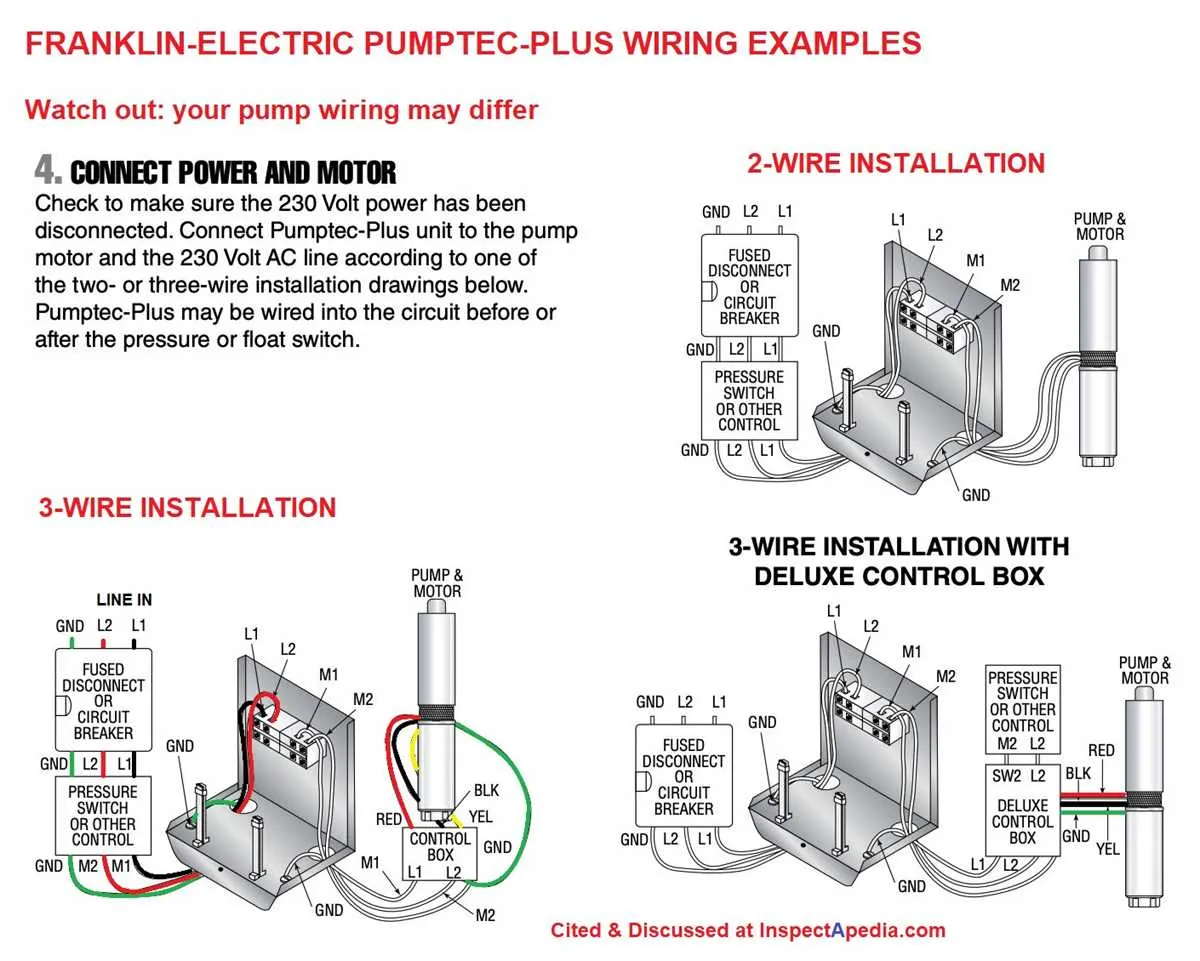
Ensure correct connections before powering up the motor system. Start by identifying the main terminals for the motor’s power input and output, ensuring the line and load connections are separated to prevent cross-wiring. These terminals are typically marked clearly on the terminal strip or panel for ease of identification.
For safety, always check the grounding connections. Ensure the green or bare wire is properly attached to the designated ground terminal to avoid electrical hazards. This step is crucial in preventing potential short circuits or faulty operation.
Incorporate appropriate fuses or circuit breakers to safeguard the system. The fuse rating should match the motor’s full-load amperage, preventing overcurrent situations while allowing the system to operate efficiently under normal conditions.
For correct operation of the start/stop switch, wire it to the designated terminal inputs of the relay or contactor. Ensure all connections are tight and secure, avoiding any loose terminals that could cause intermittent power loss or erratic motor behavior.
Test continuity and functionality of each connection before applying power. Use a multimeter to verify the absence of shorts between power terminals and ground. This simple check will help avoid potential damage to components and ensure safe startup.
Double-check wiring configurations according to the manufacturer’s provided schematics. This ensures that all components will work harmoniously together, maintaining the system’s efficiency and longevity.
