
Start by locating the main relay area near the driver’s side dashboard. This spot houses the critical electrical connections for powering various car functions, such as lights, wipers, and more. A precise layout of this section is vital for quickly troubleshooting issues that may arise with power circuits.
Next, check the layout under the hood, where the primary set of connectors and relays is situated. This area is typically found close to the engine bay, often near the battery. Proper identification of each part helps avoid unnecessary disassembly when diagnosing electrical problems.
In case you need to replace or reset any specific component, consult the accurate wiring layout. This includes knowing which circuits are linked to each relay, as improper handling can result in malfunction or damage to other parts of the vehicle’s electrical system.
Be sure to follow the correct procedure when removing or adding any electrical parts, especially the relays and connectors. Ensure that all power is switched off before making any adjustments to avoid short circuits or electrical shocks.
When working on this system, accuracy is key. Knowing the exact placement of each unit can save time and prevent errors that could lead to unnecessary repairs.
Wiring System Overview and Component Layout
To troubleshoot electrical issues, locate the power distribution panel under the dashboard and in the engine compartment. This panel controls key electrical circuits and provides easy access for replacement of faulty relays and connectors. Each circuit is labeled to avoid confusion, ensuring quick identification of components.
Check the panel on the driver’s side near the footwell for interior wiring issues. You’ll find the main power connections and critical systems like the lighting, ignition, and climate control circuits here. For engine-related electrical concerns, inspect the engine compartment panel, usually situated near the battery. This will cover circuits related to the fuel system, ignition coils, and cooling fan operation.
If a fuse blows, it’s often a sign of overloading or a short circuit in the connected system. Check the amperage rating for each circuit and replace blown fuses with a matching rating to avoid further damage. Also, consider the condition of the connectors in the panels, as corrosion can lead to intermittent electrical faults.
How to Identify and Locate the Fuse Box in a 1995 Ford F150
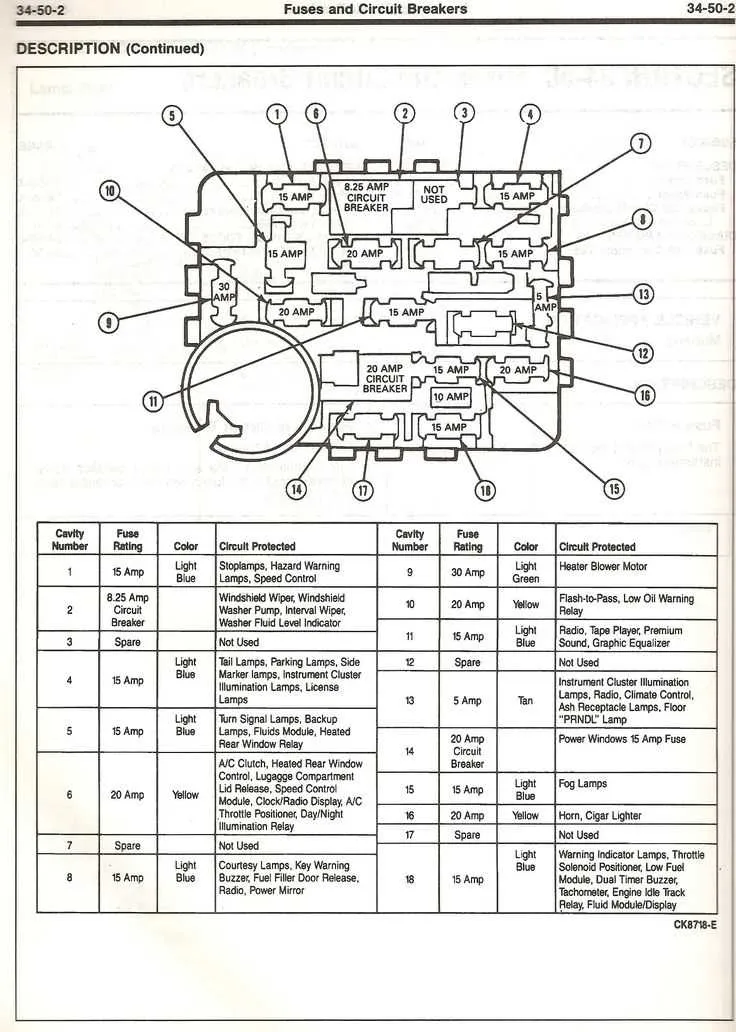
Check beneath the driver’s side dashboard near the steering column. The electrical panel is typically mounted on the lower part of the dashboard, just to the left of the brake pedal. If you can’t spot it immediately, remove the cover by pulling it towards you. You should see a grid of small switches inside.
