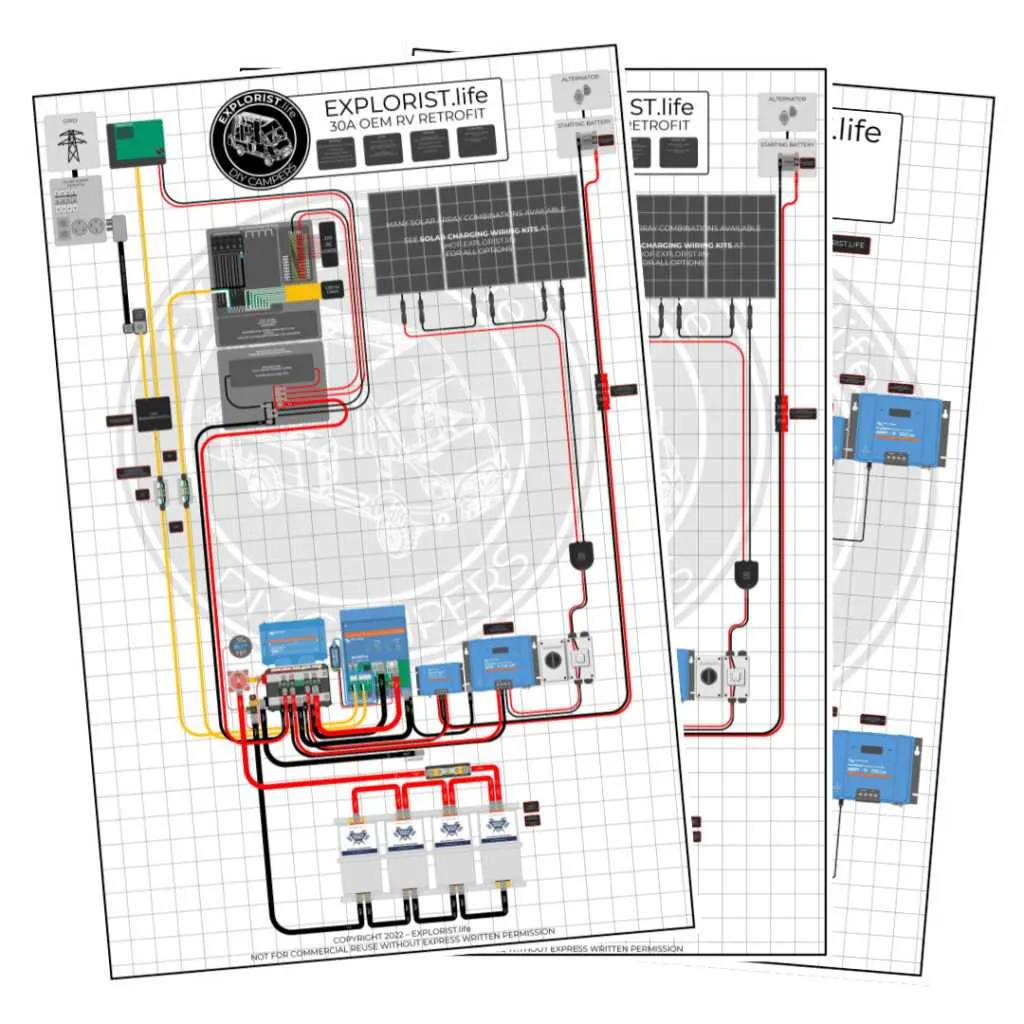
To optimize the energy flow in your recreational vehicle, connect the power source directly to the distribution panel. Begin by placing a reliable power converter near the main electrical hub, ensuring that all wiring meets the required gauge for safety and efficiency. Ensure that the power converter is properly grounded to avoid electrical issues.
Key wiring steps: First, connect the positive lead from the main battery to the input terminal of the power converter. Use a fuse or circuit breaker to protect against potential overloads. The negative lead should be connected to the grounding point, ensuring a stable and safe system.
Next, route the output lines to the distribution board, ensuring that each circuit is labeled clearly for easy identification. Make sure to check the voltage specifications on every circuit breaker to ensure compatibility with your RV’s devices and appliances. This setup will enhance energy flow and provide seamless operation.
Final check: Once the connections are made, test each component separately, starting with the power converter, followed by the various appliances. Ensure the system operates as expected under load, with no fluctuations or power surges that could harm your equipment.