Wiring Instructions for Motor Connection Panel
Ensure correct installation by connecting the power supply leads to the designated terminals. Begin by attaching the live (L) wire to the terminal marked for incoming power, typically labeled as “L1” or “L2.” The neutral wire should be placed on the terminal marked “N.” For proper grounding, connect the ground wire to the green or metal ground screw to avoid electrical hazards.
For the motor connection, align the three-phase leads to the appropriate motor terminals. Typically, the motor connections are made at positions marked “U,” “V,” and “W.” Ensure that each lead is securely fastened to its respective terminal, as poor connections can result in overheating or malfunction.
When integrating a thermal overload relay, place the sensor leads between the incoming power and the motor connections. This will protect the motor from overheating by automatically interrupting power in the event of excessive current draw. Always verify that the sensor is correctly calibrated and set to the motor’s rated current.
For proper phase rotation, check the sequence using a phase rotation meter. If necessary, swap any two of the three power leads to correct the direction of rotation. Incorrect phase rotation will cause the motor to run in the wrong direction, potentially damaging both the motor and connected machinery.
Once all connections are made, double-check that each terminal is tightly secured and that there is no exposed wire. Conduct a continuity test with a multimeter to ensure the circuit is properly connected and there are no shorts before powering up the system.
After installation, perform a functional test to ensure that all components are operating as intended, with no unusual noise or heating. In case of any issues, refer to the user manual for troubleshooting tips specific to the motor and control system used in the setup.
Understanding the Key Components of a Motor Protection Unit
Start by identifying the terminal block. This is where incoming power lines connect to the unit. The block allows for proper distribution of power to various internal components. Ensure that connections are secure and that there are no signs of wear or corrosion, which could affect performance.
Next, focus on the overload relay. It serves to protect the motor from overheating due to excessive current. Set the relay to the correct value based on the motor’s full load amperage (FLA). This step is crucial for preventing damage during high load conditions.
The capacitor is another critical part, especially for single-phase motors. It helps improve motor starting and running efficiency. Check the condition of the capacitor regularly, as a failing capacitor can cause the motor to stall or overheat.
In addition to these, a contactor controls the motor’s power flow. It opens and closes the circuit depending on the status of the switch. Make sure that the contactor contacts are clean and free from carbon buildup to ensure reliable operation.
Finally, examine the control panel for any signs of damage or wear. A well-maintained panel ensures the safe operation of the system and helps avoid electrical hazards. Keep it clean and verify that all fuses or circuit breakers are in proper working order.
How to Properly Connect the Components in a Motor Management System
To ensure a safe and effective connection of the elements in the motor management system, follow these guidelines:
- 1. Verify Power Supply: Before starting, check that the main power source is turned off. Use a multimeter to confirm the absence of voltage in the system.
- 2. Grounding: Proper grounding is essential. Connect the ground wire to the designated terminal to prevent any electrical faults and ensure safety.
- 3. Terminal Connections: Connect the wires to the correct terminals. Pay attention to the labels on the terminals to avoid incorrect connections. Ensure that each wire is tightly secured to prevent loose connections that can cause malfunction or even fire hazards.
- 4. Motor Leads: Ensure that the motor leads are connected according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Double-check the connections to ensure proper rotation direction and load handling.
- 5. Control Circuit: If connecting a relay or switch, ensure that the control circuit is connected to the appropriate terminals. Verify that the control contacts are rated for the correct voltage and current.
- 6. Check Fuse Ratings: Use fuses with proper ratings according to the system specifications to protect the components from short circuits and overloads.
Once the wiring is complete, inspect all connections to confirm that there are no exposed conductors or loose terminals. Recheck each wire for proper placement. Only after this, turn the power on and test the system’s performance. If issues arise, troubleshoot the wiring and ensure no steps were skipped in the connection process.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Pump Motor Panel Connections

If your pump motor isn’t functioning correctly, start by checking the power supply. Ensure that the voltage matches the specified requirements. A low voltage could cause the motor to run inefficiently or not start at all.
Next, verify that all connections are secure. Loose or corroded terminals can disrupt the flow of electricity, leading to operational failure. Tighten or replace any damaged connections.
In cases where the motor is running but not performing properly, inspect the overload protection circuit. An overload condition may have tripped the system, preventing normal operation. Reset the overload or replace it if necessary.
Test the capacitors for proper function. A failed capacitor can prevent the motor from starting or cause it to start erratically. Use a multimeter to check for capacitance, and replace faulty capacitors.
If there is a humming sound but no movement, check the starting relay. A malfunctioning relay can prevent the motor from switching into full operation mode. Replace the relay if it appears faulty.
Lastly, inspect the grounding system. An improper ground can lead to motor damage and safety hazards. Ensure that the motor and panel are properly grounded, and check for any signs of electrical faults.