intake, will prevent many common issues. Refer to the schematic to identify parts that may require attention during these checks.