RV Power Conversion Setup

For effective power conversion in your RV, follow these detailed steps:
- Locate the battery: Find the primary power source, typically located near the RV’s electrical panel. This is where your setup will connect to draw DC power.
- Choose the correct wiring gauge: Depending on the wattage of your power unit, use appropriate wire size to ensure safety and efficiency. A typical setup might require 10-12 gauge wiring for moderate loads.
- Connect DC cables: Attach the positive and negative cables from the power source to the DC input terminals. Ensure the polarity is correct to prevent damage.
- Position the converter unit: Install the unit near the electrical panel for easy access to connections, ensuring there is enough airflow for heat dissipation.
- Attach AC output wiring: Run AC cables from the converter’s output to your RV’s electrical system, typically through a dedicated breaker. Make sure to include a fuse or circuit breaker to protect the system from overloads.
Test the setup by turning on the power and checking all connections for stability. Always prioritize safety by using proper insulation and ensuring all components are rated for RV use.
How to Connect RV Power System to Battery Network
First, ensure your battery voltage matches the input requirements of the device. For most RV setups, the system operates on a 12V or 24V DC configuration. Select cables that can handle the maximum amperage required. Use a 4 AWG cable for a 12V system or 2 AWG for 24V, depending on your setup.
Step 1: Attach the positive terminal of the battery to the input terminal on the power converter using a properly rated cable. Secure this connection tightly with a wrench, ensuring there’s no chance of loosening.
Step 2: Connect the negative terminal from the battery to the corresponding ground terminal on the unit. It’s crucial to ensure a solid and clean connection to avoid power loss.
Step 3: For added safety, install a fuse between the battery and the device’s power input. This should be rated just above the maximum current the system will draw, typically around 150% of the maximum expected load. This will protect the system in case of a short circuit.
Step 4: Confirm polarity before completing the connections. Incorrect wiring can lead to system failure or safety hazards. If unsure, double-check the device’s manual for guidance.
Step 5: Once connected, turn on the system and monitor the voltage and current levels to ensure everything is operating within normal parameters. Perform routine checks to confirm the connections are secure and that no corrosion is present.
Important note: Always follow manufacturer guidelines and safety protocols to avoid damage to the system or risk to personal safety.
Wiring the RV Power System to AC Appliances
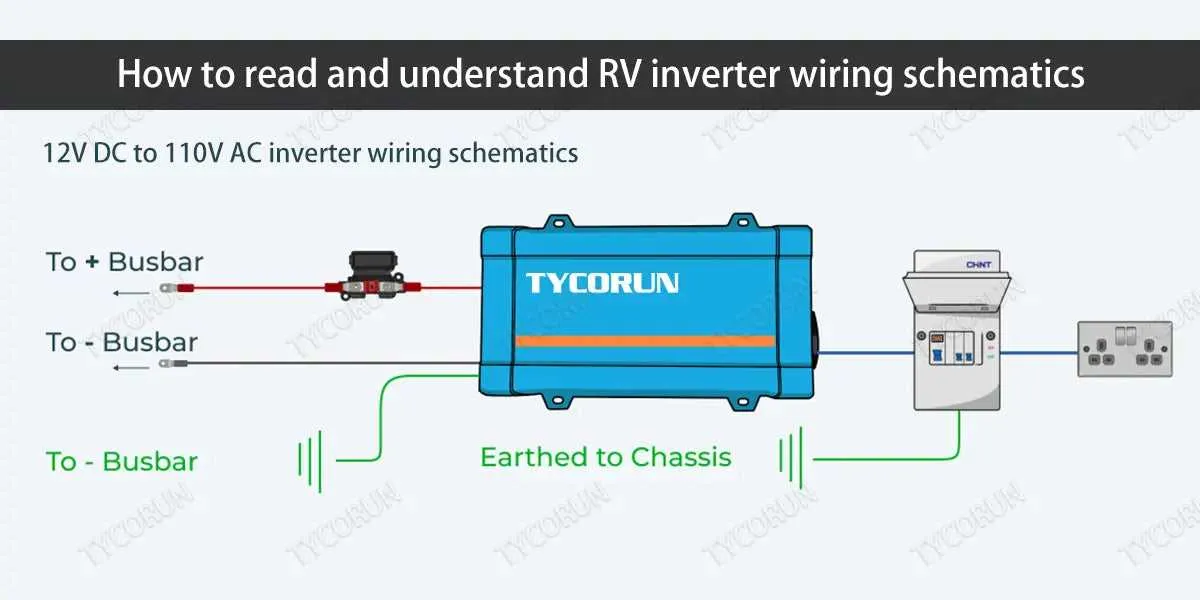
Connect the power system to your AC appliances using the proper gauge wiring. For most RV setups, 10-12 AWG wire is recommended for a 120V circuit. Ensure the wiring is rated for the correct amperage based on the appliance load. For instance, a 15-amp circuit typically requires 14 AWG wire, while a 20-amp circuit should use 12 AWG wire.
