
For precise engine speed regulation, refer to the mechanism layout of the throttle control system. Identifying the key components, such as the spring-loaded linkages and rotational parts, is essential. These parts interact to maintain a stable engine RPM under varying load conditions.
The speed control assembly uses a centrifugal force principle to adjust fuel input, ensuring smooth engine operation. The mechanism comprises a series of weights that move outward as the engine accelerates, which then adjusts the throttle valve. Pay close attention to the spring tension and its role in modulating the system’s response to changes in engine speed.
Ensure proper calibration by checking the linkage alignment between the throttle plate and speed control arm. Misalignment or wear can lead to inconsistent speed regulation or mechanical failure. If adjustments are necessary, consult the specific system layout for your engine type to ensure correct reassembly.
How to Understand the Engine Speed Control Mechanism
The engine speed regulator is essential for maintaining consistent RPM. Follow these steps to troubleshoot or replace components related to this system:
- Inspect the spring: Ensure the tension is appropriate. A loose spring can cause unstable engine speed. If damaged, replace it immediately.
- Check the weights: Verify that the weights move freely and aren’t sticking. Rust or dirt buildup can prevent them from functioning properly.
- Examine the linkage: Look for any wear or damage on the linkage that connects the throttle control to the regulator. A loose or bent linkage can cause erratic speeds.
- Assess the centrifugal arm: This part must pivot smoothly. Any binding or resistance could cause incorrect RPM regulation.
- Verify calibration: After any adjustment or replacement, check the speed setting using a tachometer to ensure accurate RPM performance.
When reassembling, ensure that all parts are correctly aligned and that the spring maintains proper tension. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, ensures long-term efficiency.
How to Read a Briggs and Stratton Governor Diagram
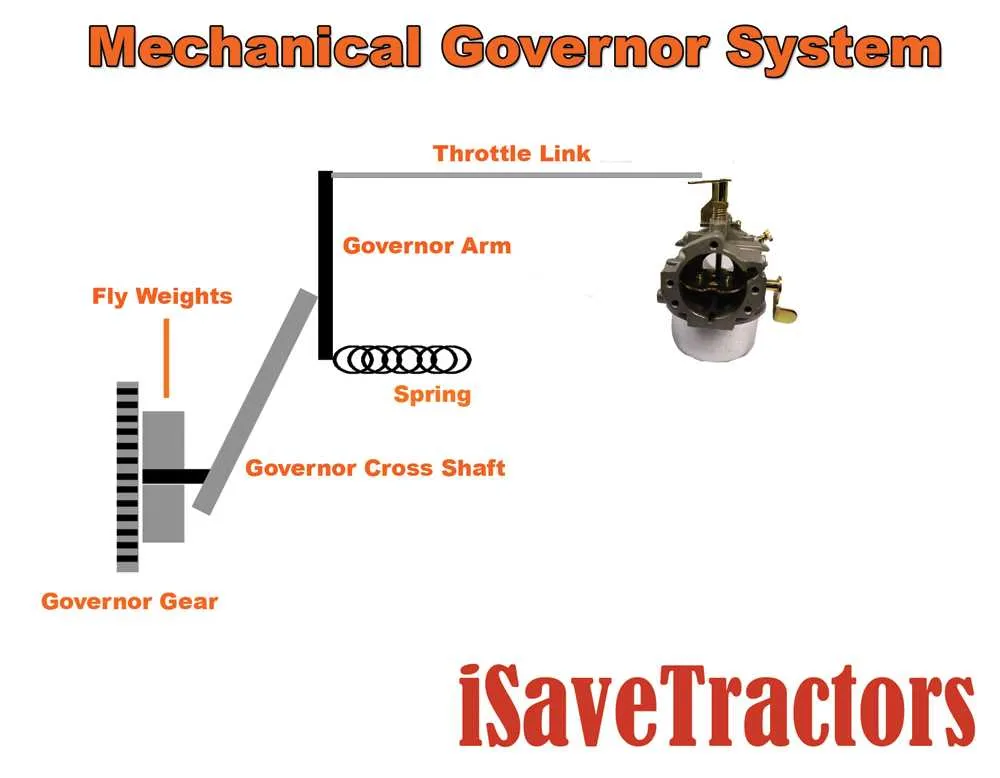
Start by identifying the key components in the illustration: the control lever, springs, linkage, and throttle. These elements work together to regulate engine speed. Focus on the spring connections as they influence the tension and the governor’s responsiveness to load changes.
