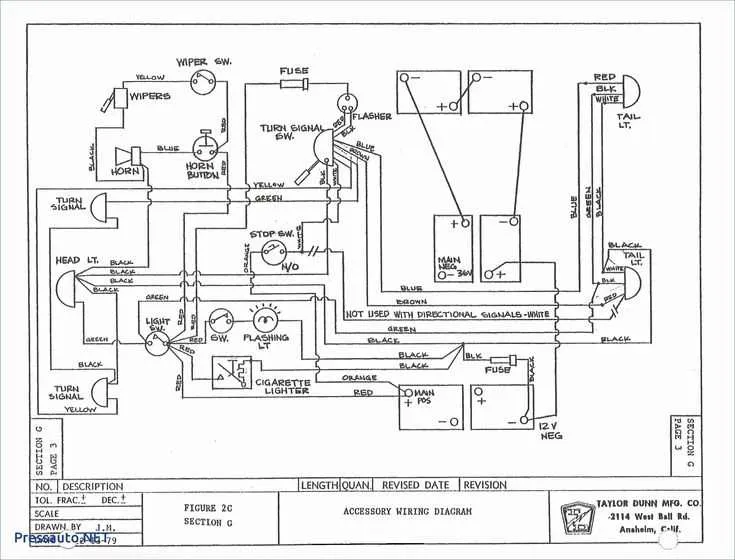
To ensure your vehicle operates efficiently, it’s crucial to comprehend the overall power system structure. Begin by familiarizing yourself with the battery connections, as these are the core of the entire power delivery process. Typically, the positive terminal connects directly to the motor, while the negative terminal is grounded to the frame, providing a stable return path for current.
Check for consistent connections at every component. Corroded or loose terminals can lead to poor performance or even failure of essential systems. Regular inspection of connectors, fuses, and switches is recommended to maintain optimal functioning. Ensure that wires are properly routed to avoid wear, especially where friction is common.
Focus on the control systems–particularly the throttle and brake circuits. These are responsible for regulating movement, so maintaining them free from damage and ensuring clear paths for signals is essential. Identify and verify the presence of fuses that protect key components from power surges.
Properly manage all power sources. Depending on the model, additional storage units or regulators may be included to extend the operational range. Confirm that all power distribution panels are correctly configured to avoid overloads that could cause system failures or reduce battery life.
Understanding Electrical Connections for Battery-Powered Vehicles
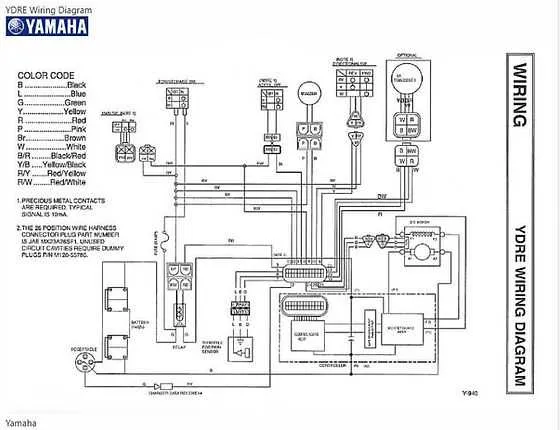
Ensure proper voltage flow by checking the connections between the power source, motor controller, and drive motor. Verify that all cables are securely attached, especially those connecting the battery to the control unit. Use high-quality, insulated cables to avoid short circuits or power loss.
When diagnosing faults, start by examining the connections at the battery terminals. Corrosion can affect the efficiency of the power transfer, so clean any buildup on the terminals regularly. Replace any worn-out or frayed cables immediately to prevent malfunctions.
For better performance, replace fuses that are rated correctly for the electrical load. Avoid using larger fuse ratings than recommended, as this could result in unprotected circuits. Pay attention to the connectors for the switch mechanism, as a loose connection here can lead to unreliable operation.
Check the resistors within the system to ensure they are functioning within the correct range. Overheated resistors may indicate an overload, which requires inspection of the overall electrical configuration to prevent further damage.
Proper grounding is essential for maintaining stability in the system. Ensure that all grounding points are clean, secure, and free from paint or dirt. A poor ground connection can lead to erratic behavior or complete failure of the electrical system.
