
If you’re working on vehicle lighting systems, accurate understanding of electrical component connections is essential. Ensure proper identification of each wire for seamless installation. Typically, the color codes of the wires follow a standardized system, which helps in ensuring the right electrical flow through the system. Always cross-check the specific wiring layout for the vehicle model you’re dealing with, as even slight variations can lead to functionality issues.
Start by identifying the positive and negative wires. The positive typically connects to the terminal that powers the light, while the negative serves as the return path to complete the circuit. For most systems, it’s common to use color-coded wires where red indicates positive and black marks negative, but always verify this with your reference materials.
When connecting wires to the terminals, it’s crucial to ensure the correct pinout to avoid short circuits. Use a multimeter to check for continuity before making the connections permanent. If you’re working with a harness, pay close attention to the locking mechanism to ensure that the wires are securely held in place. The connector type you use should match the vehicle’s design to prevent any loose connections that might result in lighting failure.
Lastly, protect the wiring with heat shrink tubing or other durable insulation materials to prevent wear and tear from vibration or exposure to elements. If you’re unsure about any part of the process, consult the vehicle’s manual or a professional technician to avoid unnecessary risks. Following these steps will help you achieve a reliable and safe setup for the lighting system in your vehicle.
Proper Electrical Setup for Automotive Lighting System
To ensure correct functionality of your vehicle’s front lighting, follow these crucial steps:
- Identify the appropriate terminals for positive and ground connections.
- Ensure proper insulation to prevent any short circuits, especially when connecting the power source to the light fixture.
- Verify the color-coding of the wires: typically, red or brown denotes the positive line, while black or green serves as the ground wire.
It’s vital to ensure that the pins are securely locked into place to avoid poor electrical contact. A loose connection can lead to intermittent light operation or failure. Always double-check that the wiring is free from frays or exposed areas to prevent potential damage or fire hazards.
- Inspect the plug and socket for any signs of wear or corrosion.
- If the system involves multiple bulbs, check the compatibility and voltage rating of each component.
- Use dielectric grease on connections to protect against moisture and corrosion.
If you’re working with a replacement component, ensure that it matches the vehicle’s electrical system specifications, including voltage and current ratings. Incorrect parts can lead to overloading and malfunction of the lighting system.
- Check the fuse ratings for the lighting circuit. Replace fuses with the correct amperage to avoid overloading the system.
- After completing the installation, test the system by turning on the lights and checking for consistent illumination.
Understanding the Pinout Configuration for Headlamp Plugs
Ensure proper identification of each terminal in the electrical socket to guarantee accurate connections and prevent malfunctions. Always begin by referencing the manufacturer’s specifications to match the pin assignments correctly. Incorrect wiring can result in damage to the components or failure to activate functions such as high beams or turn signals.
Common Pinout Arrangement: In many automotive setups, the central pin often carries the ground, while the adjacent pins handle the positive current for the low and high beams. It’s critical to verify that each pin is connected to the corresponding wire, as misplacement can lead to flickering or non-functioning lights.
Testing the Polarity: Use a multimeter to verify the polarity of each pin. The negative terminal will show no voltage, while the positive terminal should read between 12-14 volts when the vehicle is running.
Function Check: After connecting, test each function by activating the switch for low beams, high beams, and flashers. If any light fails to respond, inspect the pins for potential issues such as corrosion or loose connections.
Quick Tip: When replacing a damaged socket, always confirm that the replacement part matches the original configuration exactly. Using a mismatched component may lead to improper function or short-circuiting.
How to Identify Wires in a Lighting Harness
Start by identifying the color coding of the individual cables. Typically, manufacturers use a standardized color scheme for easier identification: white or gray for ground, black for power, and blue for signal transmission. This color scheme can vary, but it’s a reliable first step in determining the function of each wire.
Next, look for any labels or part numbers printed on the cables themselves. These identifiers can provide vital clues, as manufacturers often mark each wire for specific functions. Consult the vehicle’s manual or the manufacturer’s documentation to cross-reference these markings.
If there are no markings or color distinctions, you may need to use a multimeter. Begin by testing for voltage with the ignition on. A wire showing a voltage reading when the vehicle is powered will typically be the live wire, while the one reading ground will be for the return.
Another useful technique is checking the connector orientation. In some cases, the position of the wires inside the plug can provide clues about their function, with certain positions being reserved for specific electrical tasks.
Finally, in the absence of documentation, tracing the wire back to its source is often the most reliable method. Following the harness back to the fuse box or control module can help you figure out its role in the overall electrical system.
