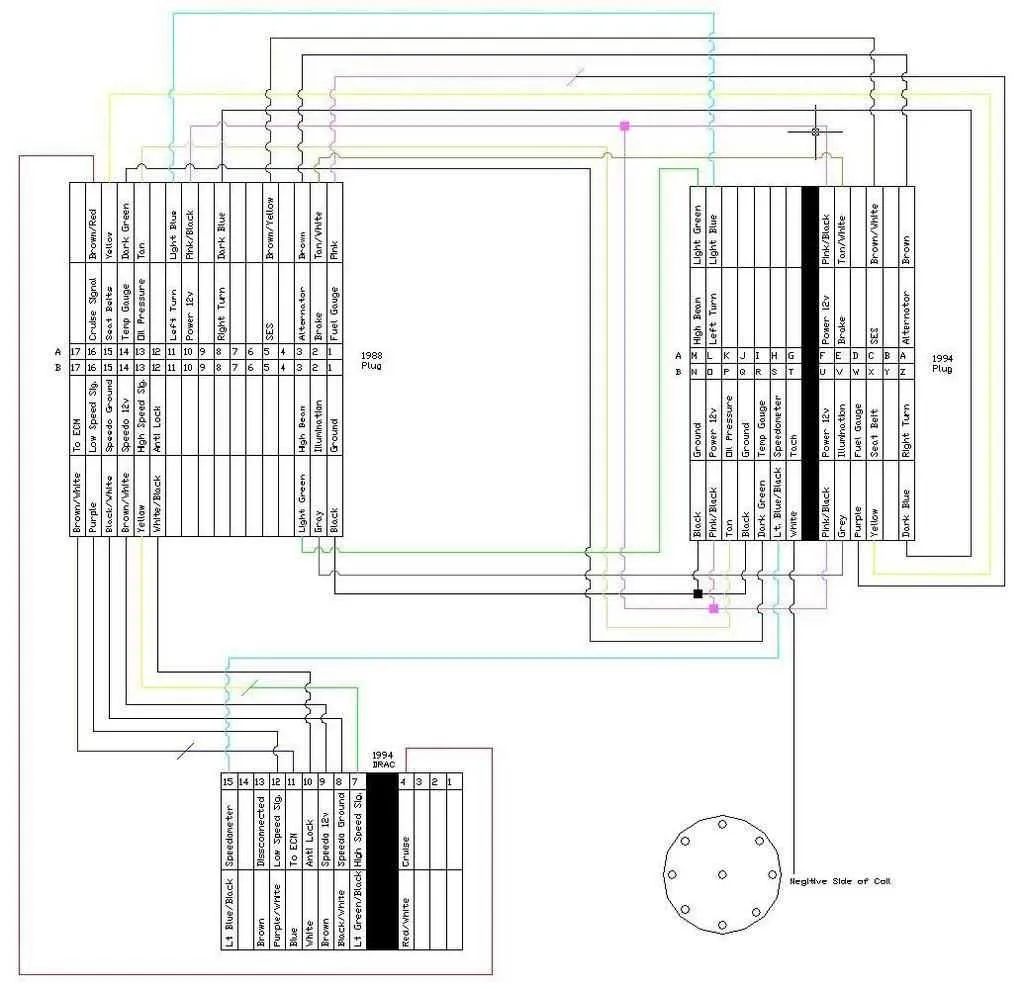
When working with the electrical connections of GM vehicle dashboards, understanding the layout of each connector is essential. This ensures proper integration of all display and control systems, leading to seamless vehicle operation. A detailed analysis of each pin and corresponding function helps technicians troubleshoot issues and perform upgrades or repairs efficiently.
Ensure proper identification of the terminals on the main connector, as incorrect wiring can cause display malfunctions or other errors in the vehicle’s control systems. Knowing the function of each pin is crucial when diagnosing problems or replacing components. Check the connector number and corresponding functions to avoid confusion during installation.
For accurate results, always refer to the vehicle’s service manual or factory specifications for the exact layout. A visual map of the connections can significantly speed up the diagnostic process, particularly when dealing with multiple wiring systems in a modern GM vehicle.
Never skip the step of double-checking each connection before powering up the system. A simple error in connection can lead to significant damage to sensitive components. Always use appropriate tools to secure the connections and confirm that the cables are intact and properly insulated.
GM Dashboard Connections Layout
To identify the correct wiring for the GM dashboard assembly, refer to the following guide for accurate connection placement. Start by locating the primary 24-pin connector, which is responsible for the majority of system inputs and outputs.