The control lever, typically attached to the throttle, adjusts the position of the linkage. As the lever moves, it either increases or decreases the speed of the engine, which is visually represented by the range of motion in the diagram. Pay attention to the direction of movement indicated by arrows, as this shows how the linkage responds to input from the throttle or governor arm.
Examine the spring tension and how it affects the rotation of the arm connected to the engine’s throttle. The stronger the spring, the less likely the engine will fluctuate under load. Check for any variations in spring size and attachment points, as these details provide insight into how finely the engine’s speed can be controlled.
Identify the pivot points and how they allow for rotational movement. These pivots play a crucial role in adjusting the balance of forces that control engine speed. The diagram will typically show a pivot point where the throttle arm and governor arm meet, indicating the control mechanism’s movement.
Finally, compare the operational ranges shown. The diagram usually marks minimum and maximum positions for the throttle, giving you a clear understanding of how adjustments can be made based on engine demand and load.
Identifying Key Components in a Engine Speed Control System
Start by locating the throttle control arm. This part connects directly to the throttle plate, which regulates airflow and engine speed. The control arm is crucial for adjusting the RPM based on load demands.
Next, focus on the spring that connects to the throttle arm. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining tension, ensuring the throttle arm returns to idle when the system is not under load. This spring needs to be tensioned correctly to avoid erratic speed variations.
The flyweight mechanism, which adjusts the tension on the spring based on engine speed, should also be examined. These weights move outward as the engine accelerates, influencing the spring’s force, which in turn alters the throttle plate’s position.
Check the linkage rods that connect the flyweights to the throttle arm. Any play or misalignment here can cause delayed or incorrect responses to load changes, resulting in engine performance issues.
Inspect the shaft that holds the flyweights. It must rotate smoothly without excessive resistance. Any friction here can cause the system to respond sluggishly to changes in speed, compromising engine control.
Lastly, ensure the governor housing is free of dirt or debris. Blockages can restrict the movement of components, affecting the accuracy of speed adjustments. Cleanliness is vital to maintaining proper function.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Engine Speed Control Mechanisms
Check the linkage for binding or wear: Inspect the throttle and spring connections to ensure they move freely. A stiff or misaligned linkage can cause erratic speed control, preventing proper response to load changes. Lubricate or replace parts as necessary.
Verify the spring tension: If the spring that regulates speed seems loose or damaged, replace it. Incorrect tension can lead to irregular engine speed, either surging or stalling. Ensure the spring is properly seated in the correct mounting points for optimal performance.
Inspect for dirty or damaged components: Accumulation of dirt, debris, or rust on moving parts can restrict function. Clean all components thoroughly, especially the pivot points. Use a non-corrosive cleaner to remove any grime buildup that could hinder operation.
Check the control lever for slack: Over time, control levers can develop slack, leading to imprecise engine speed adjustments. Tighten any loose bolts and ensure that the lever has smooth and direct movement.
Examine the flyweight mechanism: If the flyweights are stuck, dirty, or worn, they may fail to respond correctly to engine speed changes. Inspect for any signs of damage or wear and replace parts if necessary to maintain proper regulation.
Test the engine for overheating: Overheating can cause erratic speed control behavior. Ensure the engine is adequately ventilated, and check the cooling fins and fan for blockages. Clean the cooling system if needed to avoid heat-related malfunctions.