Understanding the Power Circuit in Golf Carts
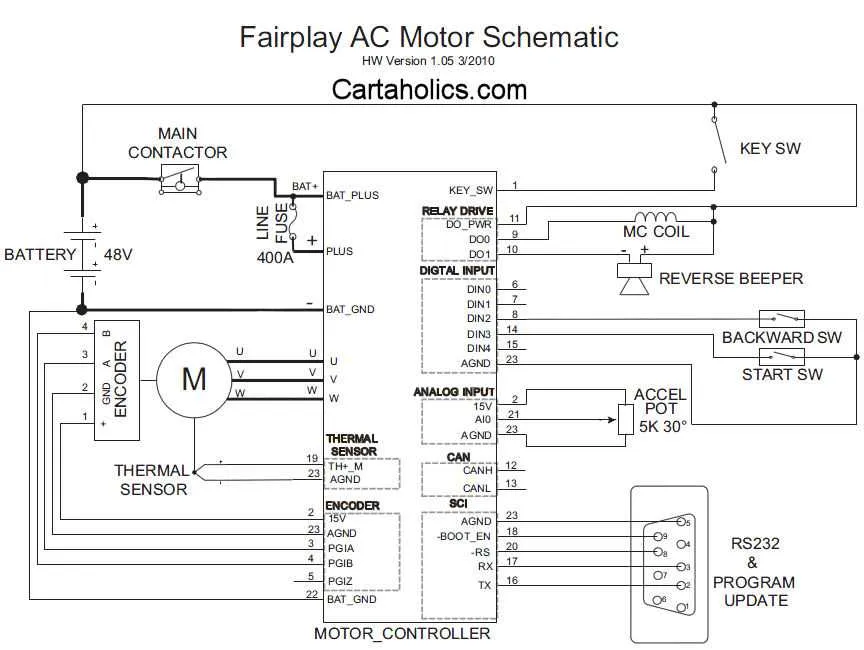
Ensure the battery is properly connected to the main power distribution system to avoid interruptions. Start by checking the battery terminals for corrosion or loose connections, as these can lead to poor performance or system failure.
Inspect the controller connections to guarantee the correct voltage is delivered to the motor. Make sure the wiring between the motor and controller is intact, as damaged wires can result in power loss or erratic behavior.
The motor’s power connections are crucial in providing the correct voltage and current. Ensure the connections are secure, and there are no signs of wear or fraying that could cause power surges or shorts.
It’s vital to use the correct gauge of wires for the power circuit. Using wires that are too thin can cause overheating, which may lead to system failure. Ensure all components are rated to handle the required current.
Lastly, always check for proper grounding throughout the system. A faulty or absent ground can lead to significant electrical issues, including short circuits or erratic performance.
Identifying Key Components in the Electrical System
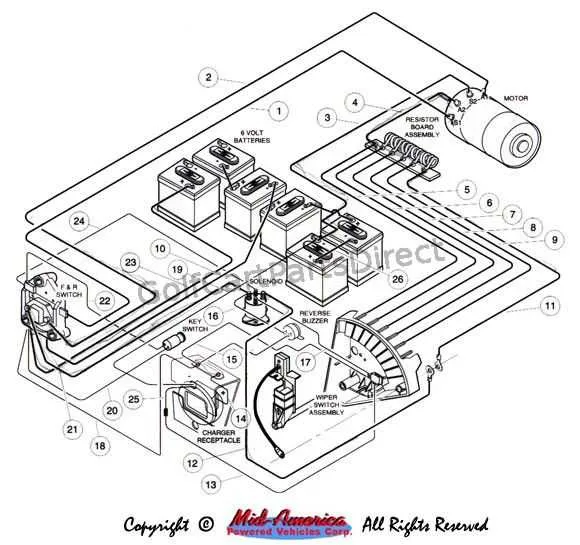
Start by ensuring proper identification of crucial elements for a functional setup. Key components include:
- Battery: Supplies the necessary power. Confirm the voltage rating matches the requirements for the vehicle.
- Motor: Translates electrical energy into movement. Verify connections are intact and clean for efficient operation.
- Controller: Acts as the brain, regulating power flow from the battery to the motor. Check for any signs of overheating or faults.
- Switches: Vital for controlling power flow. Inspect for wear and corrosion that may affect performance.
- Fuses: Protect circuits from overload. Test continuity to confirm they are functioning correctly.
- Connectors: Ensure all terminals are secure and corrosion-free for optimal conductivity.
- Charger Port: Examine for secure connections and proper charging behavior to maintain battery life.
Pay attention to these points during inspections to avoid operational issues and ensure safety.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues
Check the Battery Voltage first. Ensure that the battery is charged properly. If the voltage is too low, the system won’t function correctly. A reading of under 36V for a 48V system or under 18V for a 24V system indicates the battery needs charging or replacing.
If the vehicle is not starting or intermittently stops, inspect the connections at the battery terminals. Loose or corroded connections can result in inconsistent power delivery. Clean the terminals with a wire brush and tighten them securely.
Test the Motor Controller. If power is reaching the motor but it isn’t operating, the issue might lie in the motor controller. A faulty controller could cause the vehicle to not accelerate properly or not move at all. Verify the controller’s input and output connections for signs of wear, burning, or corrosion.
If there are issues with the throttle sensor, such as the vehicle not responding to speed adjustments, check the sensor for proper calibration. A misaligned sensor can prevent the vehicle from recognizing speed changes, leading to erratic or no movement.
Inspect the Fuse Box for blown fuses. A blown fuse will stop certain functions, such as lights or the reverse alarm, from operating. Replacing the fuse with the correct amperage can restore these functions. Always ensure fuses are replaced with the correct type to avoid further damage.
For intermittent power loss, check the solenoid. If it fails, the vehicle won’t engage the motor even if all components are functional. Ensure the solenoid’s contacts are clean and its coil is intact. If damaged, replacing the solenoid may be necessary.