Key Pin Assignments:
- Pin 1: Ground connection (Black wire)
- Pin 2: Ignition switch input (Red wire)
- Pin 3: Speed sensor input (Yellow wire)
- Pin 4: Fuel level sensor (Green wire)
- Pin 5: Voltage signal from alternator (Blue wire)
- Pin 6: Tachometer signal (White wire)
Secondary Connectors:
- Pin 7: Temperature gauge signal (Orange wire)
- Pin 8: Turn signal input (Purple wire)
- Pin 9: Warning light circuit (Brown wire)
- Pin 10: Transmission fluid pressure (Pink wire)
Always double-check the color coding and verify with a multimeter before making any connections to avoid damage. Each GM model may have minor variations, so consulting the vehicle’s service manual is crucial for precise identification.
Important Note: When working with these connections, ensure all power is off before handling. Any improper connection can lead to malfunction or permanent damage to the dashboard components.
Understanding Pinout Layout for GM Instrument Cluster
When dealing with GM dashboard electrical connections, it’s crucial to understand the layout of each terminal for accurate diagnostics and repairs. Each connector serves a specific function that controls the display, lights, and other visual indicators on the dashboard. Incorrect wiring can lead to malfunctioning gauges or even complete system failure.
Focus on identifying the power and ground terminals first. These are typically located at the edges of the connector. For precise readings, ensure that you connect the correct pins for voltage input, which will affect the performance of displays like the speedometer and tachometer. Power connections often appear in the same range of pins for ease of access.
Next, locate the communication pins. These allow the module to send and receive data from other systems within the vehicle, like the engine control unit (ECU) or transmission. Pay attention to the number of data pins and their specific assignment; an incorrect connection can lead to error codes or loss of communication.
For advanced configurations, such as models with extra features like fuel consumption monitors, check the dedicated signal transmission lines. These wires often come in unique colors or pin assignments to distinguish them from more common connections like power or ground.
Always verify the pinout labels on the connector housing or use a multimeter to ensure each terminal is correctly mapped before proceeding with any wiring adjustments. An incorrect configuration can lead to circuit damage, causing long-term issues.
Finally, if you’re working with a replacement part, confirm that the terminal layout matches the original system. In some cases, updated models may have a different configuration or require a modification in the wiring scheme to accommodate newer technologies or features.
How to Identify and Test Wiring Connections in GM Systems
Start by ensuring the power is off to avoid shorts or damage to sensitive components. Use a multimeter to check the voltage at each contact point. The correct voltage values are typically found in the system manual or service guide.
Next, check for continuity between the corresponding terminals. Set your multimeter to continuity mode and test each connection between the component and the main unit. If the circuit is open, there’s a break in the connection that needs repair.
For testing ground connections: Select the continuity function and check between the ground pin and the chassis or vehicle frame. If the multimeter beeps, the ground is properly connected.
To verify power lines: Ensure that the positive lines provide the necessary voltage when the ignition is in the “on” position. Check for any voltage drops or irregular readings that might indicate a poor connection or a fault in the system.
If you’re troubleshooting issues with certain gauges or indicators, focus on their specific pins. Cross-reference the readings with the manufacturer’s specs. Any deviation in expected results points to faulty connections or damaged components.
Be diligent in verifying any suspect areas by flexing wires and gently tugging on connectors to detect loose or corroded connections. Clean and secure connectors when necessary.
For advanced testing: Use an oscilloscope to measure waveform patterns for more intricate diagnostics, especially for digital components. This tool helps you identify irregularities in signal transmission that may not be apparent with a basic multimeter.
Common Electrical Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for GM Display Systems
If the display stops functioning properly, check the power supply first. A faulty connection to the power or ground can cause the screen to go blank. Ensure that all pins are securely connected and there is no corrosion or dirt buildup.
- Verify the voltage levels at the power input terminals; it should match the manufacturer’s specified range.
- Inspect the grounding points for any loose or corroded connectors.
- Examine the fuses related to the system, as a blown fuse can cut power to critical components.
Erratic or non-responsive gauges may indicate problems with the signal transmission. This could be due to poor connections or damaged cables.
- Check the continuity of the data lines using a multimeter to confirm if the signal is properly transmitted.
- Inspect the connectors for bent pins or signs of wear that could lead to intermittent contact.
If the display shows incorrect readings, recalibrate the sensors associated with the system. Improper calibration can lead to misrepresentation of speed, fuel levels, or other data.
- Review the sensor calibration procedure in the vehicle’s service manual.
- Ensure that all sensors are correctly aligned and functional.
- Replace any faulty sensors that could be providing incorrect input.
When backlighting fails or flickers, inspect the voltage regulator or dimmer switch settings. Voltage fluctuations can cause inconsistent lighting behavior.
- Measure the voltage at the backlight input terminals and ensure stability.
- Test the dimmer switch for functionality and check for any signs of wear or damage.
If you notice persistent malfunctions, it’s wise to review the wiring connections from the control module. Loose or damaged wiring can disrupt normal operation.
- Ensure that all connections are tight and secure, with no fraying or damage to the wires.
- Inspect the insulation for any cracks or exposed wire that could cause short circuits.