Step 1: Start by routing the wires from the DC power source to the AC panel. Use a dedicated, fused line to prevent overcurrent situations. Make sure to position the wiring in a way that avoids any contact with heat sources or sharp edges.
Step 2: For safety, ensure you have a properly rated circuit breaker installed. A 15-amp breaker will suffice for most household appliances, but larger devices like air conditioners may need 30 amps or more. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for each appliance to confirm.
Step 3: Once the breaker is in place, connect the neutral and hot wires to their respective terminals. The neutral wire should always be connected to the neutral bus bar in the AC panel, while the hot wire goes to the breaker.
Step 4: Ground the system to ensure safety. Attach the ground wire to the panel’s ground bar and connect it to a suitable grounding point on the RV chassis.
Step 5: Once everything is wired, verify all connections for tightness and integrity before turning the system on. Double-check for any potential shorts or exposed wires.
Note: If you’re not experienced with electrical systems, hiring a professional is highly recommended. Proper wiring ensures safe operation and avoids potential damage to appliances or the RV electrical system.
Safety Precautions During RV Power System Setup
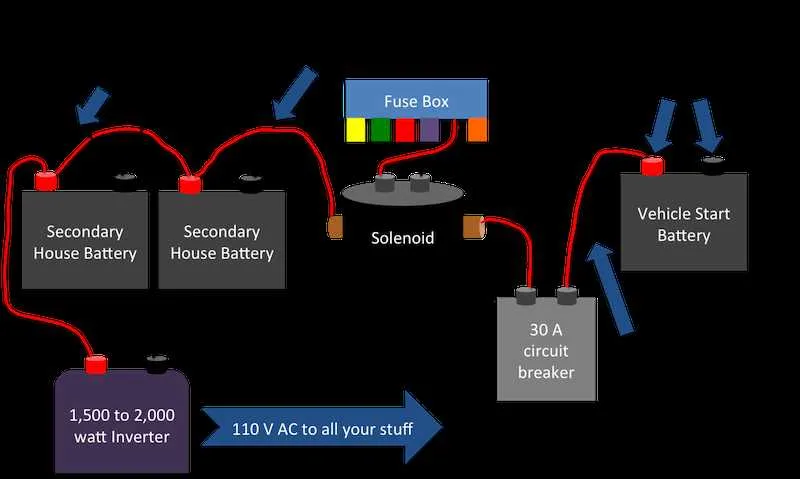
Ensure all power sources are disconnected before starting any work. This includes both the vehicle’s main power and the external shore power. Failure to turn off these sources can result in serious electrical shocks or short circuits during the process.
Use insulated tools to avoid accidental contact with live wires. Insulated tools provide an extra layer of protection when working near electrical components, reducing the risk of electric shock.
Wear safety gloves and goggles while handling electrical components. Protective gear minimizes the risk of burns or electrical injuries and provides a shield from debris and sharp objects inside the system.
Check wiring integrity before connecting any components. Damaged wires or faulty connections can cause electrical failures or fires. Replace any worn-out or damaged cables immediately.
Verify voltage ratings for each device you connect. Mismatched voltages can damage your equipment or pose a fire hazard. Always ensure compatibility between the power supply and your system’s components.
Ground the system properly to prevent electrical surges. Ensure that all grounding points are securely connected to the vehicle’s frame to safely redirect any excess electricity.
Use a circuit breaker or fuse to protect the system. This safety feature will cut off the power in case of a short circuit or overload, preventing damage to your components and reducing the risk of fire.
Double-check connections before powering up. Loose or improperly secured connections can lead to system failures or fires. Ensure that all terminals are tightly secured, and there’s no risk of accidental disconnection.