Common Issues and Fixes in Lighting System Electrical Connections
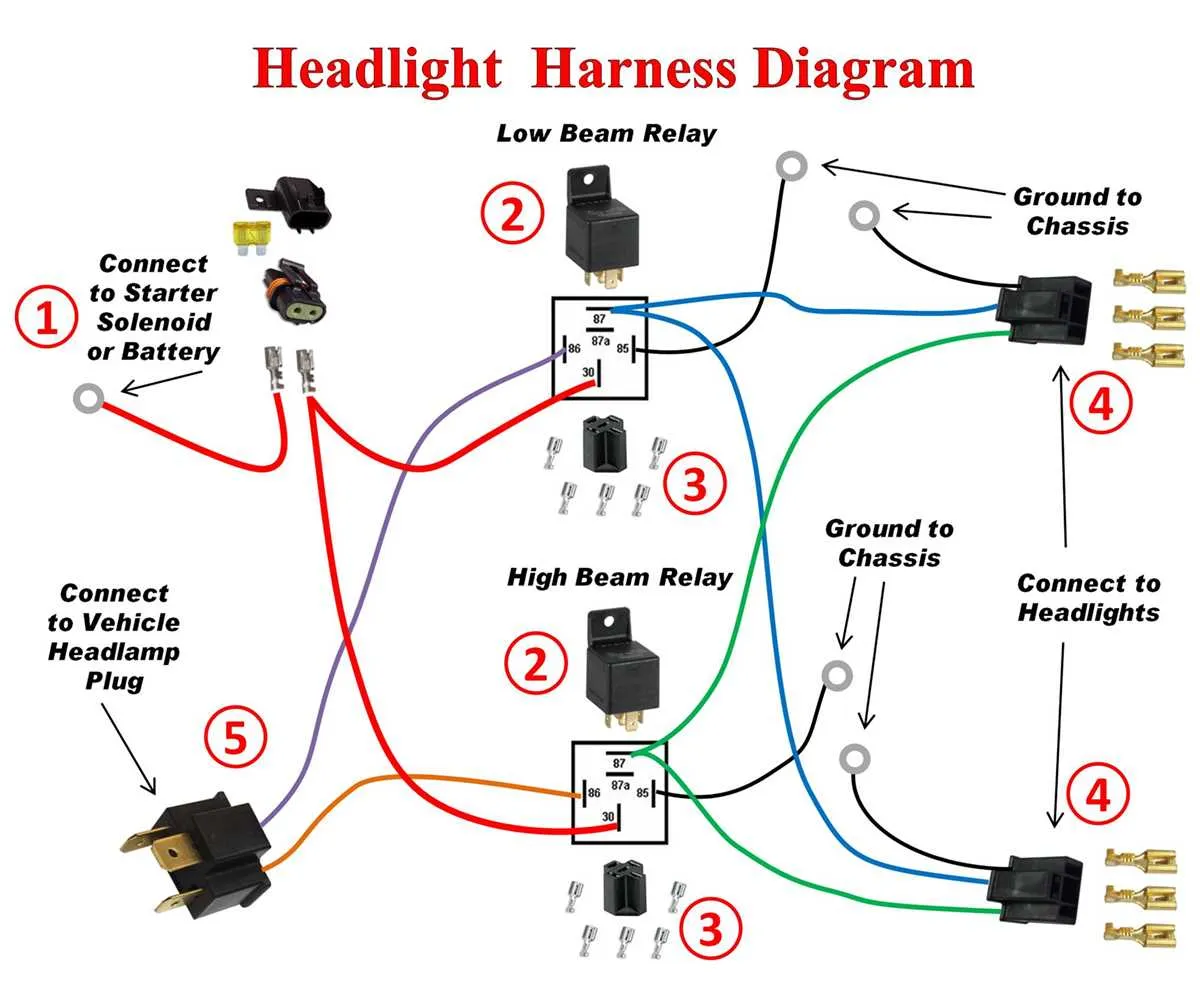
Ensure the electrical terminals are free from corrosion. Oxidation on metal parts disrupts the flow of current, leading to dim or non-functional bulbs. Use a contact cleaner and wire brush to remove any buildup. After cleaning, apply dielectric grease to prevent further corrosion.
Check for frayed or damaged cables. A common problem is wear and tear that exposes internal wires, which can cause intermittent failure or short circuits. If you find any damage, replace the affected section of the cable, ensuring proper insulation to prevent future issues.
If the lights are flickering or not turning on consistently, inspect the connectors for a loose fit. Over time, the pins can loosen or bend, reducing the connection quality. Gently adjust the pins with needle-nose pliers or, if necessary, replace the connector to ensure a secure link.
Ensure proper grounding. A poor ground connection can result in inconsistent electrical flow, leading to malfunctioning lighting. Inspect the ground wire and terminal, making sure there’s no rust or dirt, and reattach it tightly to a clean metal surface.
If the system is not responding at all, test the voltage output from the power source. A multimeter can help you determine whether the circuit is delivering the appropriate voltage. If the voltage is low or absent, trace the issue back to the fuse box or relay, which may need replacing.
Another common issue is the misalignment of the electrical pins in the socket. Over time, pins can shift or bend, preventing proper contact with the bulb. Gently realign or replace the socket to restore function.
Lastly, if there’s a persistent issue even after checking these elements, consider replacing the entire assembly. Sometimes, repeated electrical problems indicate deeper issues within the assembly, and replacing it can be a more cost-effective solution in the long run.