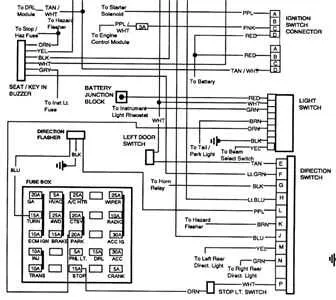
To ensure proper connection and troubleshooting of electrical components in your vehicle, refer to the detailed circuit layout specific to your model. This will help in identifying the right wires and connections for various parts, such as the ignition, lighting, and power systems.
Start with the battery connections. Verify that all terminals are clean and corrosion-free to maintain the flow of power. Pay close attention to the ground wire as it plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the electrical system.
Next, focus on the fuse box. The arrangement of fuses can differ across vehicle models, so confirm which fuses control essential functions like the headlights, alternator, and climate control system. A fuse that is blown can often cause significant issues such as loss of power or malfunctioning components.
Check the control modules. Each system in your truck may have a dedicated module, and understanding their connection is vital for diagnosing faults. Understanding the layout and flow of electrical signals will help identify potential issues quickly.
For complex electrical issues, use a multimeter to test continuity across circuits. Always ensure that the system is powered off before making any modifications or repairs to avoid short circuits or damage.
Always consult your truck’s manual for model-specific instructions.
Electrical Layout for GMC Pickup
Ensure correct identification of the components before starting the electrical connections on your vehicle. The first step is to locate the central fuse box and identify the key relays, which regulate power to essential systems. Next, examine the terminals for the ignition system, ensuring proper continuity and avoiding shorts. Pay close attention to the wire color codes to match them with corresponding systems like lights, air conditioning, and engine control.
For the powertrain system, make sure all connections related to sensors and actuators are firmly attached. Incorrect wiring of these connections can lead to malfunctions in engine management or transmission behavior. It’s advisable to use wire crimping tools for reliable and durable connections, especially when dealing with high-current circuits.
Double-check grounding points, which are crucial for stable system operation. Poor grounding can result in erratic electrical behavior, including flickering lights and malfunctioning sensors. Also, verify the alternator wiring, as an improper connection can lead to battery charging issues and affect electrical system performance.
After performing the checks, ensure all connections are insulated with quality electrical tape to prevent corrosion and accidental shorts. Conduct a final inspection, making sure all components are correctly positioned and secured to avoid wire chafing or damage during vehicle operation.
How to Interpret the Electrical System Blueprint
To correctly interpret the electrical blueprint for your vehicle, start by identifying the color codes used for each wire. These codes indicate the function of each wire, such as power supply, ground, or signal. Ensure you understand the meaning behind the colors, as this will guide you through connections and troubleshoot problems accurately.
Key steps:
- Color Codes: Red typically indicates a constant power source, while black is often used for ground connections. Other colors represent different circuits, so referencing the vehicle manual is essential.
- Symbols: Arrows and lines indicate direction and connection points. A dashed line may represent a component that isn’t directly connected but is related to the system.
- Pinouts: Locate the pinouts for connectors. They show which wire corresponds to each pin on the connector, making it easier to trace and verify electrical flow.
Common Issues: If you’re unsure about any part of the electrical flow, verify the continuity with a multimeter. Pay attention to the power supply lines and fuses, as these are often sources of electrical problems.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting in Electrical Systems
Ensure proper grounding connections to prevent electrical malfunctions. Faulty grounds often lead to voltage drops, causing components to malfunction or fail intermittently.
- Inspect grounding points for corrosion or loose connections.
- Check for continuity between the ground point and the battery negative terminal.
- Replace corroded or damaged grounding wires immediately.
Another frequent issue is blown fuses. These protect circuits from overload, but if they’re regularly blowing, the root cause needs to be identified and fixed.
- Examine the fuse box for signs of damaged fuses or burnt-out connections.
- Identify whether an overcurrent situation is occurring in the circuit.
- Replace fuses with the correct rating to prevent future damage.
Loose or frayed connectors can cause electrical signals to become erratic. These failures are usually easy to spot and require immediate attention.
- Inspect connector pins and wires for signs of wear, burn marks, or bent prongs.
- Clean and secure any loose connections using the appropriate tools and materials.
- For worn-out wires, replace them to restore system integrity.
Intermittent power issues often arise due to poor contact between relays and their sockets.
- Examine relay connections for corrosion, rust, or signs of wear.
- Ensure proper fitment of relays, as a loose relay can lead to inconsistent operation.
- Swap out any malfunctioning relays with high-quality replacements to restore proper function.
Finally, incorrect voltage readings can be an indication of deeper system issues, such as faulty voltage regulators or short circuits.
- Use a multimeter to verify voltage levels at key points in the system.
- Ensure voltage regulators are functioning within the specified range.
- Check for short circuits or damaged insulation along conductors.
Step-by-Step Guide for Connecting Components in Your Pickup
Start by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery to prevent any accidental shorts or electrical damage. Ensure you have the correct tools: wire strippers, crimping tool, electrical tape, and a multimeter for testing. Next, identify the main power source and ground points. The power supply should be connected to the fuse block, while the ground should be attached to a metal part of the frame.
Proceed to connect the essential components one by one. For the headlights, locate the appropriate terminals on the light assembly. Use a connector that ensures a firm and secure fit. For more complex connections, such as the ignition system, ensure you follow the specific pinouts and use proper gauges of wire to handle the current load.
When connecting the sensors or auxiliary components, ensure proper insulation is applied to each connection. This helps prevent exposure to moisture and rust. For a more professional finish, use heat shrink tubing instead of electrical tape. This ensures a tighter seal and better long-term durability.
Once all connections are made, use a multimeter to verify the continuity of each circuit. This step is crucial to avoid any potential issues that could arise from poor connections or faulty components. If all tests are successful, reconnect the vehicle’s battery and test the functionality of all components before finalizing the installation.
Key Tip: Always double-check the current ratings for each component and wire used to ensure safety and efficiency. Components that require higher currents should have appropriately rated wires to prevent overheating and electrical failures.