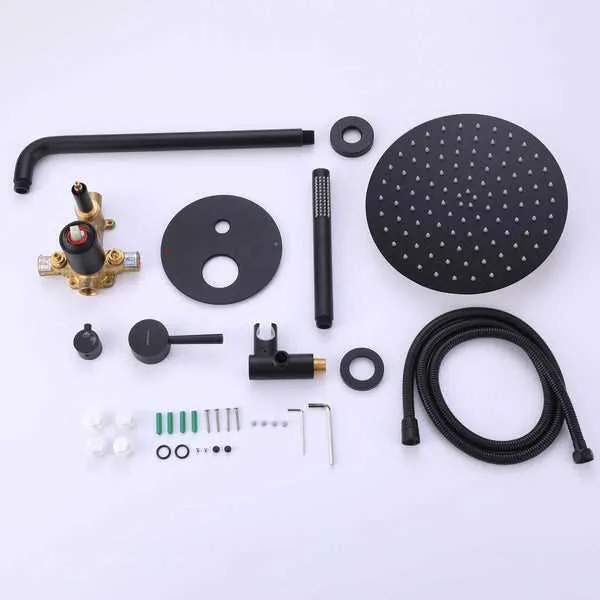

To ensure optimal performance and prevent issues, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the essential elements of your water control unit. When working with this system, identifying the key functional pieces will save time during installation, maintenance, or troubleshooting.
Valves play a critical role in regulating water flow, allowing you to adjust temperature and pressure efficiently. Commonly found in both single and multi-handle designs, these devices are often the first thing to check when facing any water control issues. Make sure they are securely in place and free from debris.
The spout is where the water exits, and it needs to be carefully selected based on the design and functionality required. A mismatch here can lead to poor water distribution, which could affect performance. Consider the type of finish and material for long-lasting durability.
Cartridges or valve stems serve as the heart of temperature regulation, offering precise control over water flow and heat. These components should be periodically inspected for wear and tear, as they can degrade over time, causing leaks or inconsistent performance.
Another important part to consider is the escutcheon plate, which covers the rough-in area behind the wall. It prevents water from leaking into hidden spaces, thus reducing the risk of mold or rust buildup.
Lastly, ensure that the handle mechanism is easily operable and securely attached. A loose or broken handle can make adjustments difficult, leading to frustration. Regular tightening and replacement can prolong the lifespan of this component.
Essential Components of a Bathroom Water Control System
To effectively repair or replace a water control system in your bathroom, it’s crucial to understand the individual components that make up the assembly. The main control unit usually consists of a valve body, control lever, and trim pieces, each serving a distinct function.
Valve Body – This is the central mechanism responsible for regulating the flow of water. It typically houses the pressure-balancing system and is often made of brass or a durable plastic composite. Over time, mineral buildup can affect its function, requiring cleaning or replacement.
Control Lever – Positioned above the valve body, the lever or knob allows the user to adjust water temperature and flow. This component often features a cartridge inside that controls both temperature mixing and water pressure. When the handle feels loose or doesn’t turn smoothly, the cartridge may need to be replaced.
Escutcheon Plate – The escutcheon plate is the decorative trim that covers the area where the pipe connects to the wall. It ensures a clean look while also preventing water leaks around the pipe junction. If water starts to seep around the edges, it might indicate a need to reseal or replace the plate.
Cartridge – Found inside the control unit, this small, cylindrical component is responsible for regulating water temperature and pressure. A faulty cartridge can result in erratic water temperature or reduced pressure. Replacing it is a common maintenance task.
Spout – This is the part where water is dispensed from the system. If water flow is weak or irregular, the spout may be clogged with debris or mineral deposits. Cleaning or replacing the spout is a simple solution to restore full water flow.
Showerhead – The showerhead disperses water in a controlled manner. If you notice uneven water pressure or a spray pattern that is not consistent, it may be time to clean or replace the showerhead. Hard water buildup often causes clogs in the nozzles.
O-Rings and Seals – These small rubber components are crucial for preventing leaks. When worn or damaged, they can lead to water escaping from the system, often around the valve or handle. Regular inspection and replacement of seals can help maintain efficiency.
Identifying Key Components in a Shower Faucet Diagram
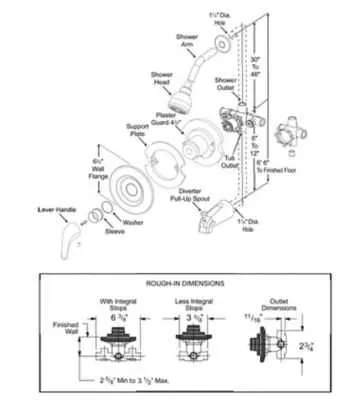
Start by focusing on the valve assembly. It controls water flow and temperature. Look for the diverter, which channels water between different outlets. Check the handle mechanism, often seen near the valve, to adjust the temperature. The spout is a critical element for directing water to the desired location. The trim plate is used to cover any exposed areas and provide an aesthetic finish. Additionally, inspect the cartridge or valve core, which regulates water pressure and temperature mixing. Ensure that the mounting hardware is securely in place to avoid leaks or improper installation. These components are essential for understanding the system’s functionality and troubleshooting issues effectively.
Understanding the Functionality of Shower Faucet Valves
Start by identifying the valve type: pressure-balancing, thermostatic, or manual mixer. Each model regulates water temperature and flow differently. A pressure-balancing unit maintains consistent output by adjusting to fluctuations in supply lines, minimizing scalding risks during toilet flushes or dishwasher cycles.
Thermostatic designs use a wax or bi-metal element to control temperature with high precision. These are ideal where water temperature stability is critical, especially in homes with young children or elderly residents. Always check for an adjustable limit stop to prevent excessively hot water output.
If you’re dealing with a manual variant, expect less control over temperature regulation. In such cases, replace standard cartridges with ceramic disk alternatives for improved durability and smoother control. Ensure compatibility with existing trim kits to avoid leaks or misalignment.
When troubleshooting temperature issues, inspect the cartridge for mineral buildup or O-ring damage. A faulty cartridge can restrict flow or cause temperature swings. Use manufacturer-specific models during replacement–generic substitutes may compromise performance or void warranties.
For installations behind tiled walls, choose a unit with a service stop feature. This allows maintenance without shutting off the main water supply. Mark the hot and cold sides clearly during installation to avoid reversed flow, which can disrupt performance and safety.
Common Issues and Fixes in Shower Faucet Assemblies
Replace worn cartridge seals immediately if water leaks behind the handle. Delayed action increases risk of internal corrosion and damage to adjacent components.
- Inconsistent water temperature: Check the thermostatic mixing valve. Mineral buildup around the temperature sensor often prevents accurate regulation. Soak the valve in a 1:1 vinegar solution for 30 minutes, then rinse thoroughly.
- Low pressure from the outlet: Remove and clean the flow restrictor inside the diverter. Sediment clogs are common, especially in older plumbing systems. If cleaning fails, install a new restrictor.
- Stiff control handle: Detach the escutcheon and apply silicone-based grease to the stem and O-rings. Avoid petroleum lubricants–they degrade rubber components.
- Drips after shutoff: Inspect the valve seat for pitting. Use a seat wrench to remove and resurface or replace the seat entirely if damage exceeds 1 mm depth.
- Handle misalignment: Verify spline engagement between trim and stem. If the fit is loose, replace the adapter or stem extension to restore alignment.
Always shut off the main supply and release pressure before disassembly. Use non-marring tools to prevent finish damage on decorative trims.