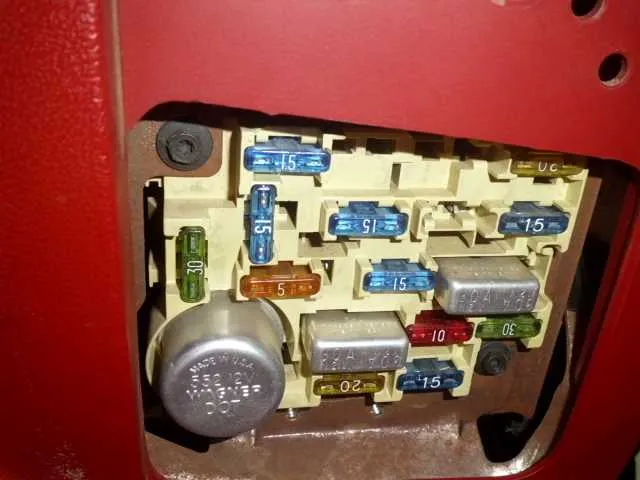
Another location is under the hood. Open the vehicle’s front cover, and look for a black rectangular component near the battery. This compartment houses the main electrical switches for key vehicle systems. It will have a snap-on cover that you can remove to access the components inside.
Consult the vehicle’s manual to confirm the exact positioning if needed, as the placement can vary slightly based on the model and trim level. The labels inside each panel indicate which switch controls each function.
Understanding Fuse Positions and Their Functions

To troubleshoot electrical issues, first identify the correct position of each component within the panel. Each slot serves a specific purpose, ensuring various systems operate smoothly. Pay close attention to the numbering system to avoid confusion. For instance, slots for the engine, air conditioning, and lighting circuits are typically located in separate sections for quick identification.
For power distribution, the components like the ignition switch and main relay often occupy central positions, while accessories such as the radio or wipers are found in the outermost rows. Checking the amperage rating of each component helps prevent circuit overloads and ensures the proper function of connected elements. Refer to the label next to the panel for an exact match between slot and component for easy troubleshooting.
When replacing a blown unit, ensure the new component matches the amperage of the one you are removing. Over or under-amp units can damage connected systems. Keep a spare kit handy for quick replacements, especially for high-demand systems like the starter motor or headlights, which tend to wear out faster due to frequent use.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues
Start by inspecting the main power relay. This component controls several critical circuits, and a malfunction here can cause a range of electrical failures.
If you’re experiencing power loss in certain systems, check the individual terminals. Look for signs of corrosion or loose connections, as these can disrupt the electrical flow.
- Step 1: Locate the relays under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
- Step 2: Use a multimeter to test each relay for continuity. If any show no reading, replace them.
- Step 3: Ensure the relay sockets are clean and free of corrosion.
For issues with specific electrical functions, check the smaller circuit breakers that control individual components like lights or wipers. Replace any faulty breakers to restore functionality.
- Step 1: Find the breaker for the malfunctioning part (e.g., headlights, wipers).
- Step 2: Test the breaker with a simple voltage tester.
- Step 3: Replace any non-functional breakers.
If problems persist, examine the ground connections. A poor ground can prevent electrical circuits from completing properly, leading to partial or total failure of certain systems.
- Step 1: Identify all ground points near the electrical components.
- Step 2: Clean and tighten the ground wires to ensure a solid connection.
Finally, for intermittent power loss, inspect the main wiring harness. Damaged wires can cause a temporary disconnection, leading to erratic performance. Look for frayed, cracked, or exposed wiring.
- Step 1: Visually inspect the wiring for any signs of wear.
- Step 2: Use electrical tape or heat shrink tubing to repair any damaged areas.