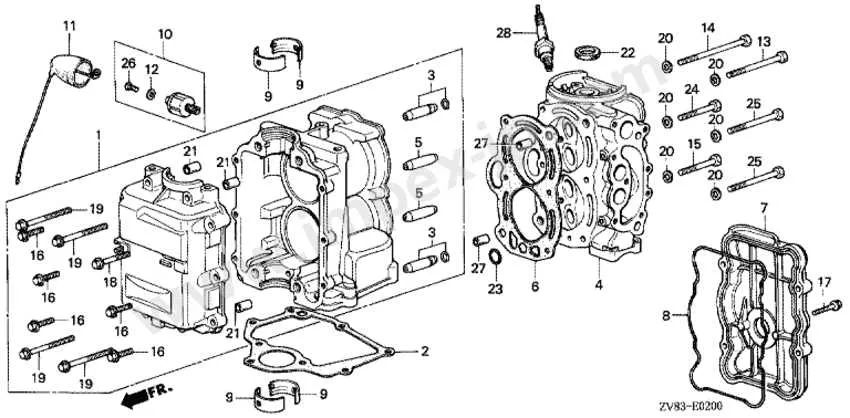
For accurate repairs and maintenance, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the layout of internal components. Refer to a detailed breakdown to quickly identify each piece and its role in the system. This visual aid significantly reduces troubleshooting time and enhances repair efficiency.
Focus on key elements like the ignition, fuel, and cooling systems, ensuring every connection is intact and properly adjusted. Keep a record of any signs of wear or damage, as these may indicate larger issues that need to be addressed immediately.
When disassembling, be methodical–label and organize each component. This practice prevents confusion during reassembly and ensures all parts are restored to their correct positions. Always use manufacturer-recommended replacement parts to maintain peak performance.
Don’t overlook the smaller components such as the seals and gaskets. While they may seem minor, these play an essential role in preventing leaks and ensuring the efficiency of your system.
Understanding Key Components for Marine Engine Maintenance
To efficiently maintain your marine engine, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the layout and functionality of its primary elements. This knowledge aids in troubleshooting and ensures optimal performance. Below is a breakdown of critical engine components to focus on for upkeep.
- Propulsion System: Check the propeller regularly for wear and tear. Ensure it is properly secured to avoid slippage during operation.
- Cooling Unit: Overheating can lead to significant damage. Inspect the water pump and cooling pipes for blockages or leaks.
- Ignition Mechanism: The spark plug should be cleaned or replaced every season. A faulty spark plug can prevent the engine from starting or running smoothly.
- Fuel Delivery: Ensure the fuel line is intact and free from cracks. Regularly clean or replace the fuel filter to prevent clogging.
- Exhaust System: Examine the exhaust components for corrosion. A damaged exhaust system can impact engine performance and fuel efficiency.
For better understanding, always refer to the maintenance manual specific to your model. Regular checks can prevent major repairs and extend the engine’s lifespan.
Common Troubleshooting Tips
- If the engine starts but stalls shortly after, inspect the fuel filter and spark plugs.
- Unusual vibrations often indicate a loose or damaged propeller. Tighten or replace it if necessary.
- Engine overheating may be due to a clogged water intake or malfunctioning cooling components.
Understanding the Components of Marine Engines
Start by familiarizing yourself with the key elements that keep your watercraft’s engine running smoothly. The power unit consists of several crucial sections: the powerhead, which houses the engine’s combustion chamber and the drive system, as well as the gearcase that links the engine to the propeller. Make sure to inspect the fuel system regularly, ensuring the fuel pump and carburetor are free from debris to avoid performance issues.
The cooling system is another critical area to check. The impeller and thermostat regulate the engine temperature; failure of these components can result in overheating, causing severe damage. Pay attention to the exhaust system, which directs gases away from the engine–clogs or leaks here can impair efficiency and even lead to dangerous situations.
Additionally, the ignition and electrical systems are pivotal for proper startup and consistent operation. Examine the spark plugs, coils, and wiring for corrosion or wear. Keeping these parts clean and free from damage is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
The shift linkage and throttle controls must operate smoothly to ensure precise handling. Regular lubrication of moving parts is a must to reduce friction and prevent wear. Lastly, the propeller and associated components should be inspected for any damage or misalignment to avoid poor fuel efficiency and instability while navigating.
How to Identify and Replace Common Components in Marine Engines
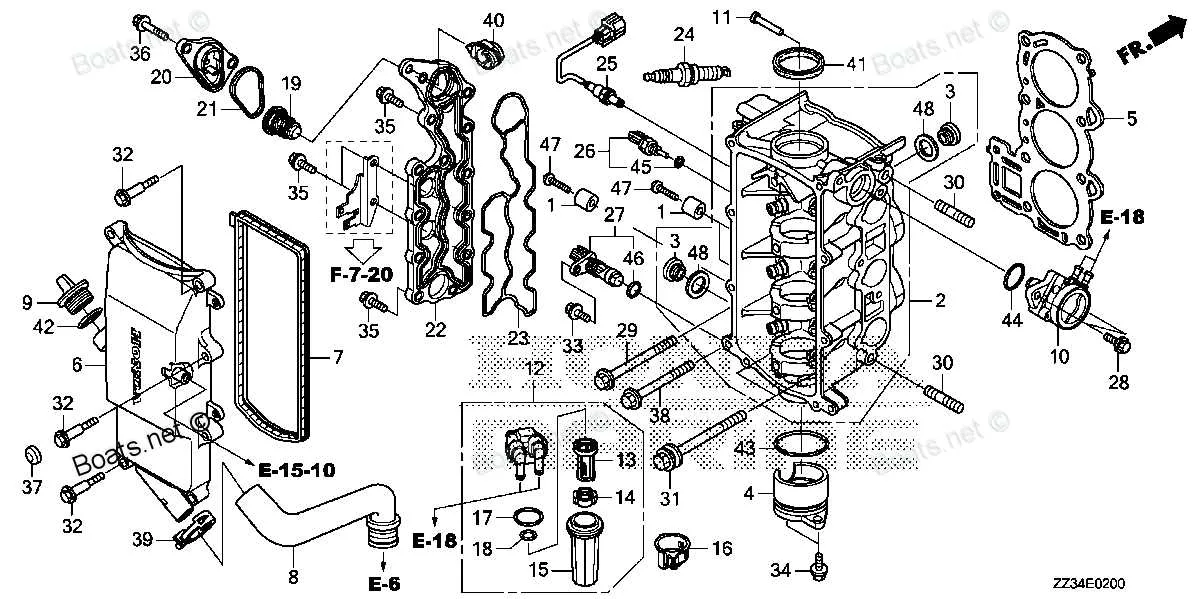
Start by identifying the component you need to replace. Consult the service manual for your specific engine model to locate the serial number, which will help you find the exact replacement item. The most common issues arise with the ignition system, fuel filter, and propeller. Each part has a specific wear pattern, which can be observed visually or through performance decline.
For ignition coils, check for signs of corrosion or visible damage. If the engine struggles to start or misfires, it’s often a sign of coil failure. Replace the coil by removing the securing bolts and disconnecting the wiring. Ensure that the new part matches the exact specifications.
If the fuel filter is clogged, it can cause poor performance and engine stalling. Look for discoloration or debris in the filter. Replacing it involves disconnecting the fuel line, unscrewing the old filter, and fitting the new one tightly in place to avoid leaks. Always use the correct filter model specified in the manual.
For the propeller, check for cracks, dents, or excessive wear. Inspect the hub and blades for damage, as this can cause inefficient propulsion. To replace it, remove the retaining nut and slide the propeller off the shaft. Install the new one by aligning it correctly on the shaft and securing the nut firmly.
Ensure all components are installed correctly to avoid engine malfunctions. Regularly maintain these parts to extend the life of your engine and prevent costly repairs.
Detailed Troubleshooting Tips Using Engine Component Illustrations
Start by checking the fuel system for blockages or leaks. Ensure the fuel lines are intact and free from cracks. Examine the fuel filter for clogging and replace it if necessary. Confirm that the fuel is fresh, as old gasoline can cause starting issues.
If the engine fails to start, inspect the spark plug. Remove it and check for wear, corrosion, or deposits. Clean or replace the spark plug if it’s damaged or dirty. Make sure the gap is correctly set according to the specifications in the component illustration.
Next, verify the ignition system. Look for loose or corroded connections in the wiring. A damaged coil or faulty ignition switch can prevent proper operation. Use the component layout to check each part’s continuity with a multimeter.
Inspect the cooling system by ensuring that water flows freely through the intake and outlet. Clogs in the water pump or cooling passages may cause overheating. Clean the passages and replace any worn-out components to restore optimal cooling performance.
For poor performance, review the throttle and carburetor areas. Check for blockages or malfunctioning parts, such as the throttle valve or choke. Use the component schematics to ensure that everything is aligned and functioning correctly.
Lastly, verify the electrical system by checking the battery’s charge and connections. A weak or dead battery can cause intermittent starting problems. Inspect the alternator and voltage regulator to make sure they are working within proper ranges.